Market Economic Presentation
| Introduction to Market Economics | ||
|---|---|---|
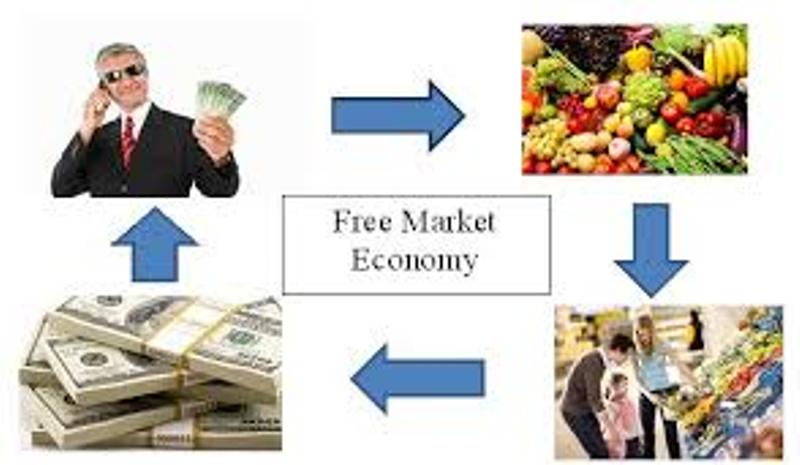
| Market economics is an economic system where the prices of goods and services are determined by the interactions of buyers and sellers in a competitive market. In market economics, the government does not control the production, distribution, or allocation of resources. Market economics is characterized by private ownership of resources, profit motive, and competition. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Features of Market Economics | ||
|---|---|---|
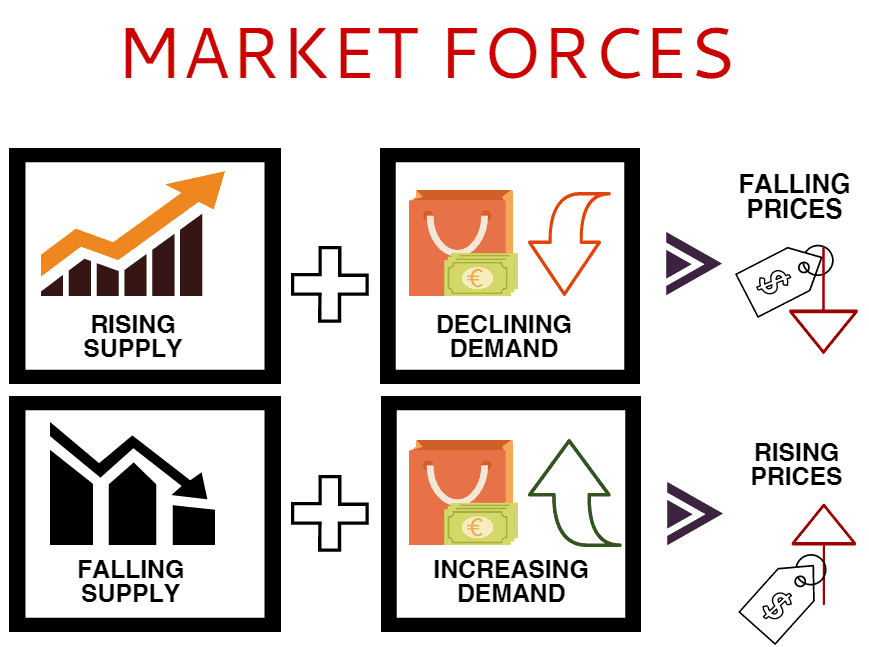
| Freedom of choice: Individuals and firms have the freedom to make economic decisions, such as what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. Price mechanism: Prices are determined by the forces of supply and demand, signaling the scarcity or abundance of goods and services. Market competition: Multiple buyers and sellers compete for the best deals, fostering efficiency, innovation, and consumer welfare. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Advantages of Market Economics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Efficient allocation of resources: Market forces of supply and demand ensure that resources are allocated to their most valued uses. Incentives for innovation and productivity: The pursuit of profit motivates firms to innovate, improve productivity, and meet consumer demands. Consumer sovereignty: Consumers have the power to influence production decisions through their purchasing choices. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Disadvantages of Market Economics | ||
|---|---|---|
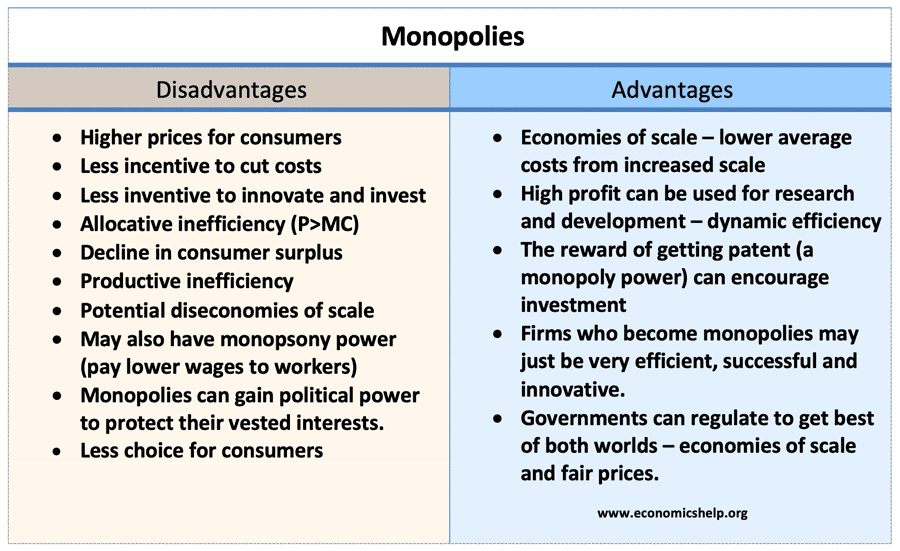
| Income inequality: Market economies can lead to income disparities as some individuals and firms amass wealth while others struggle. Externalities: Market failures can occur when the cost or benefit of a transaction is not fully reflected in the price, leading to negative impacts on society or the environment. Lack of public goods provision: Public goods, such as defense or infrastructure, may be underprovided in a purely market-based system. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Role of Government in Market Economics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ensuring competition: Governments enforce antitrust laws to prevent monopolies or unfair market practices. Regulation: Governments implement regulations to protect consumers, workers, and the environment. Provision of public goods: Governments provide public goods and services that are not efficiently supplied by the market. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Examples of Market Economies | ||
|---|---|---|
| United States: The U.S. has a market-based economy with a mix of private and public ownership. Germany: Germany has a social market economy that combines market principles with a strong welfare state. Singapore: Singapore has a highly developed market economy with a focus on trade and investment. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Market economics is an economic system driven by the forces of supply and demand, where prices are determined by market interactions. It offers advantages such as efficient resource allocation, incentives for innovation, and consumer sovereignty. However, it also has disadvantages like income inequality and market failures, requiring government intervention to address these issues. | ||
| 7 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mankiw, N. G., & Taylor, M. P. (2014). Econom... Samuelson, P. A., & Nordhaus, W. D. (2010). E... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 8 | ||


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/market-economy-characteristics-examples-pros-cons-3305586-v4-5b4df98146e0fb0037756bd2.png)