Malassezia Associated With Pachydermatitis Presentation
| Introduction to Malassezia associated with pachydermatitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Malassezia is a genus of yeast-like fungi commonly found on the skin of humans and animals. Pachydermatitis refers to a condition characterized by thickened skin, often associated with chronic inflammation. The presence of Malassezia on the skin can contribute to the development of pachydermatitis. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Understanding Malassezia | ||
|---|---|---|
| Malassezia is a normal part of the skin flora, but overgrowth can lead to various skin disorders. It thrives in areas with increased sebum production, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. Malassezia can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation and skin lesions. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Factors Contributing to Malassezia overgrowth | ||
|---|---|---|
| Excessive sebum production provides a favorable environment for Malassezia growth. Humid and warm climates create ideal conditions for Malassezia proliferation. Imbalances in the skin microbiome or weakened immune system can contribute to Malassezia overgrowth. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Malassezia associated with Pachydermatitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pachydermatitis is often seen in dogs, characterized by thickened, lichenified skin. Malassezia is frequently isolated from the affected skin in dogs with pachydermatitis. The presence of Malassezia can exacerbate inflammation and worsen the clinical signs of pachydermatitis. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Clinical Symptoms of Malassezia-associated Pachydermatitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dogs with Malassezia-associated pachydermatitis may present with red, itchy, and thickened skin. Affected areas may have a greasy appearance and a distinct odor. Scratching, licking, and chewing at the affected areas are common signs in dogs. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Diagnosis of Malassezia-associated Pachydermatitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis is based on clinical signs, history, and microscopic examination of skin samples. Presence of Malassezia organisms in large numbers is indicative of Malassezia-associated pachydermatitis. Additional tests like skin cultures or allergy testing may be performed to rule out other possible causes. | ||
| 6 | ||
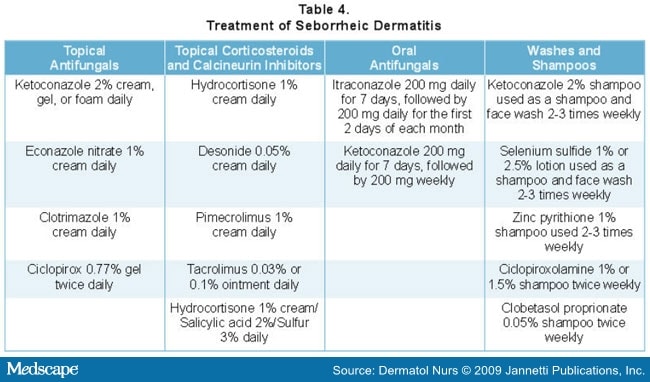
| Treatment Options | ||
|---|---|---|
| Topical therapies, such as antifungal shampoos or creams, are commonly used to treat Malassezia-associated pachydermatitis. Systemic antifungal medications may be prescribed in severe or recurrent cases. Identifying and addressing any underlying factors contributing to Malassezia overgrowth is crucial for successful treatment. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Prevention and Management Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular bathing and grooming can help control Malassezia growth and prevent pachydermatitis. Avoiding excessive use of corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications can reduce the risk of Malassezia overgrowth. Maintaining a healthy skin barrier through proper nutrition and regular veterinary care is essential in preventing and managing Malassezia-associated pachydermatitis. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Prognosis and Long-term Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| With appropriate treatment and management, most cases of Malassezia-associated pachydermatitis can be controlled. Long-term control may require ongoing maintenance therapy, including regular bathing and antifungal treatments. Regular veterinary check-ups are important to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Malassezia overgrowth is a common contributor to pachydermatitis in dogs. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing Malassezia-associated pachydermatitis. Preventive measures and long-term management strategies are crucial in controlling the condition and improving the quality of life for affected animals. | ||
| 10 | ||