Lifting Line Theory Presentation
| Lifting Line Theory | ||
|---|---|---|
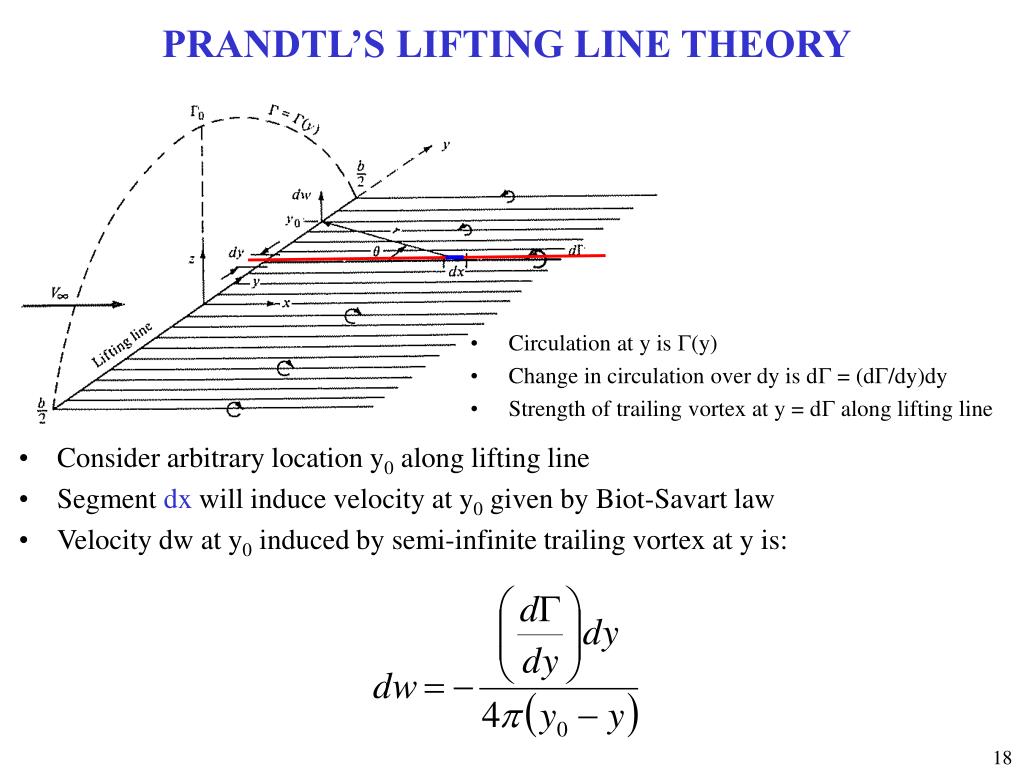
| Lifting line theory is a mathematical model used to analyze the aerodynamic properties of wings. It assumes that the wing is infinitely long and the flow is steady and two-dimensional. Lifting line theory helps in understanding the distribution of lift and spanwise flow along the wing. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Assumptions | ||
|---|---|---|
| The wing is symmetric and has a constant chord along its span. The flow is inviscid, meaning there is no skin friction or boundary layer effects. The lift distribution along the wing span is linear, with the maximum lift occurring at the center. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Lift Distribution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lifting line theory predicts the lift distribution along the wing span. The lift distribution is represented by a dimensionless function called the lift coefficient. The lift coefficient is influenced by the angle of attack, wing geometry, and airfoil characteristics. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Induced Drag | ||
|---|---|---|
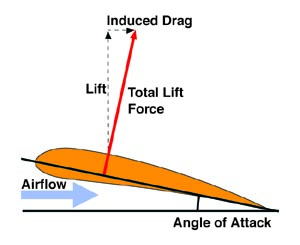
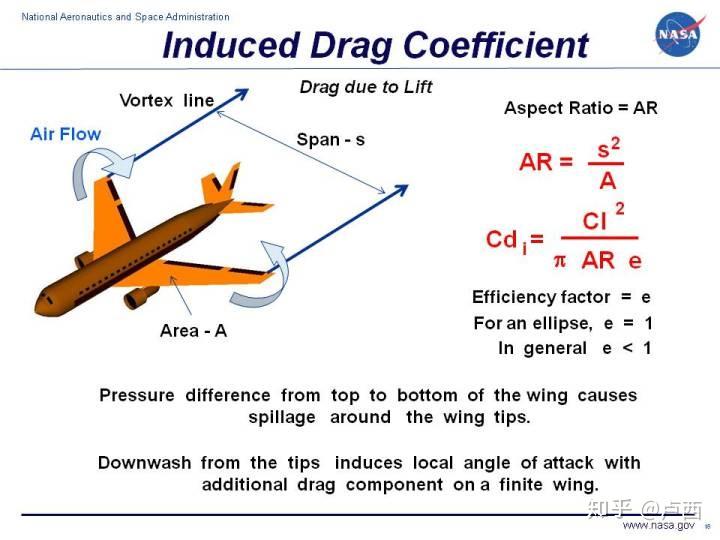
| Induced drag is the component of drag that arises due to the generation of lift. Lifting line theory helps in analyzing and minimizing induced drag. The induced drag decreases as the aspect ratio of the wing increases. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Spanwise Flow | ||
|---|---|---|
| Spanwise flow is the flow of air in the spanwise direction along the wing. Lifting line theory allows us to calculate the spanwise flow velocity distribution. The spanwise flow affects the lift distribution and the induced drag. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Downwash and Upwash | ||
|---|---|---|
| Downwash is the downward flow of air behind the wing. Upwash is the upward flow of air ahead of the wing. Lifting line theory provides insights into the magnitude and distribution of downwash and upwash. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Angle of Attack | ||
|---|---|---|
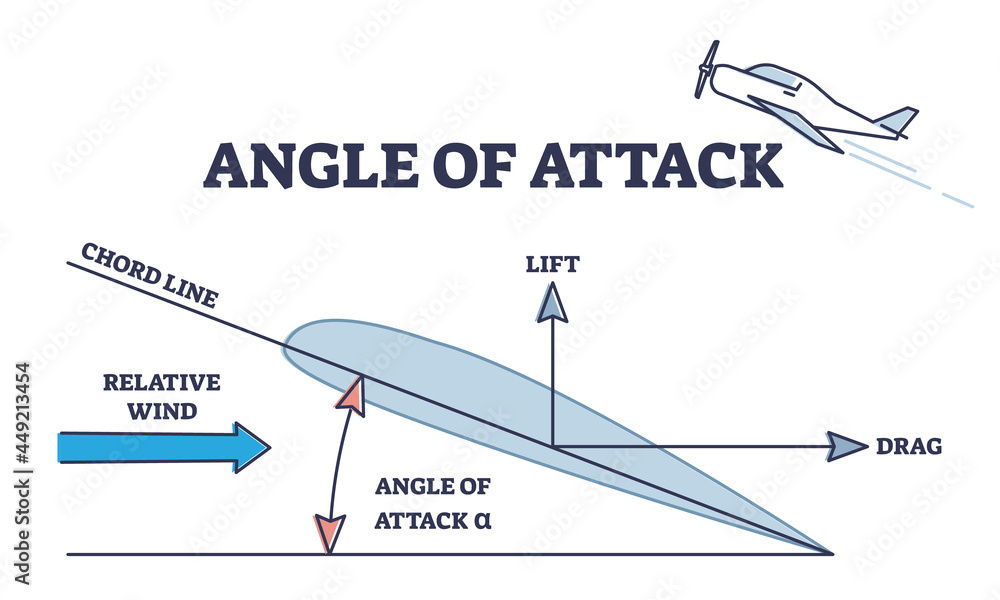
| The angle of attack is the angle between the wing chord line and the oncoming airflow. Lifting line theory helps in understanding the variation of lift coefficient with the angle of attack. The lift coefficient increases with increasing angle of attack until it reaches the stall angle. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lifting line theory is widely used in the design and analysis of aircraft wings. It helps in optimizing wing geometry for specific performance requirements. Lifting line theory also aids in predicting the behavior of wings in different flight conditions. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Limitations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lifting line theory assumes idealized conditions and simplifies the complex reality of aerodynamics. It neglects the effects of wingtip vortices, three-dimensional flow, and viscous drag. Lifting line theory is most accurate for wings with high aspect ratios and low angles of attack. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lifting line theory is a valuable tool for understanding the aerodynamics of wings. It provides insights into lift distribution, induced drag, and spanwise flow. While it has limitations, lifting line theory remains a key concept in aircraft design and analysis. | ||
| 10 | ||