Japanese Balance Trade Presentation
| Introduction to Japanese Balance Trade | ||
|---|---|---|
| Japanese balance trade refers to the difference between the value of exports and imports of goods and services in Japan. It is a critical indicator of a country's economic performance and competitiveness in the global market. Japan, being one of the world's largest economies, has a significant impact on global trade dynamics. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Historical Overview | ||
|---|---|---|
| Japan has traditionally been known as an export-oriented economy, with a focus on manufacturing and high-tech industries. The country experienced rapid export growth during the post-World War II period, known as the "Japanese economic miracle." However, in recent decades, Japan has faced challenges due to the appreciation of its currency and increased competition from emerging economies. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Trade Surplus | ||
|---|---|---|
| Historically, Japan has maintained a trade surplus, meaning that its exports exceed its imports. This surplus has been driven by industries such as automobiles, electronics, machinery, and chemicals. The trade surplus has contributed to the accumulation of foreign reserves and helped finance Japan's public debt. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Shift to Trade Deficit | ||
|---|---|---|
| In recent years, Japan has experienced a shift toward a trade deficit, where imports exceed exports. This shift can be attributed to factors such as increasing energy imports, a declining population, and a rise in production costs. The trade deficit has put pressure on Japan's economy and highlighted the need for structural reforms. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Impact on GDP | ||
|---|---|---|
| The balance trade has a direct impact on Japan's gross domestic product (GDP). A trade surplus contributes positively to GDP growth, while a trade deficit acts as a drag on economic performance. Japan has been working to boost exports and reduce its dependence on imports to mitigate the negative impact on GDP. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Trade Partners | ||
|---|---|---|
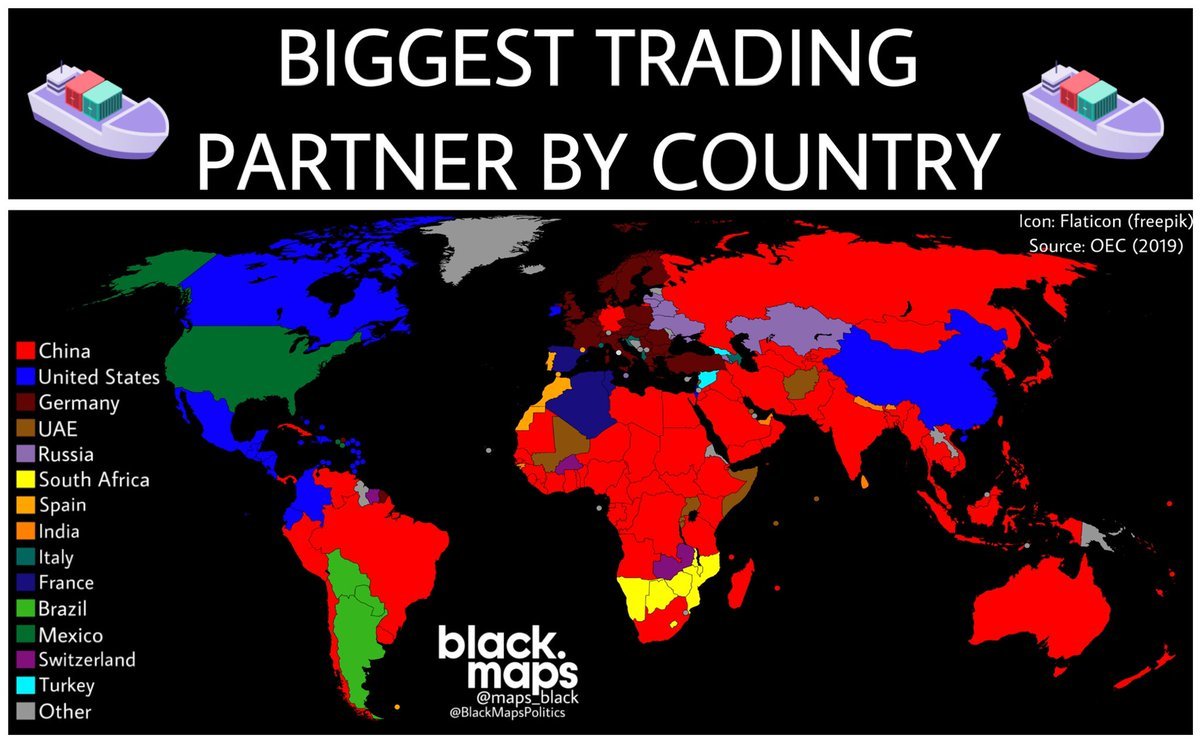
| Japan has a diverse range of trade partners, with its largest trading partners being China, the United States, and South Korea. These countries account for a significant portion of Japan's total trade volume. Japan also engages in trade with other Asian countries, Europe, and the Middle East. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Trade Policies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Japan has implemented various trade policies to promote exports and address trade imbalances. These policies include free trade agreements (FTAs), export promotion initiatives, and measures to attract foreign direct investment. The government has also focused on improving market access for Japanese products in foreign markets. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Impact of Exchange Rates | ||
|---|---|---|
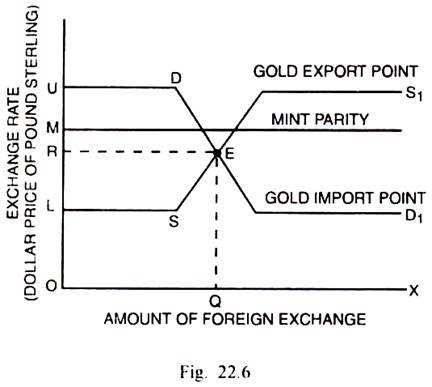
| Exchange rates play a crucial role in determining the balance trade. A stronger Japanese yen makes exports more expensive and imports cheaper, potentially leading to a trade deficit. The government has occasionally intervened in foreign exchange markets to stabilize its currency and support export competitiveness. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Future Outlook | ||
|---|---|---|
| Japan is taking steps to address its trade deficit by promoting innovation, investing in research and development, and expanding into new markets. The country aims to diversify its export base and reduce its dependence on a few industries. The success of these strategies will be crucial for Japan's future balance trade and overall economic growth. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Japanese balance trade is a vital aspect of the country's economy, reflecting its competitiveness and global trade dynamics. While Japan has historically maintained a trade surplus, it has recently faced challenges leading to a trade deficit. Through policy measures and strategic initiatives, Japan aims to address its trade imbalance and ensure sustainable economic growth. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Finance Japan. (2021). Balance of... World Bank. (2021). Japan Trade Summary. Retr... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||