JIT And Working Of JIT Presentation
| Introduction to JIT | ||
|---|---|---|
| JIT stands for Just-in-Time. It is a production strategy that focuses on producing goods or services at the exact time they are needed. JIT aims to minimize inventory costs and waste by synchronizing production with customer demand. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Principles of JIT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Elimination of waste: JIT aims to reduce or eliminate all forms of waste, such as overproduction, excess inventory, defects, and waiting time. Continuous improvement: JIT promotes a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are encouraged to find ways to optimize processes and eliminate inefficiencies. Pull system: JIT operates on a pull system, where production is initiated based on customer demand, rather than pushing products through the production process. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Benefits of JIT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reduced inventory costs: By producing goods or services just in time, JIT minimizes the need for excessive inventory, saving storage and holding costs. Improved efficiency: JIT streamlines production processes, reduces setup times, and eliminates bottlenecks, leading to improved overall efficiency. Enhanced quality: JIT emphasizes quality control throughout the production process, resulting in fewer defects and customer complaints. | ||
| 3 | ||
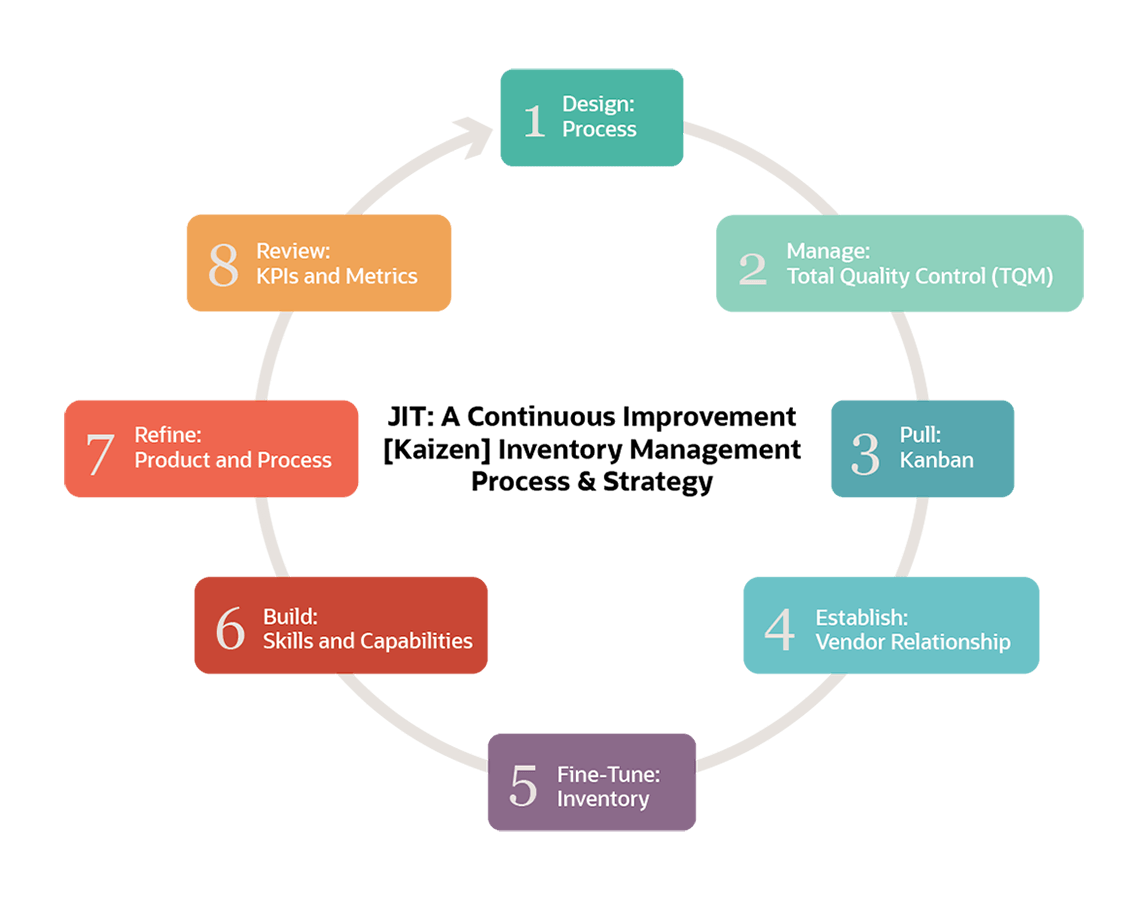
| Working of JIT - Step 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Forecasting customer demand: The first step in JIT is to accurately forecast customer demand to determine production requirements. Communication with suppliers: Once demand is forecasted, communication with suppliers is crucial to ensure timely delivery of raw materials and components. Production planning: Based on customer demand and supplier capabilities, production planning is done to determine the required quantity and schedule. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Working of JIT - Step 2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Just-in-time production: JIT production involves producing goods or services in small batches, based on actual customer orders or demand. Kanban system: The kanban system is commonly used in JIT, where visual signals or cards are used to indicate when to produce or reorder items. Efficient workflow: JIT emphasizes smooth and efficient workflow, with minimal movement and handling of materials, and well-organized workstations. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Working of JIT - Step 3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Quality control: JIT places a strong emphasis on quality control at every stage of production, with regular inspections and feedback loops. Continuous improvement: JIT encourages employees to identify and implement improvements in processes, equipment, and quality standards. Employee empowerment: JIT fosters a culture of employee empowerment, where workers are actively involved in decision-making and problem-solving. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges of JIT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Supply chain vulnerability: JIT heavily relies on timely delivery of materials, making it vulnerable to disruptions in the supply chain, such as weather events or supplier issues. High coordination requirements: JIT requires close coordination among different departments, suppliers, and customers, which can be challenging to achieve. Limited flexibility: JIT may struggle to respond quickly to sudden changes in customer demand or unexpected disruptions in the production process. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| JIT is a production strategy that focuses on producing goods or services at the exact time they are needed. It aims to minimize waste, improve efficiency, and enhance quality. By implementing JIT, organizations can reduce inventory costs, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve a competitive advantage in the market. | ||
| 8 | ||