Introduction Java Presentation
| Introduction to Java | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java is a high-level programming language. It was first developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in 1995. Java is platform-independent, allowing programs to run on any device with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). | ||
| 1 | ||
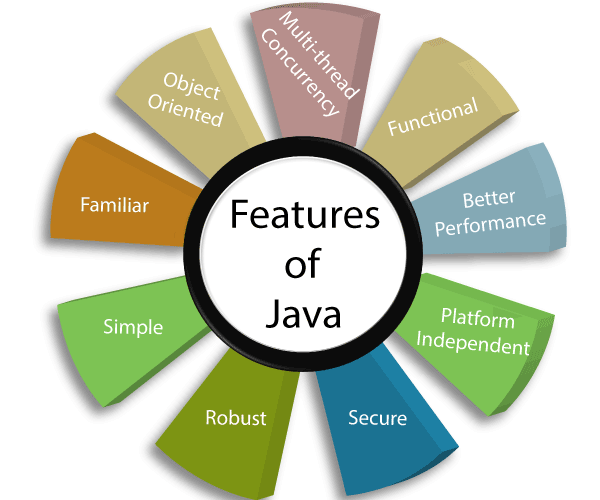
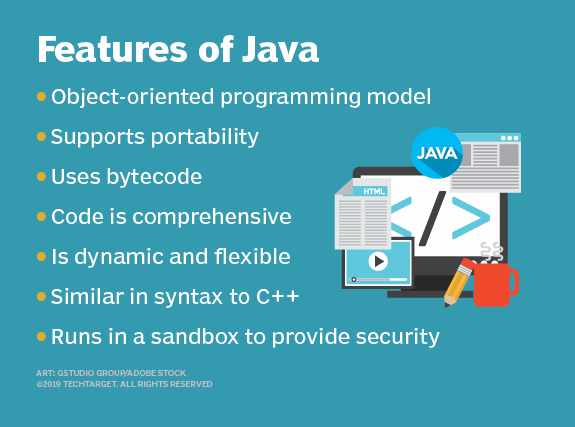
| Key Features of Java | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java is object-oriented, allowing for modular and reusable code. It has automatic memory management through garbage collection. Java supports multithreading, enabling concurrent execution of multiple tasks. | ||
| 2 | ||
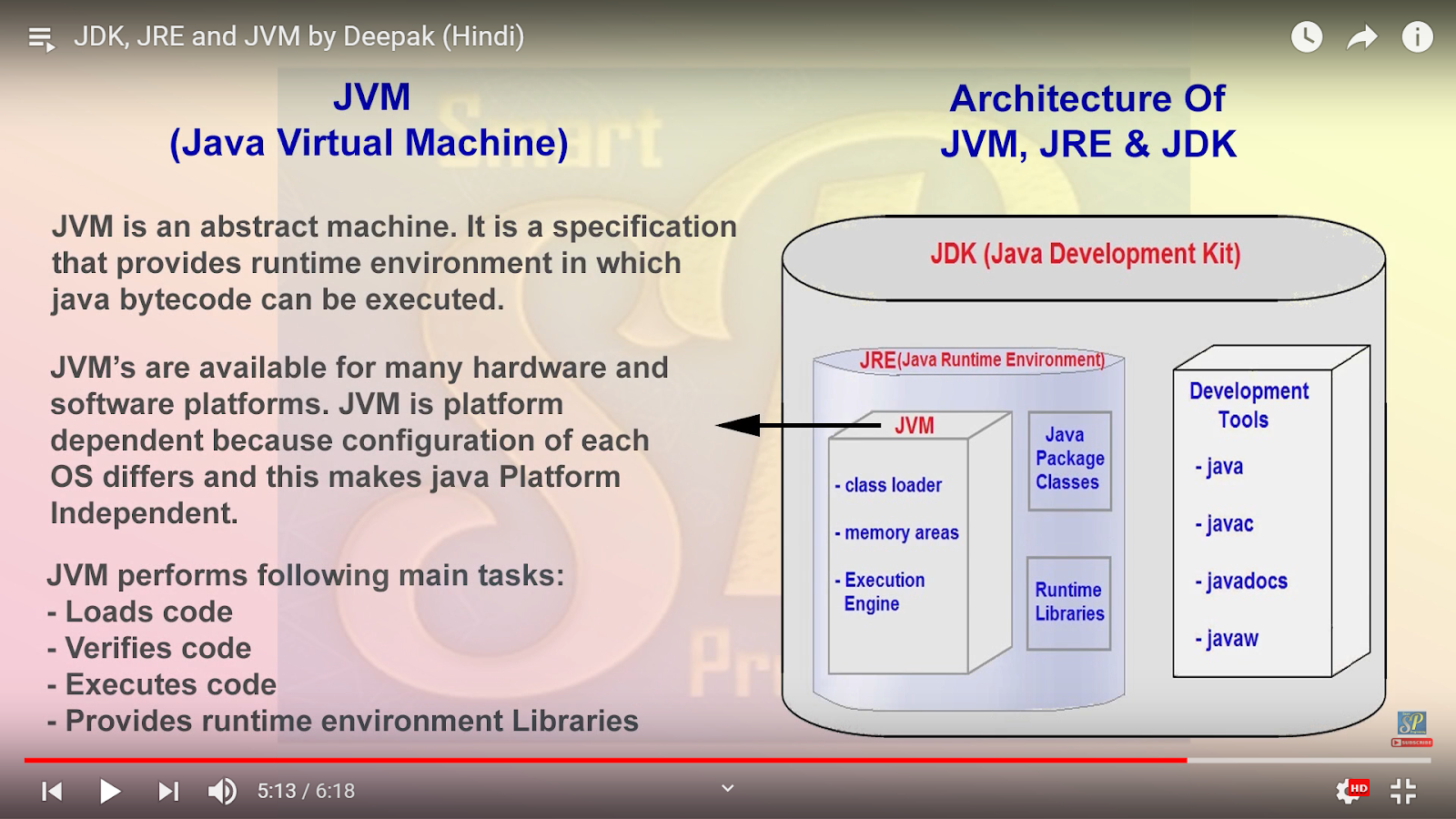
| Java Development Environment | ||
|---|---|---|
| To develop Java applications, you need a Java Development Kit (JDK). The JDK includes a compiler, debugger, and other tools necessary for development. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Eclipse and IntelliJ IDEA provide a user-friendly environment for coding in Java. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Syntax and Structure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java programs are organized into classes. Each class contains methods, variables, and other elements. The main method is the entry point for Java programs. | 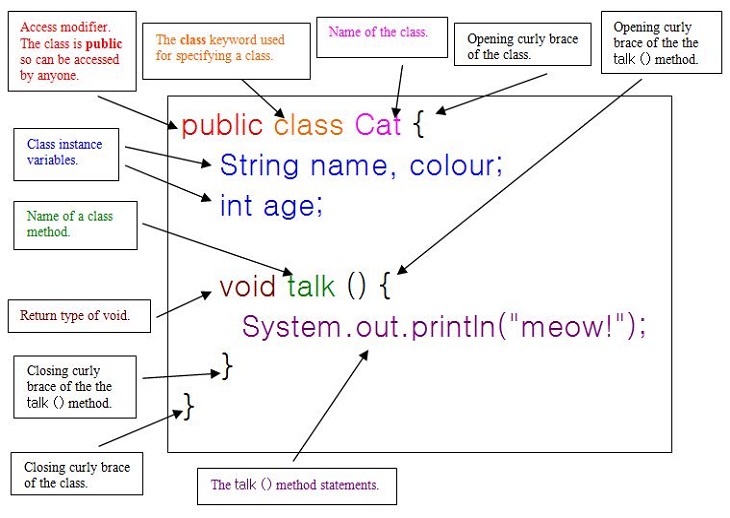 | |
| 4 | ||
| Variables and Data Types | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java supports various data types, including primitive types like int, double, and boolean. Variables in Java must be declared with a specific type before they can be used. Variables can be assigned values and manipulated throughout the program. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Control Flow | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java provides control flow statements like if-else, for, while, and switch. These statements allow programmers to control the flow of execution based on conditions. Loops enable repetitive execution of code blocks. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Object-Oriented Programming in Java | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java follows the principles of object-oriented programming (OOP). OOP concepts in Java include encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Classes and objects form the foundation of OOP in Java. | ||
| 7 | ||
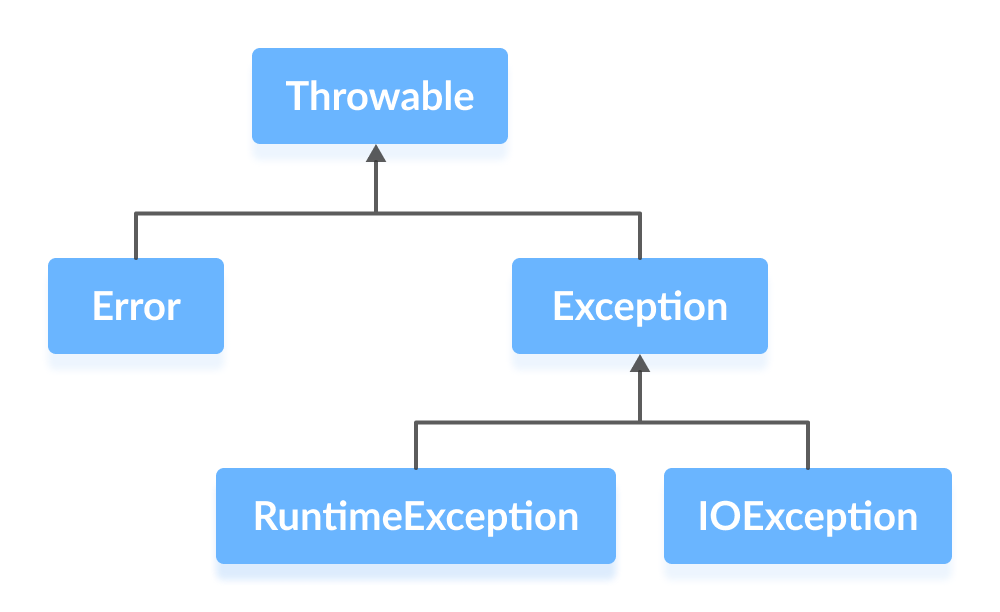
| Exception Handling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java provides built-in mechanisms for handling exceptions. Exceptions are events that occur during the execution of a program that disrupt normal flow. try-catch blocks are used to catch and handle exceptions gracefully. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Input and Output in Java | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java provides classes and methods to handle input and output operations. The java.io package provides classes for reading and writing files. The java.util.Scanner class is commonly used for user input. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Java is a versatile and widely-used programming language. It is known for its portability, security, and scalability. Learning Java opens up opportunities for various domains like web development, mobile app development, and more. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Oracle. (n.d.). The Java Tutorials. Retrieved... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||