Introduction,construction Of Bjt,types Presentation
| Introduction to Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) | ||
|---|---|---|
| BJTs are electronic devices used for amplification and switching of electrical signals. They consist of three layers of semiconductor material: the emitter, base, and collector. BJTs are divided into two main types: NPN (negative-positive-negative) and PNP (positive-negative-positive). | ||
| 1 | ||
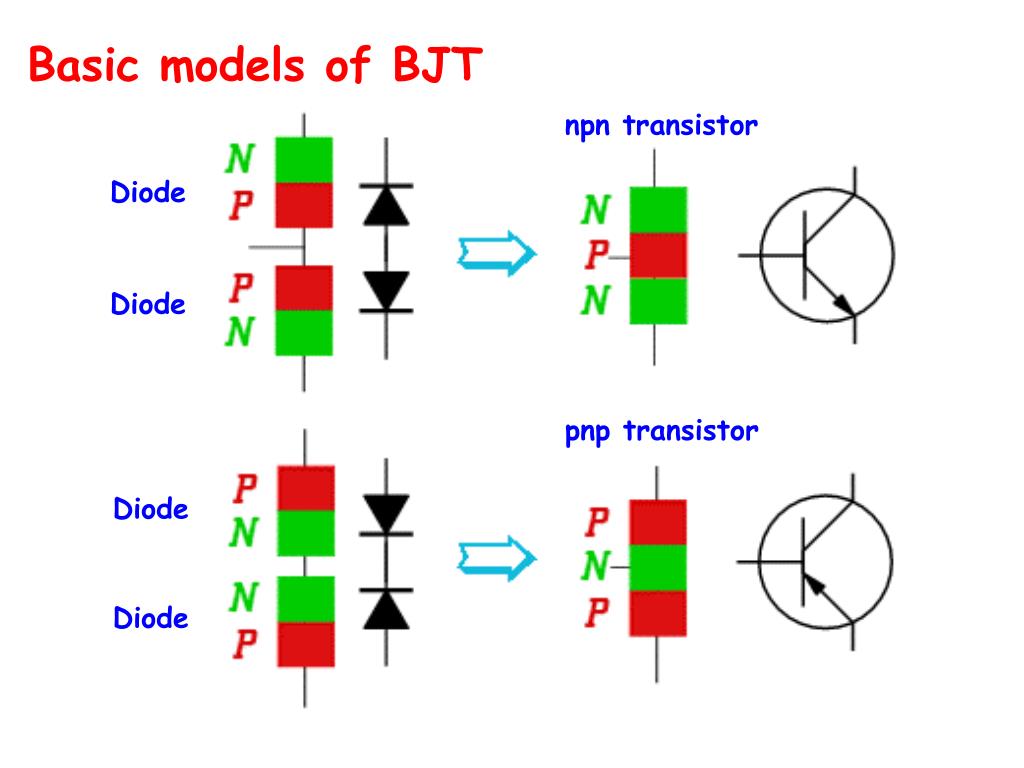
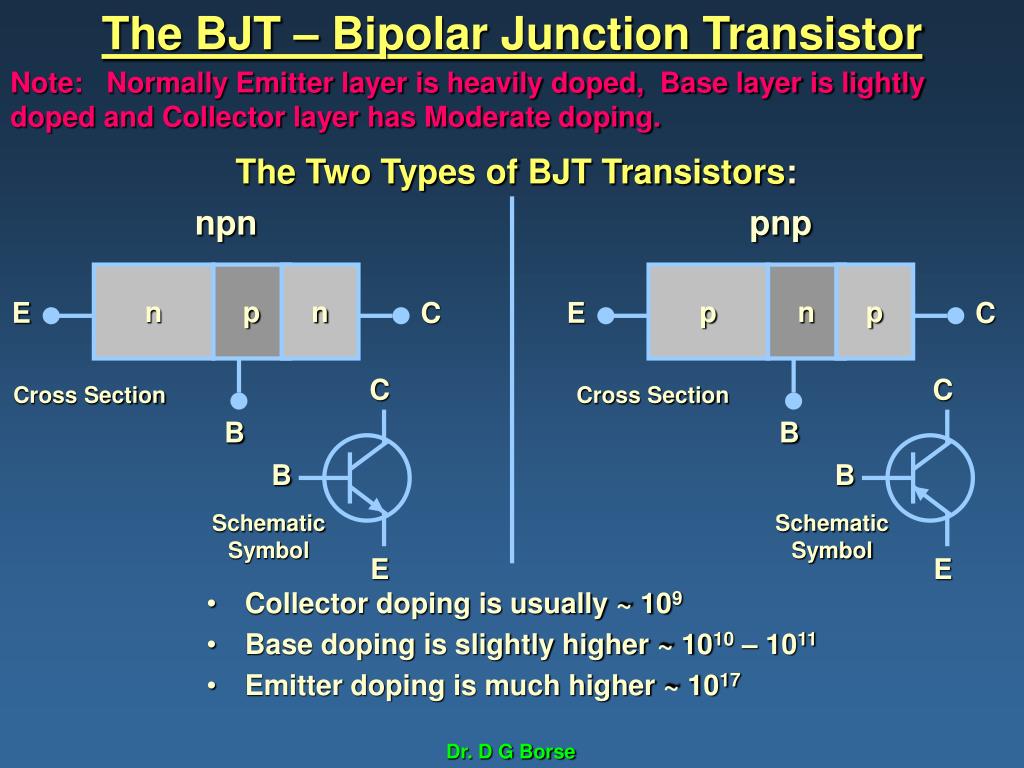
| Construction of a BJT | ||
|---|---|---|
| A BJT is formed by sandwiching two differently doped regions (P and N) between a third region (N or P). The P region, known as the base, is sandwiched between two N regions, called the emitter and collector. The emitter is heavily doped, while the collector is lightly doped, creating a concentration gradient. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Construction of a NPN BJT | ||
|---|---|---|
| In an NPN BJT, the emitter is made from a heavily doped N-type material. The base is made from a lightly doped P-type material. The collector is made from a moderately doped N-type material. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Construction of a PNP BJT | ||
|---|---|---|
| In a PNP BJT, the emitter is made from a heavily doped P-type material. The base is made from a lightly doped N-type material. The collector is made from a moderately doped P-type material. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Types of Bipolar Junction Transistors | ||
|---|---|---|
| General Purpose NPN/ PNP BJTs: Used in a wide range of applications, such as amplifiers and switches. Darlington Transistors: Consist of two BJTs connected in a specific configuration, offering high current gain. Power BJTs: Designed to handle high power levels, commonly used in power amplifiers and motor control circuits. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Types of Bipolar Junction Transistors (Contd.) | ||
|---|---|---|
| High-Frequency BJTs: Optimized for high-frequency applications, such as radio frequency amplifiers. Low-Noise BJTs: Minimize noise interference in sensitive circuits, commonly used in audio amplifiers and communication systems. Digital BJTs: Specifically designed for digital logic circuits, offering fast switching speeds. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| BJTs are electronic devices used for amplification and switching of electrical signals. They consist of three layers: emitter, base, and collector. BJTs are classified into NPN and PNP types. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Summary (Contd.) | ||
|---|---|---|
| NPN BJTs have a heavily doped N-type emitter, lightly doped P-type base, and moderately doped N-type collector. PNP BJTs have a heavily doped P-type emitter, lightly doped N-type base, and moderately doped P-type collector. Your third bullet | ||
| 8 | ||
| Summary (Contd.) | ||
|---|---|---|
| There are various types of BJTs, including general-purpose, Darlington, power, high-frequency, low-noise, and digital BJTs. Each type is optimized for specific applications and performance requirements. Your third bullet | ||
| 9 | ||
| Questions? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Any questions regarding the introduction, construction, or types of bipolar junction transistors? Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 10 | ||