Internet Of Things Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to connect and exchange data. IoT aims to enhance efficiency, convenience, and automation in various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and smart homes. By 2025, it is estimated that there will be around 41.6 billion connected IoT devices globally. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Components | ||
|---|---|---|
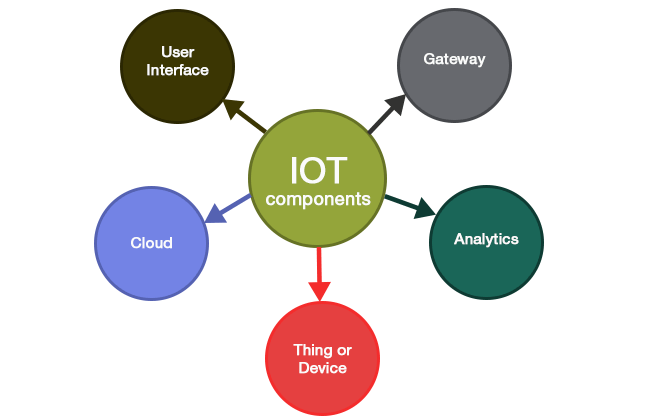
| IoT consists of three main components: devices or objects, connectivity, and data analytics. Devices or objects include sensors, actuators, and embedded systems that collect and transmit data. Connectivity enables these devices to communicate with each other and with the cloud or network infrastructure. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| IoT has numerous applications in various sectors:
- In healthcare, IoT devices can monitor patients' vital signs, track medication adherence, and enable remote patient monitoring.
- In agriculture, IoT sensors can monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health to optimize irrigation and improve yield.
- In transportation, IoT enables vehicle tracking, smart traffic management, and autonomous driving.
- In smart homes, IoT devices control lighting, temperature, security systems, and appliances, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency. Your second bullet Your third bullet |  | |
| 3 | ||
| Benefits | ||
|---|---|---|
| IoT offers several benefits:
- Improved efficiency and productivity through automation and real-time data analysis.
- Enhanced safety and security through remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Cost savings through optimized resource utilization and reduced downtime.
- Improved decision-making by leveraging data-driven insights.
- Enhanced quality of life through personalized and convenient services. Your second bullet Your third bullet |  | |
| 4 | ||
| Challenges | ||
|---|---|---|
| Despite its benefits, IoT poses several challenges:
- Security and privacy concerns due to the large number of interconnected devices.
- Interoperability issues as different devices and platforms may use different protocols and standards.
- Data management and storage challenges due to the volume, velocity, and variety of IoT data.
- Ethical concerns regarding data collection, usage, and potential biases.
- Limited scalability and network capacity in some regions. Your second bullet Your third bullet |  | |
| 5 | ||
| Future Trends | ||
|---|---|---|
| IoT is expected to witness several future trends:
- Edge computing: Processing data closer to the source to reduce latency and bandwidth requirements.
- 5G network adoption: Enabling faster and more reliable connectivity for IoT devices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration: Enhancing data analytics and enabling autonomous decision-making.
- Blockchain technology: Enhancing security, trust, and data integrity in IoT transactions.
- Expansion of IoT into new sectors, such as smart cities, industrial automation, and wearable devices. Your second bullet Your third bullet |  | |
| 6 | ||
| Case Study - Smart Cities | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smart cities leverage IoT technologies to optimize resource usage, improve sustainability, and enhance quality of life. IoT sensors and data analytics enable efficient waste management, traffic management, and energy consumption. Smart city initiatives often focus on improving public services, such as smart lighting, parking, and public transportation. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Case Study - Healthcare | ||
|---|---|---|
| IoT plays a crucial role in healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and personalized medicine. Wearable devices and sensors collect vital signs and health data, allowing for early detection and prevention of health issues. IoT also helps improve medication adherence, hospital management, and healthcare delivery in remote areas. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing various industries by connecting devices, enabling data-driven insights, and enhancing automation. With its vast potential, IoT is expected to continue expanding and transforming the way we live and work. As IoT adoption grows, addressing security, interoperability, and privacy concerns will be crucial for its successful implementation. | ||
| 9 | ||