Insulin Presentation
| Introduction to Insulin | ||
|---|---|---|
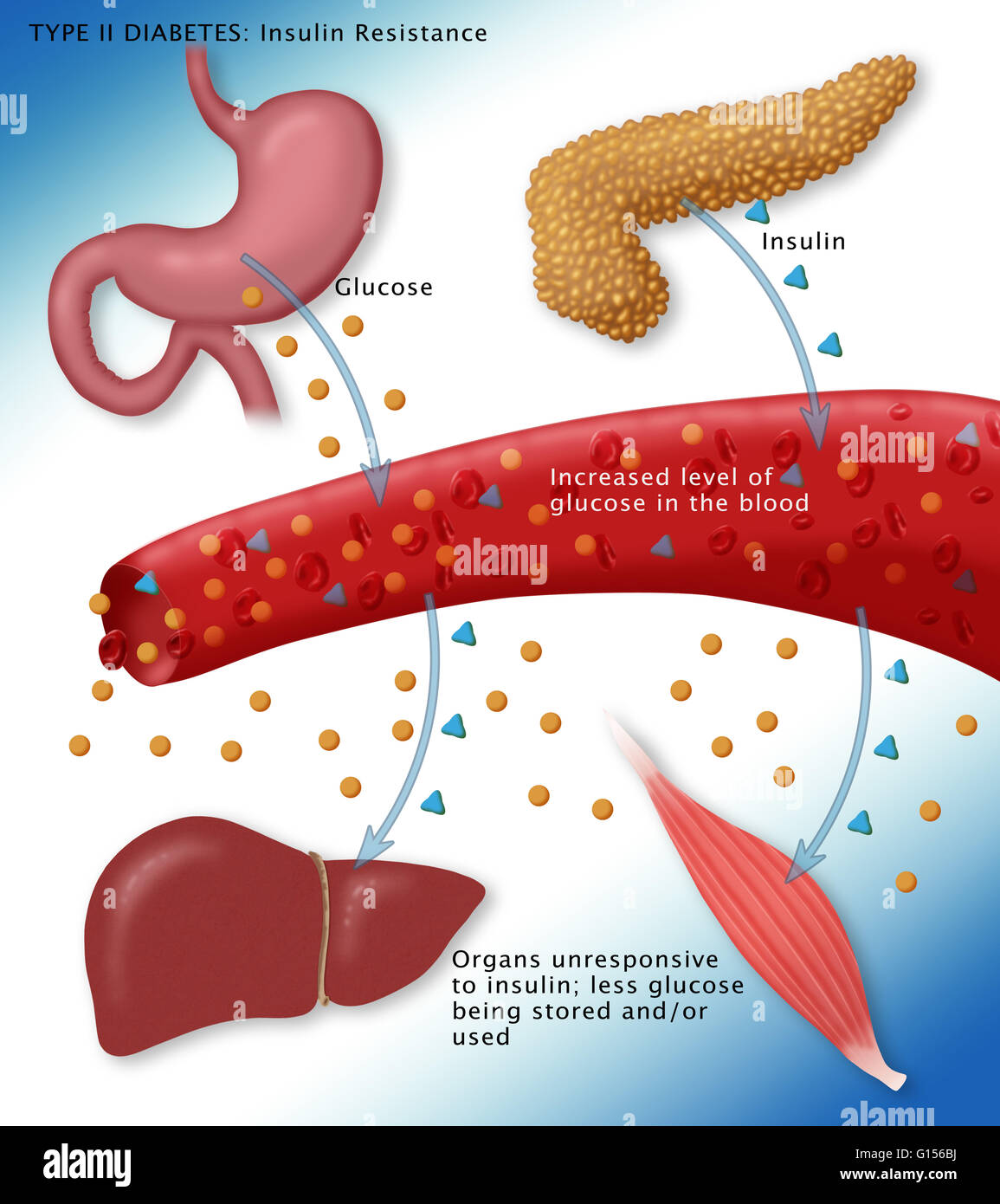
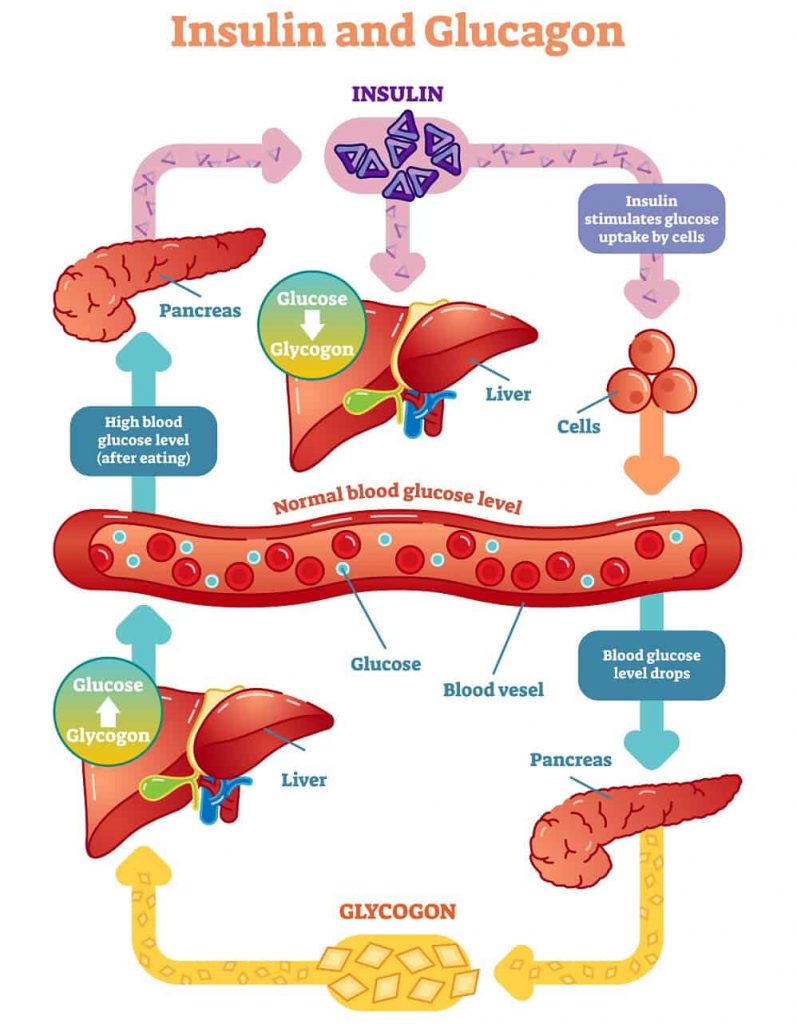
| Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin allows glucose to enter cells for energy production. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Functions of Insulin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Insulin helps to lower blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake in cells. It stimulates the liver to convert excess glucose into glycogen for storage. Insulin inhibits the breakdown of glycogen, preventing the release of glucose into the bloodstream. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Insulin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rapid-acting insulin starts working within 15 minutes and peaks after 1-2 hours. Short-acting insulin begins working within 30 minutes and peaks after 2-4 hours. Intermediate-acting insulin takes effect within 1-2 hours and peaks after 4-12 hours. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Insulin Delivery Methods | ||
|---|---|---|
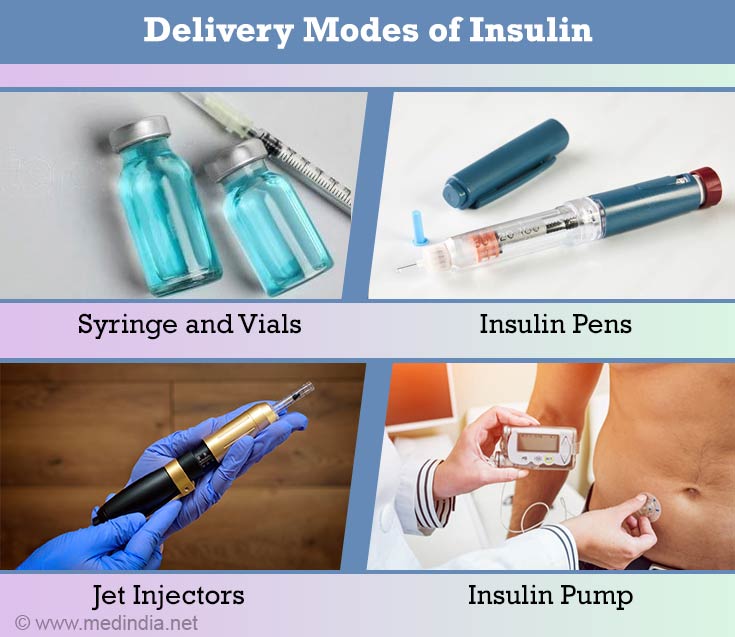
| Insulin injections involve using a syringe or insulin pen to administer the hormone subcutaneously. Insulin pumps deliver a continuous flow of insulin through a catheter placed under the skin. Inhalable insulin is a newer method that allows insulin to be absorbed through the lungs. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Insulin and Diabetes | ||
|---|---|---|
| People with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin injections or pumps to survive. Type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy if other medications and lifestyle changes are insufficient. Insulin therapy helps to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications of diabetes. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Insulin Side Effects | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is a common side effect of insulin therapy. Weight gain can occur due to insulin's ability to promote glucose storage. Allergic reactions to insulin are rare but can include redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Insulin Storage and Handling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Insulin should be stored in the refrigerator but not frozen. Insulin vials or pens in use can be kept at room temperature for up to 28 days. Insulin should be protected from extreme heat or direct sunlight. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Insulin and Exercise | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the need for higher insulin doses. It is important to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise when using insulin. Adjustments to insulin dosage may be necessary based on the intensity and duration of physical activity. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Future Developments in Insulin Therapy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Researchers are exploring the use of oral insulin formulations that can be taken in pill form. Advances in insulin pump technology aim to improve accuracy and ease of use. Artificial pancreas systems integrating insulin delivery and continuous glucose monitoring show promise in automated blood sugar control. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Insulin is a vital hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and is essential for those with diabetes. Various types of insulin and delivery methods are available to meet individual needs. Ongoing research and advancements in insulin therapy continue to improve the management of diabetes. | ||
| 10 | ||