Ibs Presentation
| Introduction to IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder. It affects the large intestine and causes abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits. IBS is a chronic condition that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Symptoms of IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal pain and cramping are the most common symptoms of IBS. Bloating and excess gas can also occur. Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation, are often experienced by individuals with IBS. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Causes of IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but several factors may contribute. Abnormalities in the gut-brain axis and increased sensitivity to pain in the digestive system are believed to play a role. Genetic, environmental, and psychological factors may also contribute to the development of IBS. | ||
| 3 | ||
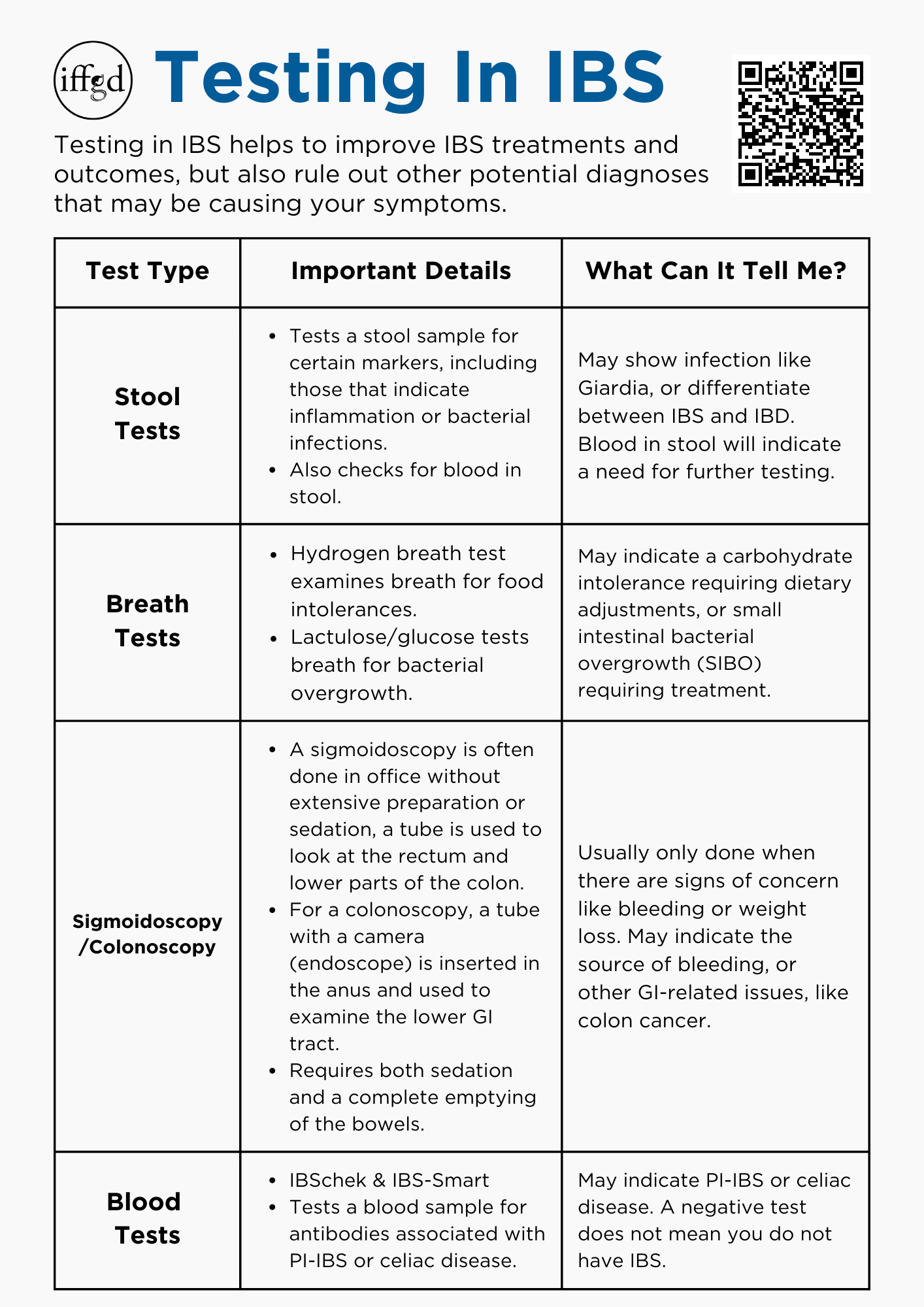
| Diagnosis of IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| There is no specific test for diagnosing IBS. Diagnosis is often based on the presence of specific symptoms and the exclusion of other conditions. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, review medical history, and order certain tests to rule out other potential causes. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Treatment Options for IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications and stress management, are often the first line of treatment for IBS. Medications, including antispasmodics and laxatives, may be prescribed to relieve symptoms. Psychological therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and relaxation techniques, can help manage stress and improve symptoms. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Dietary Modifications for IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Avoiding trigger foods, such as those high in FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols), can help reduce symptoms. Increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated can improve bowel regularity. Keeping a food diary and working with a registered dietitian can help identify individual triggers and develop a personalized diet plan. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Stress Management for IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stress can exacerbate IBS symptoms, so stress management techniques are crucial. Regular exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress levels. Seeking support from friends, family, or a support group can also be beneficial. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Medications for IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Antispasmodics, such as dicyclomine, can help relieve abdominal pain and cramping. Laxatives, such as polyethylene glycol, can be used to alleviate constipation. Probiotics may also be recommended to promote a healthy gut microbiome. | ||
| 8 | ||
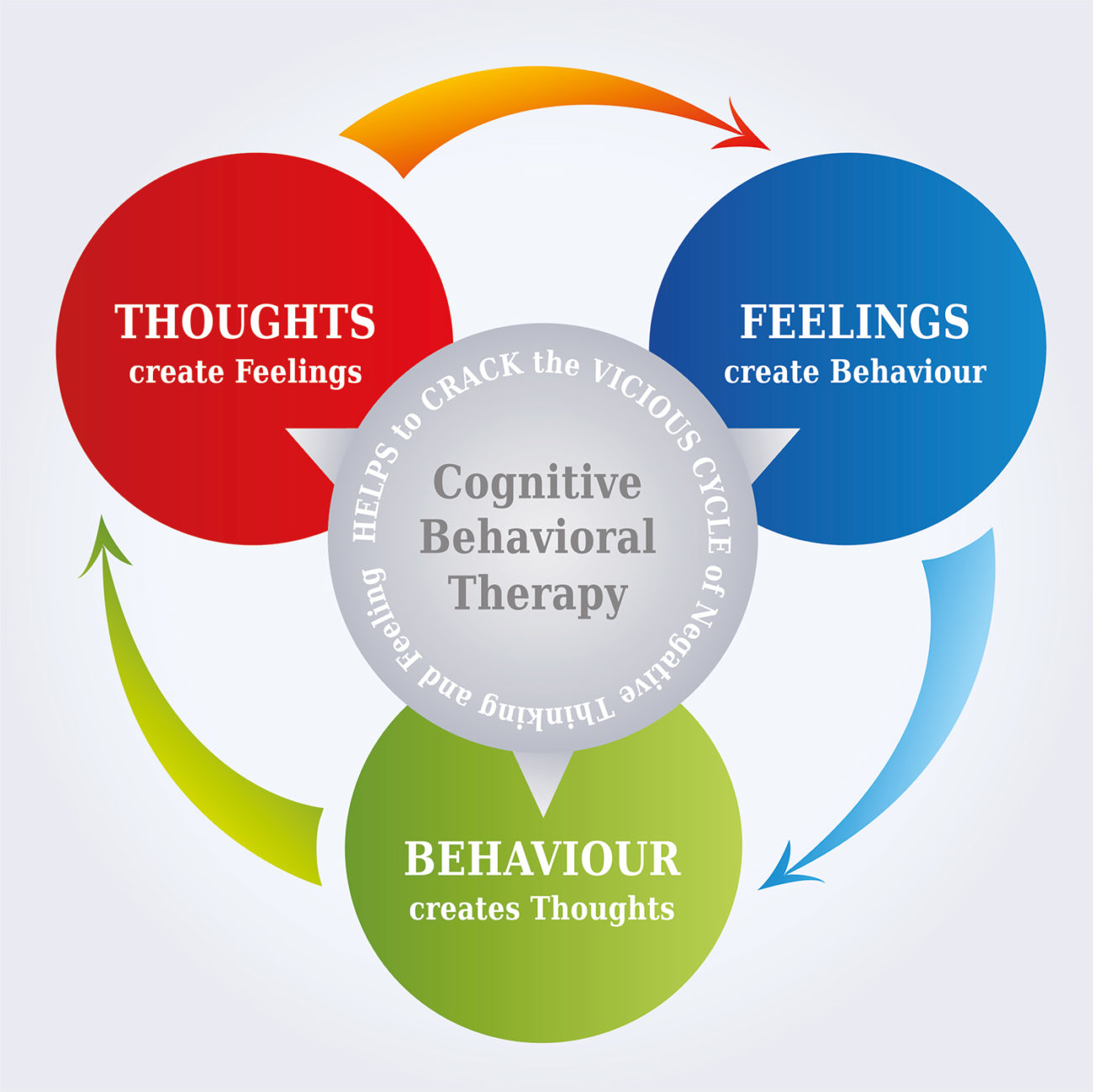
| Psychological Therapies for IBS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals manage stress, anxiety, and depression associated with IBS. Relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation and guided imagery, can promote relaxation and reduce symptoms. Hypnotherapy has shown promising results in improving symptoms and overall well-being in individuals with IBS. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| IBS is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. It is important to work with healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan. By implementing lifestyle changes, managing stress, and utilizing appropriate therapies, individuals with IBS can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| American College of Gastroenterology. (2020).... Mayo Clinic. (2021). Irritable bowel syndrome... National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive ... |  | |
| 11 | ||