IOT Presentation
| Introduction to IoT | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects or "things" that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and exchange data. IoT enables these objects to be controlled or monitored remotely, creating a seamless integration between the physical and digital world. IoT has the potential to revolutionize various industries such as healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and more. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Components of IoT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sensors: IoT devices are equipped with sensors that collect data from the environment or the object itself. Connectivity: IoT devices use various communication technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks to transmit data to other devices or the cloud. Cloud Computing: The collected data from IoT devices is processed and stored in the cloud, allowing for easy access and analysis. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Benefits of IoT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Improved Efficiency: IoT enables automation and real-time monitoring, leading to increased efficiency in various processes. Enhanced Safety: IoT can provide early warnings and alerts, improving safety measures. Cost Savings: IoT can optimize resource usage, reduce maintenance costs, and enable predictive maintenance, resulting in significant cost savings. | ||
| 3 | ||
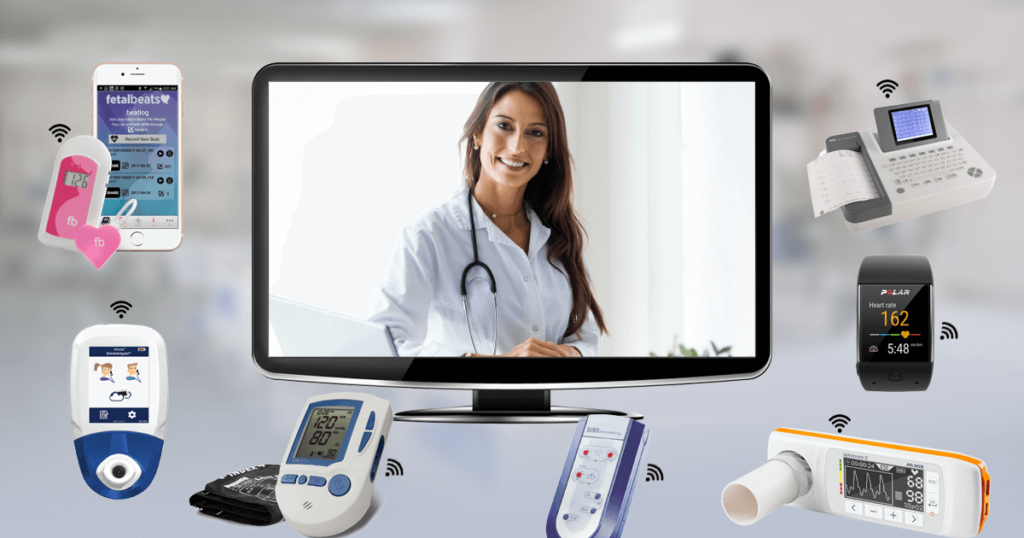
| Applications of IoT in Healthcare | ||
|---|---|---|
| Remote Patient Monitoring: IoT devices can continuously monitor vital signs and send real-time data to healthcare providers, enabling proactive and remote healthcare. Smart Pills: IoT-enabled pills can transmit data when ingested, providing insights into medication adherence and effectiveness. Asset Tracking: IoT can be used to track medical equipment, ensuring their availability and preventing loss. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Examples of IoT in Smart Homes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home Automation: IoT allows for controlling various devices in a home, such as lights, thermostats, and appliances, remotely or through voice commands. Security Systems: IoT-enabled security cameras and sensors can provide real-time monitoring and alerts in case of any suspicious activity. Energy Management: IoT can optimize energy consumption by monitoring and controlling devices like smart plugs and smart meters. | ||
| 5 | ||
| IoT in Transportation and Logistics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fleet Management: IoT sensors in vehicles enable tracking, route optimization, and maintenance scheduling, leading to better efficiency and reduced costs. Supply Chain Optimization: IoT devices can track the location and condition of goods in real-time, providing insights for better inventory management and delivery planning. Smart Parking: IoT can help drivers find available parking spots, reducing congestion and saving time. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges and Concerns with IoT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Security: With more devices connected to the internet, there is an increased risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. Privacy: IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about data privacy and consent. Interoperability: As IoT devices come from different manufacturers and use different communication protocols, ensuring compatibility and seamless integration can be challenging. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Future Trends in IoT | ||
|---|---|---|
| Edge Computing: Processing and analyzing data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements. Artificial Intelligence: AI can enhance IoT capabilities by enabling better data analysis, predictive maintenance, and automation. 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable connections, unlocking new possibilities for IoT applications. Note: The above information is for illustrative purposes only. Please ensure to validate and update the content as per your specific needs and requirements. |  | |
| 8 | ||





+security+challenges.png)