IBM MQ Presentation
| Introduction to IBM MQ | ||
|---|---|---|
| IBM MQ is a messaging middleware that enables communication between applications. It provides reliable, secure, and scalable messaging capabilities. IBM MQ supports various communication protocols like TCP/ IP, HTTP, and more. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Features of IBM MQ | ||
|---|---|---|
| Message Queuing: Messages are sent and received in a reliable and asynchronous manner. Secure Communication: IBM MQ ensures end-to-end encryption and authentication. Scalability: It can handle high volumes of messages and supports clustering for increased capacity. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Benefits of Using IBM MQ | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reliable Messaging: Messages are guaranteed to be delivered and processed in the correct order. Flexibility: IBM MQ supports multiple platforms and programming languages. Seamless Integration: It easily integrates with existing systems and applications. | ||
| 3 | ||
| IBM MQ Components | ||
|---|---|---|
| Queue Manager: Manages message queues, handles communication, and enforces security. Channels: Enable communication between different queue managers. Queues: Store and organize messages to be processed by applications. | ||
| 4 | ||
| IBM MQ Architecture | ||
|---|---|---|
| Client/ Server Model: Applications can connect to remote queue managers using client connections. Publish/ Subscribe Model: Allows one-to-many messaging, where messages are published to topics and subscribed by interested parties. Multi-instance Queue Managers: Provides high availability and disaster recovery capabilities. | ||
| 5 | ||
| IBM MQ Use Cases | ||
|---|---|---|
| Financial Services: Securely exchange messages between banking systems, ATMs, and payment gateways. Supply Chain Management: Enable real-time communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers. Internet of Things (IoT): Handle massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices and ensure reliable communication. | ||
| 6 | ||
| IBM MQ Security Features | ||
|---|---|---|
| SSL/ TLS Encryption: Protects messages in transit by encrypting the data. Access Control: Granular permissions and authentication mechanisms to control who can access queues and channels. Message Integrity: Ensures that messages are not tampered with during transmission. | ||
| 7 | ||
| IBM MQ Monitoring and Management | ||
|---|---|---|
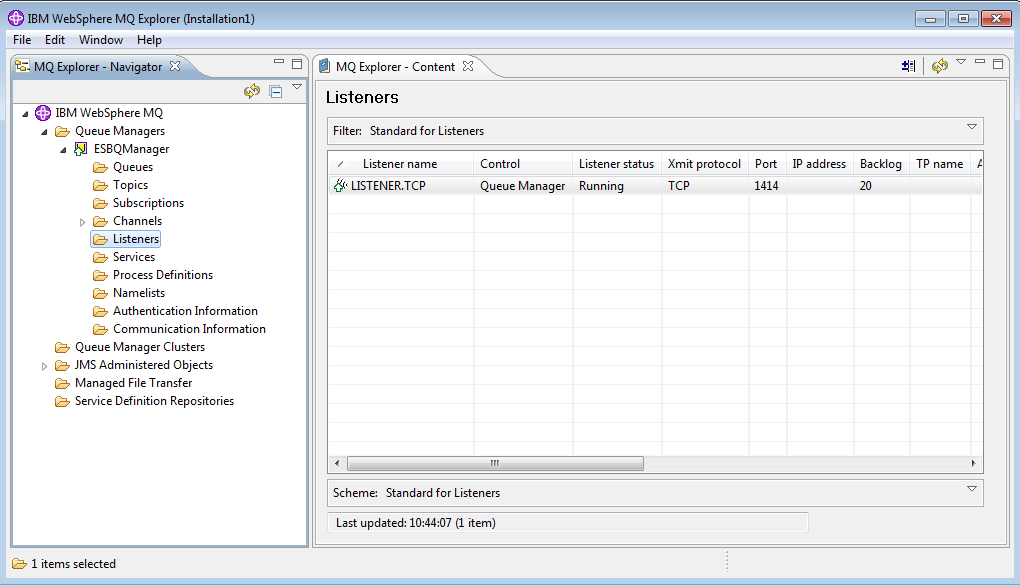
| IBM MQ Explorer: A graphical tool for managing queue managers, channels, and queues. MQ Console: Web-based interface for monitoring and managing IBM MQ instances. Integration with Monitoring Tools: IBM MQ integrates with various monitoring tools like IBM Cloud Pak for Integration, IBM Operations Analytics, and more. | ||
| 8 | ||
| IBM MQ Deployment Options | ||
|---|---|---|
| On-Premises: Install and manage IBM MQ on your own hardware and infrastructure. IBM Cloud: Deploy IBM MQ on IBM Cloud for a fully managed and scalable messaging solution. Hybrid: Combine on-premises and cloud deployments for a flexible and integrated messaging environment. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| IBM MQ is a robust messaging middleware that provides reliable and secure communication between applications. It offers a wide range of features like message queuing, scalability, and seamless integration. With its strong security measures and monitoring capabilities, IBM MQ is suitable for various industries and use cases. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| IBM MQ Documentation: https:// www.ibm.com/ d... IBM MQ Overview: https:// www.ibm.com/ cloud/... IBM MQ Features: https:// www.ibm.com/ cloud/... |  | |
| 11 | ||