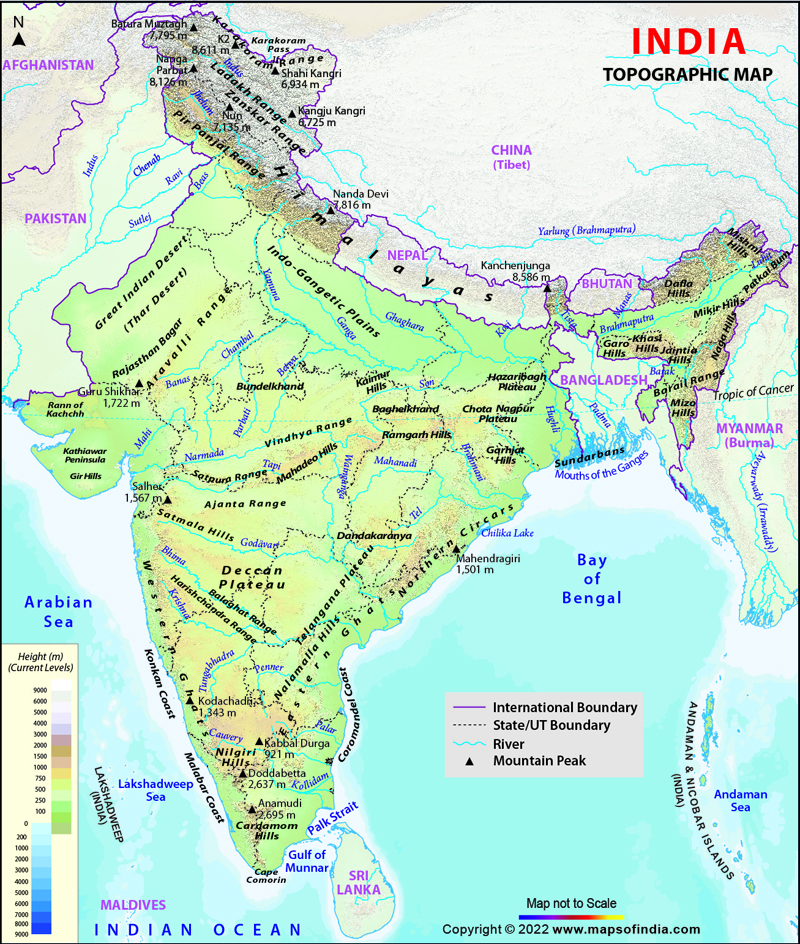
Himalayan River Presentation
| Introduction to Himalayan River | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Himalayan River is a network of rivers flowing through the Himalayan mountain range. These rivers originate from the glaciers and snowmelt in the Himalayas. They play a crucial role in the ecology and livelihoods of millions of people in the region. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Major Himalayan Rivers | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Ganges River: It is one of the most sacred rivers in Hinduism and supports a large population in India and Bangladesh. The Brahmaputra River: It originates in Tibet and flows through India and Bangladesh, providing water for irrigation and hydropower generation. The Indus River: It flows through India, Pakistan, and China, supporting agriculture and supplying water to major cities. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Importance of Himalayan Rivers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Water supply: These rivers provide a significant water source for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. Biodiversity: The rivers sustain diverse ecosystems, hosting numerous species of fish, amphibians, and birds. Hydropower generation: The fast-flowing rivers are ideal for hydropower projects, providing renewable energy to the region. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Challenges and Threats | ||
|---|---|---|
| Glacial melt: With climate change, the Himalayan glaciers are melting at an alarming rate, affecting the river's flow and water availability. Pollution: Unregulated industrial and domestic waste disposal pollutes the rivers, impacting water quality and aquatic life. Deforestation: Rampant deforestation in the Himalayan region leads to soil erosion, increasing sedimentation in the rivers. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Cultural Significance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Religious importance: Himalayan rivers have a spiritual significance in Hinduism, Buddhism, and other religions practiced in the region. Rituals and ceremonies: Various rituals and ceremonies, such as river bathing and water offerings, are performed along the riverbanks. Pilgrimage sites: Many pilgrimage sites are located near these rivers, attracting devotees from all over the world. | ||
| 5 | ||
| River Conservation Efforts | ||
|---|---|---|
| International cooperation: Countries sharing the Himalayan rivers collaborate to manage and conserve water resources sustainably. Watershed management: Implementing afforestation and soil conservation measures to reduce soil erosion and sedimentation. Awareness campaigns: Educating local communities about the importance of river conservation and promoting sustainable practices. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Economic Contributions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture: The fertile plains along the rivers support agriculture, contributing to the economy of the region. Fishing industry: The rivers provide a livelihood for communities engaged in fishing and aquaculture activities. Tourism: The scenic beauty and cultural significance of the Himalayan rivers attract tourists, boosting the local economy. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Future Outlook | ||
|---|---|---|
| Climate change adaptation: Developing strategies to cope with the changing hydrological patterns and the impact on water availability. Sustainable development: Balancing economic growth with environmental conservation to ensure the long-term health of the rivers. Research and monitoring: Continued research and monitoring of the rivers' health to understand their dynamics and plan conservation efforts effectively. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Himalayan rivers are essential lifelines for millions of people, supporting ecosystems, economies, and cultural practices. Conservation and sustainable management are crucial to ensure the longevity and health of these rivers. Collaboration and awareness are key to effectively address the challenges and threats faced by the Himalayan rivers. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| "Himalayan Rivers: An Overview." Internationa... "The Ganges-Brahmaputra River Basin." World W... "The Indus River System." Indus River System ... |  | |
| 10 | ||