Half Wave Rectifier Presentation
| Introduction to Half Wave Rectifier | ||
|---|---|---|
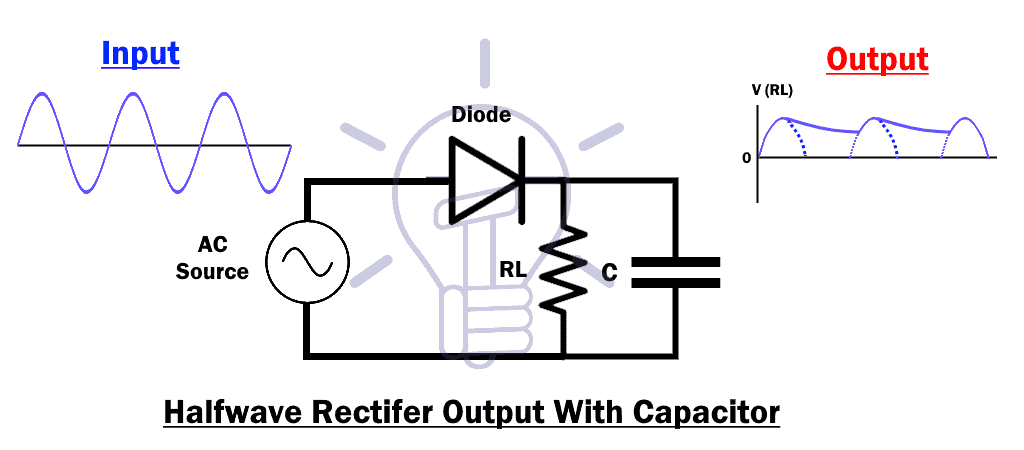
| A half wave rectifier is a type of rectifier that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It utilizes a diode as a key component in the rectification process. The output of a half wave rectifier is a pulsating DC waveform. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Working Principle | ||
|---|---|---|
| During the positive half-cycle of the input AC signal, the diode conducts and allows current to flow through the load. During the negative half-cycle of the input AC signal, the diode becomes reverse-biased and blocks current flow. As a result, only the positive half-cycles of the input AC signal are rectified and appear in the output. | ||
| 2 | ||
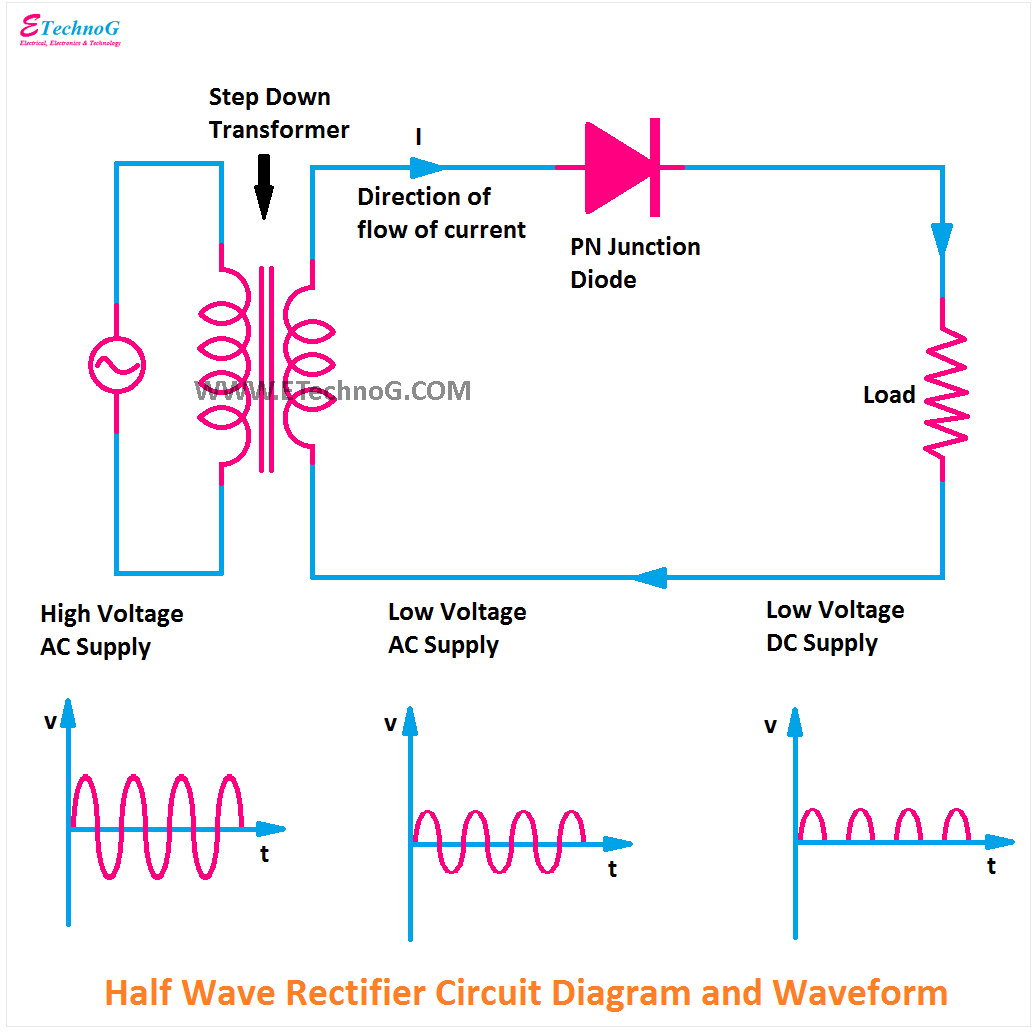
| Circuit Diagram | ||
|---|---|---|
| The circuit consists of a diode, a load resistor, and an AC input source. The diode is connected in series with the load resistor, with its cathode connected to the load. The AC input is connected to the anode of the diode. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Output Waveform | ||
|---|---|---|
| The output waveform of a half wave rectifier is a pulsating DC waveform. It consists of only the positive half-cycles of the input AC signal. The negative half-cycles are completely removed from the output. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Rectification Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
| The rectification efficiency of a half wave rectifier is relatively low. The output waveform has a large ripple factor due to the absence of the negative half-cycles. The rectification efficiency is calculated as the ratio of DC power output to the AC power input. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Half wave rectifiers are commonly used in applications where a low rectification efficiency is acceptable. They are used in battery charging circuits, power supplies for electronic devices, and voltage regulators. They are also used in simple radio receivers and signal detectors. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Advantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| The circuit complexity of a half wave rectifier is relatively low. It requires only a single diode, making it cost-effective and easy to implement. It can be used for small-scale applications where rectification efficiency is not a critical factor. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Disadvantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| The rectification efficiency of a half wave rectifier is comparatively low. The output waveform has a high ripple factor, which can cause problems in sensitive electronic circuits. It is not suitable for high-power applications due to its low efficiency. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Comparison with Full Wave Rectifier | ||
|---|---|---|
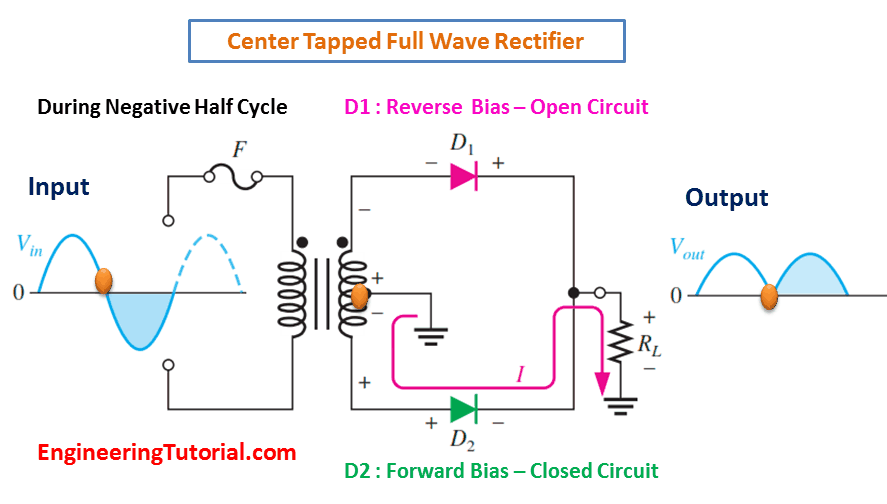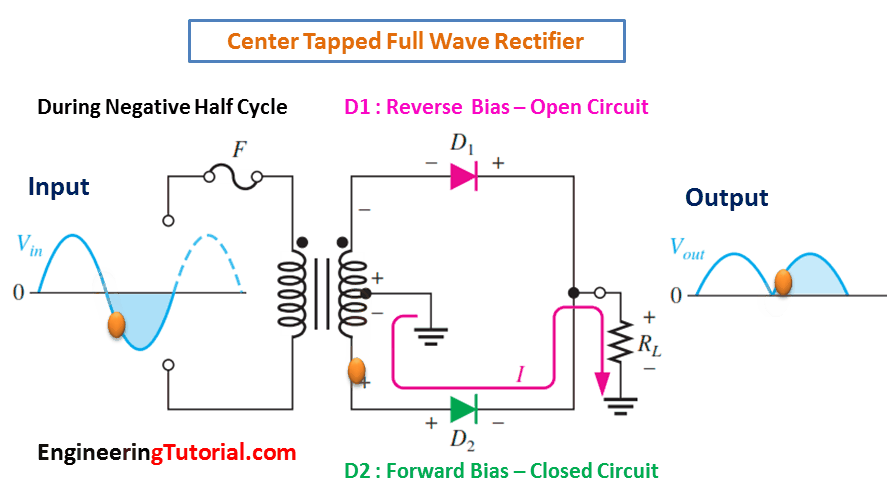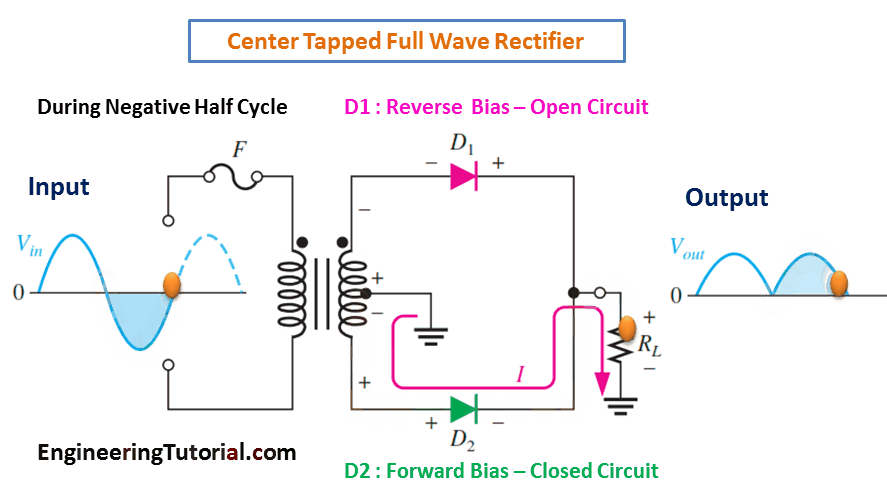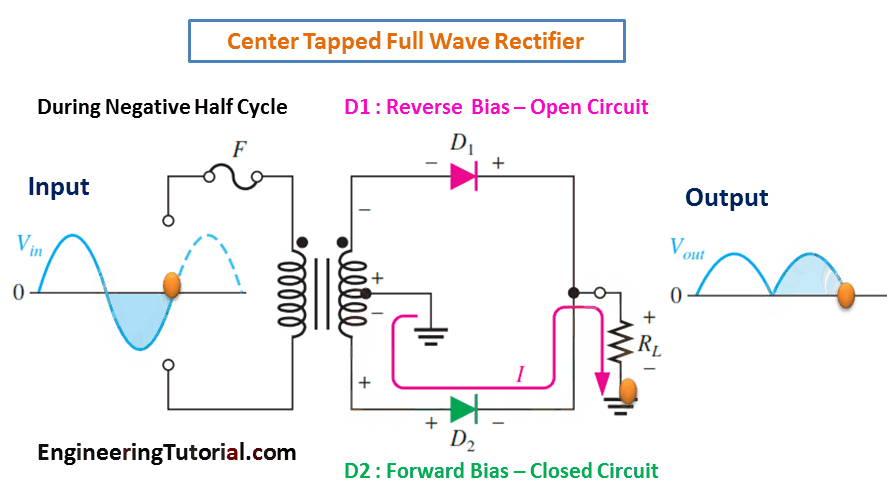
| A full wave rectifier utilizes both the positive and negative half-cycles of the input AC signal. It provides a more efficient rectification and lower ripple factor compared to a half wave rectifier. However, it requires a more complex circuit configuration with additional diodes. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| A half wave rectifier is a simple and cost-effective solution for converting AC to DC. It is suitable for low-power applications where rectification efficiency is not critical. For high-power applications and better rectification efficiency, a full wave rectifier is preferred. | ||
| 10 | ||