Green Computing Presentation
| Introduction to Green Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green computing refers to the practice of using computers and other IT resources in an environmentally-friendly manner. It focuses on reducing the carbon footprint and energy consumption associated with technology. Green computing aims to promote sustainability and minimize the impact of IT on the environment. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Benefits of Green Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Energy efficiency: Green computing helps reduce energy consumption, leading to lower electricity bills and decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Cost savings: By optimizing resource usage and implementing energy-efficient practices, organizations can save money in the long run. Environmental conservation: Green computing contributes to preserving natural resources, minimizing e-waste, and promoting a healthier planet. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Strategies for Green Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
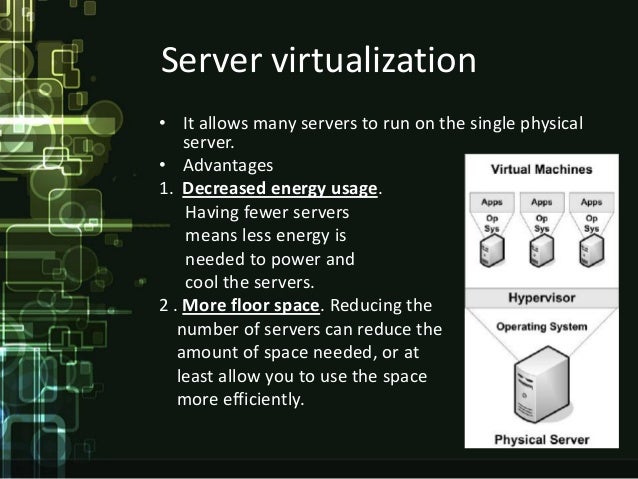
| Virtualization: Utilizing virtual machines and consolidating servers can reduce energy consumption and optimize hardware resources. Power management: Implementing power management settings, such as sleep or hibernate modes, can significantly reduce energy usage. Cloud computing: Moving to the cloud allows for resource sharing and improved energy efficiency, as data centers can be operated at scale. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Recycling and E-waste Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Recycling: Properly recycling electronic devices helps recover valuable materials and prevents harmful substances from contaminating the environment. E-waste management: Organizations should adhere to responsible e-waste disposal practices, including partnering with certified recycling facilities. Donation and refurbishment: Instead of discarding old devices, they can be donated or refurbished, extending their lifespan and reducing waste. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Green Data Centers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Energy-efficient hardware: Using energy-efficient servers, cooling systems, and power distribution units (PDUs) can reduce data center energy consumption. Server virtualization: Consolidating servers through virtualization can optimize resource usage and decrease overall energy consumption. Renewable energy sources: Data centers can be powered by renewable energy, such as solar or wind, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Green Software Development | ||
|---|---|---|
| Efficient code: Developers can write efficient code that minimizes resource usage, leading to reduced energy consumption. Algorithmic optimization: Optimizing algorithms can improve software performance and reduce the computational power required. Software lifecycle management: Managing software updates, patches, and end-of-life processes can help minimize waste and improve security. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Green Networking | ||
|---|---|---|
| Energy-efficient network devices: Using energy-efficient switches, routers, and network equipment can reduce power consumption. Network optimization: Implementing network optimization techniques, such as traffic management and load balancing, can reduce energy usage. Virtual private networks (VPNs): Using VPNs can help reduce travel and associated carbon emissions by facilitating remote work and meetings. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Green Computing in Education | ||
|---|---|---|
| Energy-efficient hardware: Educational institutions can opt for energy-efficient computers, projectors, and other IT equipment. Digital textbooks and online resources: Using digital resources instead of printed materials reduces paper waste and deforestation. Awareness and education: Promoting green computing practices among students and faculty can foster a sustainable mindset and behavior. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green computing is essential for minimizing the environmental impact of technology and promoting sustainability. By adopting green computing strategies, organizations can save costs, reduce energy consumption, and contribute to a greener future. It is crucial for individuals, businesses, and institutions to embrace green computing practices and work towards a more sustainable future. | ||
| 9 | ||