Gobal Warming Presentation
| Introduction to Global Warming | ||
|---|---|---|
| Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth's average surface temperature. It is primarily caused by the release of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, into the atmosphere. The effects of global warming are far-reaching, impacting ecosystems, weather patterns, and human health. | ||
| 1 | ||
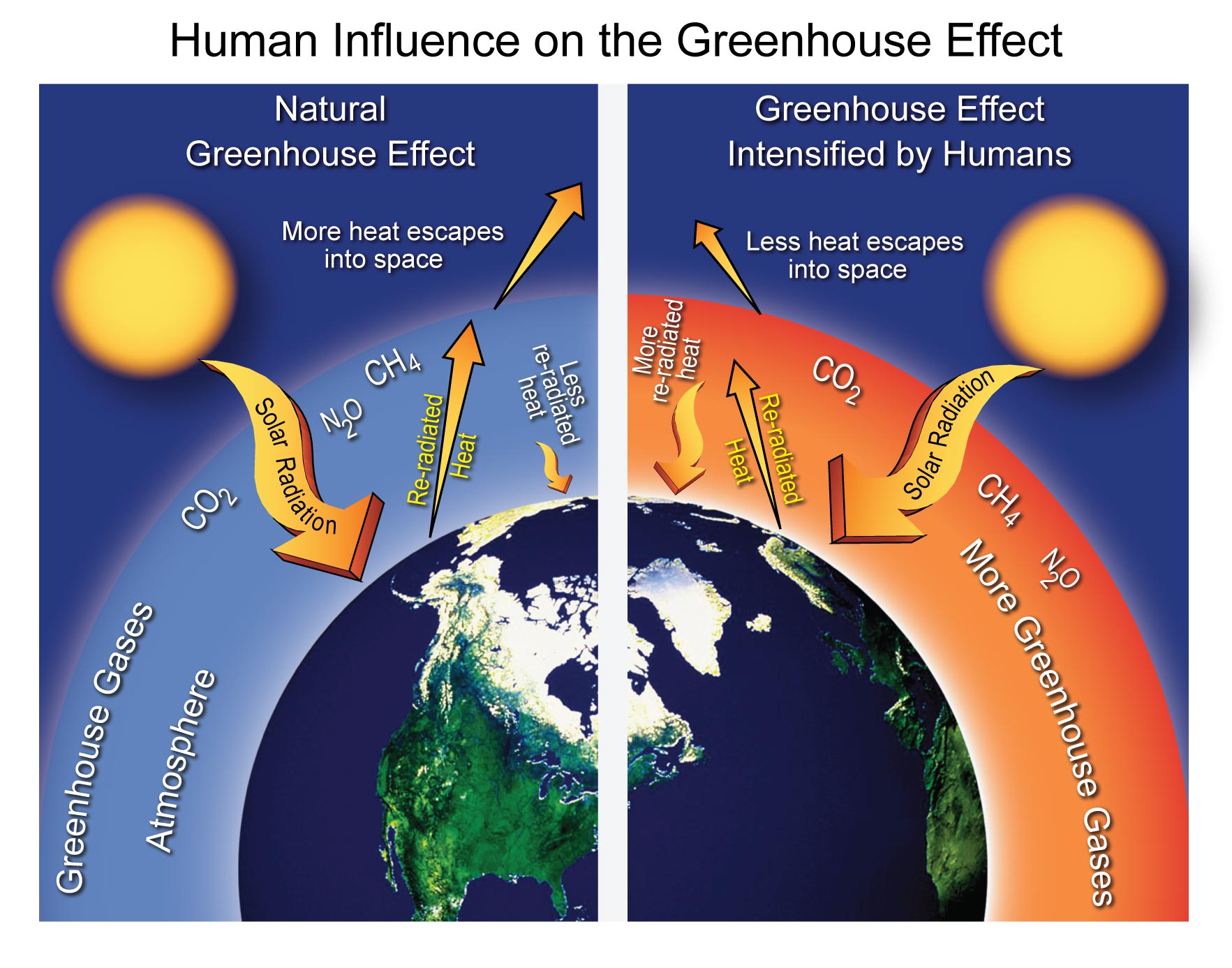
| Greenhouse Effect | ||
|---|---|---|
| The greenhouse effect is a natural process that keeps the Earth's surface warm. It occurs when certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun. However, human activities have enhanced the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Causes of Global Warming | ||
|---|---|---|
| Burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the largest contributor to global warming. Deforestation and land-use changes also release significant amounts of carbon dioxide. Other factors include industrial processes, agriculture, and waste management. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Consequences of Global Warming | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rising temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, causing sea levels to rise. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, become more frequent and intense. Changes in precipitation patterns can result in floods, water scarcity, and negative impacts on agriculture. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Impact on Ecosystems | ||
|---|---|---|
| Global warming disrupts ecosystems, leading to the loss of biodiversity. Many species struggle to adapt to rapid changes in temperature and habitat loss. Coral reefs, forests, and polar regions are particularly vulnerable to the effects of global warming. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Human Health Impacts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rising temperatures increase the prevalence of heat-related illnesses and deaths. Poor air quality, resulting from increased smog and pollution, worsens respiratory conditions. Vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, spread more easily in warmer climates. | ||
| 6 | ||
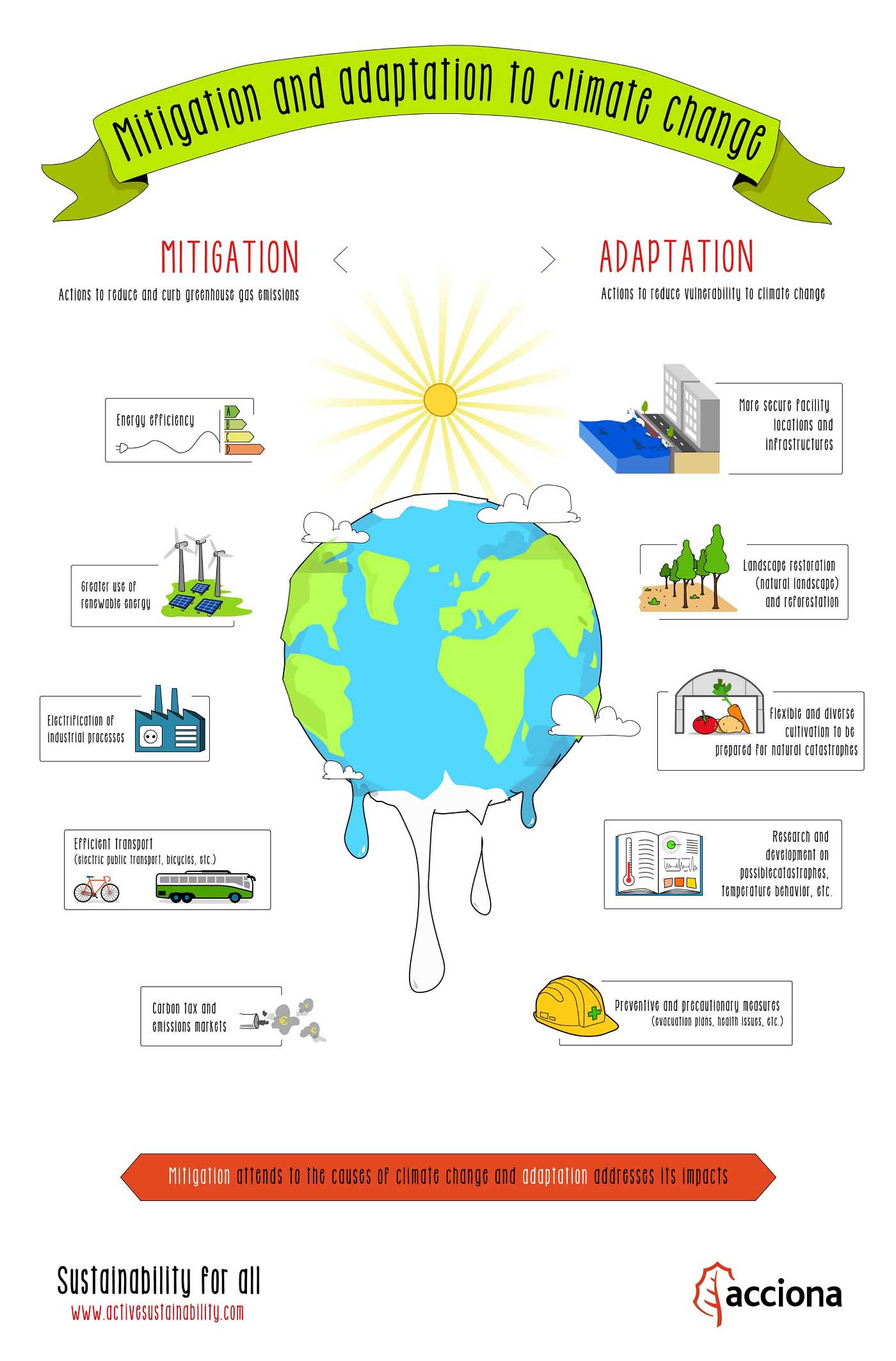
| Mitigation Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Energy efficiency improvements in buildings, transportation, and industries are crucial in mitigating global warming. Forest conservation and reforestation efforts help absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Adaptation Measures | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adapting to global warming involves implementing strategies to reduce vulnerability to climate change impacts. This includes building resilient infrastructure, implementing sustainable agriculture practices, and developing early warning systems. International cooperation and policy frameworks are essential for effective adaptation measures. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Global warming is a pressing issue that requires immediate action. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting sustainable practices, we can mitigate the impacts of global warming. It is crucial for individuals, communities, and governments to work together to create a more sustainable and resilient future. |  | |
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IP... www.ipcc.ch... National Aeronautics and Space Administration... |  | |
| 10 | ||