GST ACCOUNTING EXPLAIN IN BREAF Presentation
| Introduction to GST Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
| GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. It is a consumption-based tax that is levied on the supply of goods and services. GST accounting refers to the process of recording and reporting GST-related transactions. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Components of GST Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
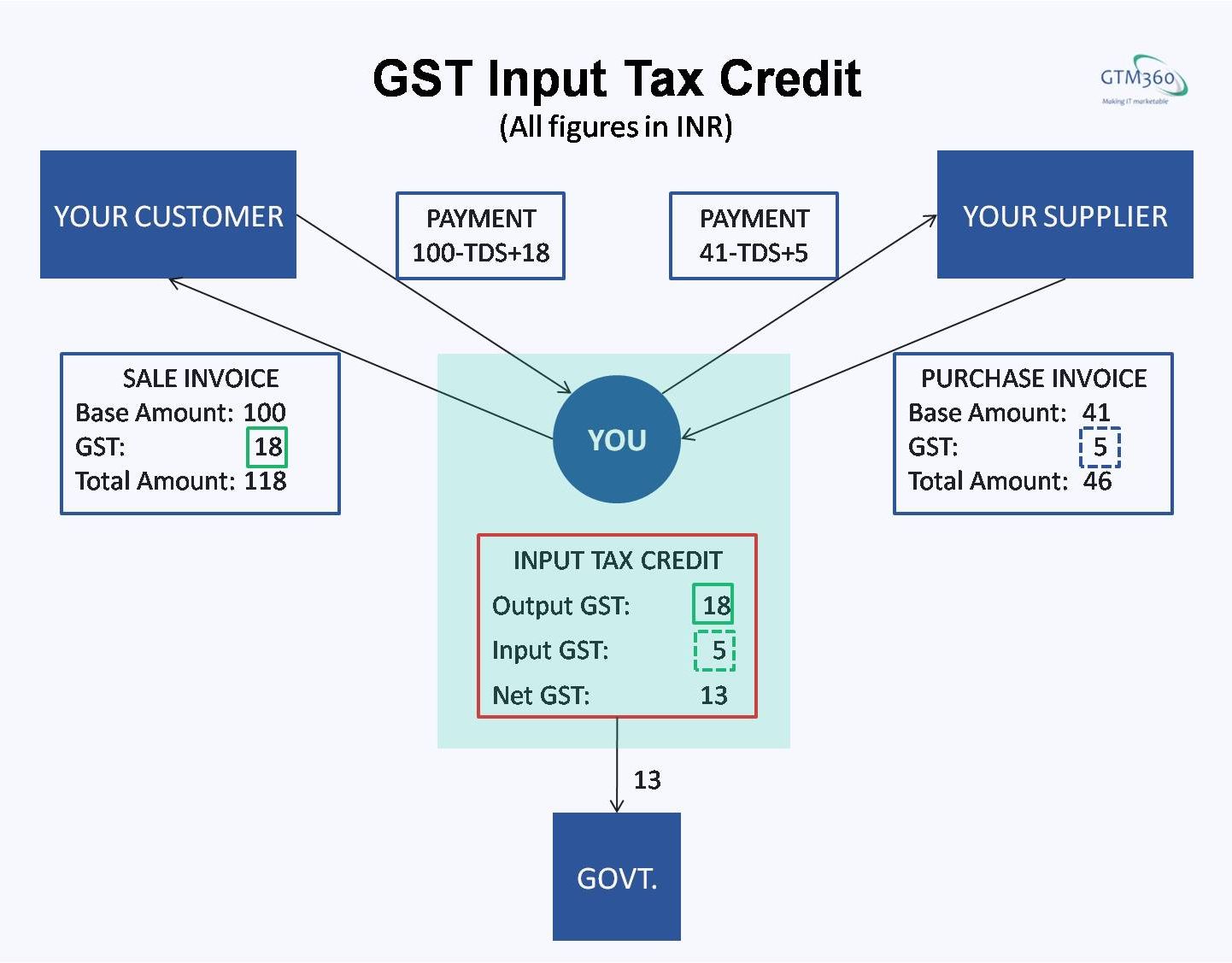
| Input Tax Credit (ITC) - Businesses can claim credit for the GST paid on their purchases and expenses. Output Tax - Businesses collect GST from their customers and must remit it to the government. GST Returns - Regular filing of GST returns is mandatory, which includes reporting taxable supplies, ITC, and payment of GST liabilities. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Importance of GST Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compliance - Proper GST accounting ensures businesses meet their legal obligations and avoid penalties or audits. Accurate Financial Reporting - GST accounting helps in accurately calculating taxable income and presenting financial statements. Cash Flow Management - Tracking input tax credits and output tax helps businesses manage their cash flow effectively. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Methods of GST Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
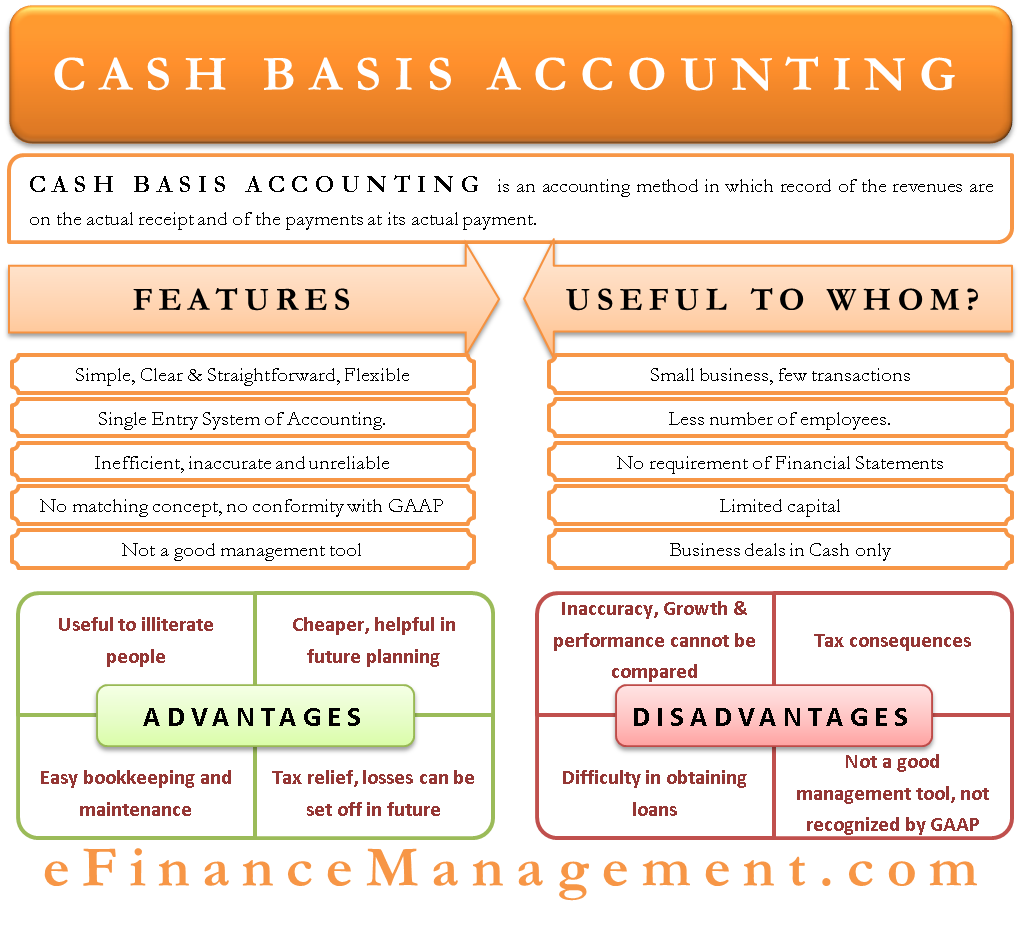
| Cash Basis - GST is accounted for when payment is received or made. Accrual Basis - GST is accounted for when the invoice is issued or received, irrespective of payment. Hybrid Basis - A combination of cash and accrual basis, depending on the nature of transactions. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| GST accounting is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance, accurate financial reporting, and effective cash flow management. It involves recording and reporting input tax credits, output tax, and filing regular GST returns. Different methods of GST accounting can be adopted based on the business's requirements and nature of transactions. | ||
| 5 | ||