Future Scope In Fuel Cells In Industrial Applications Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
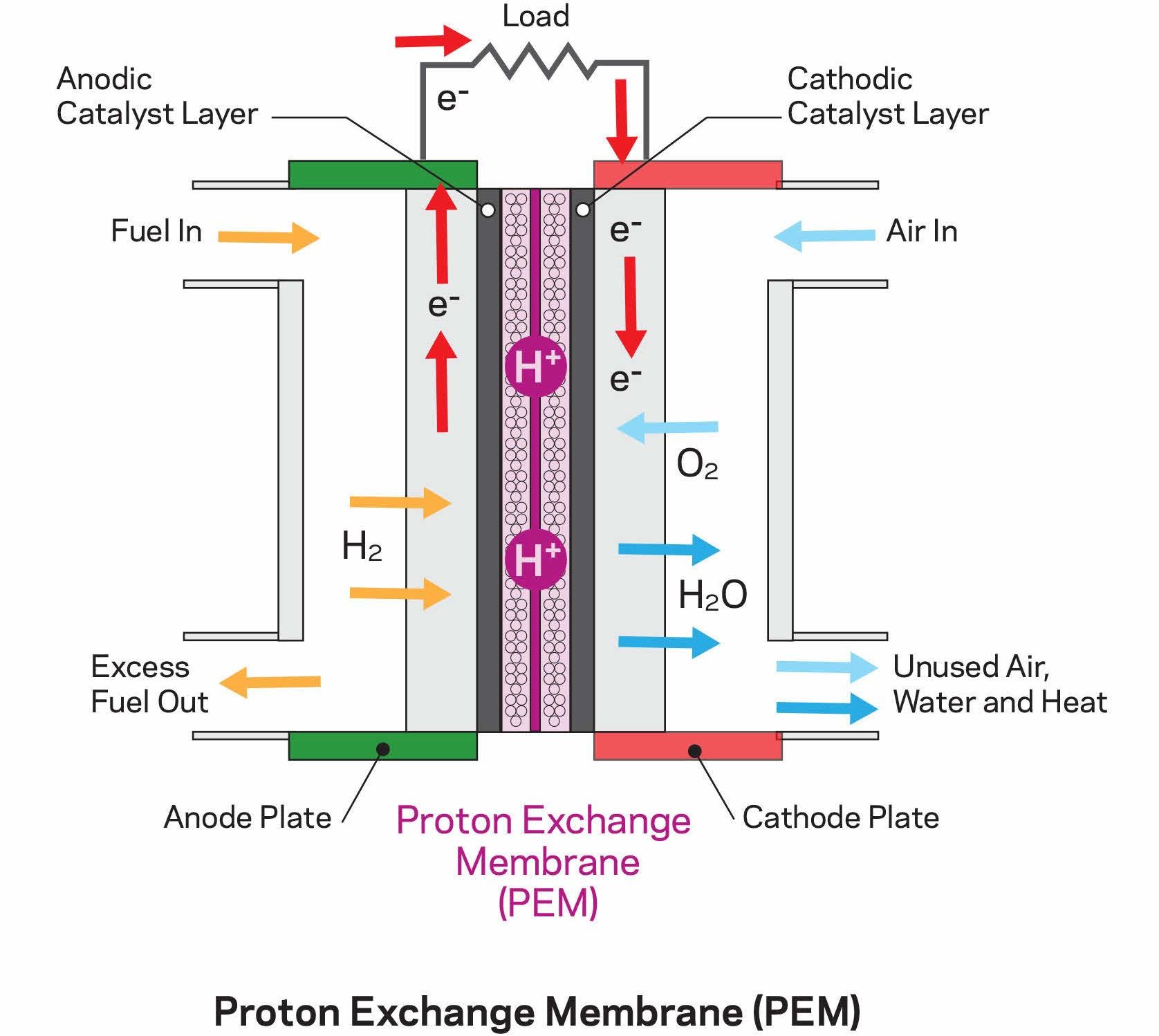
| Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that generate electricity by converting chemical energy from a fuel into electrical energy. In recent years, fuel cells have gained significant attention for their potential in industrial applications due to their high efficiency and low environmental impact. This presentation will explore the future scope of fuel cells in various industrial sectors. | ||
| 1 | ||
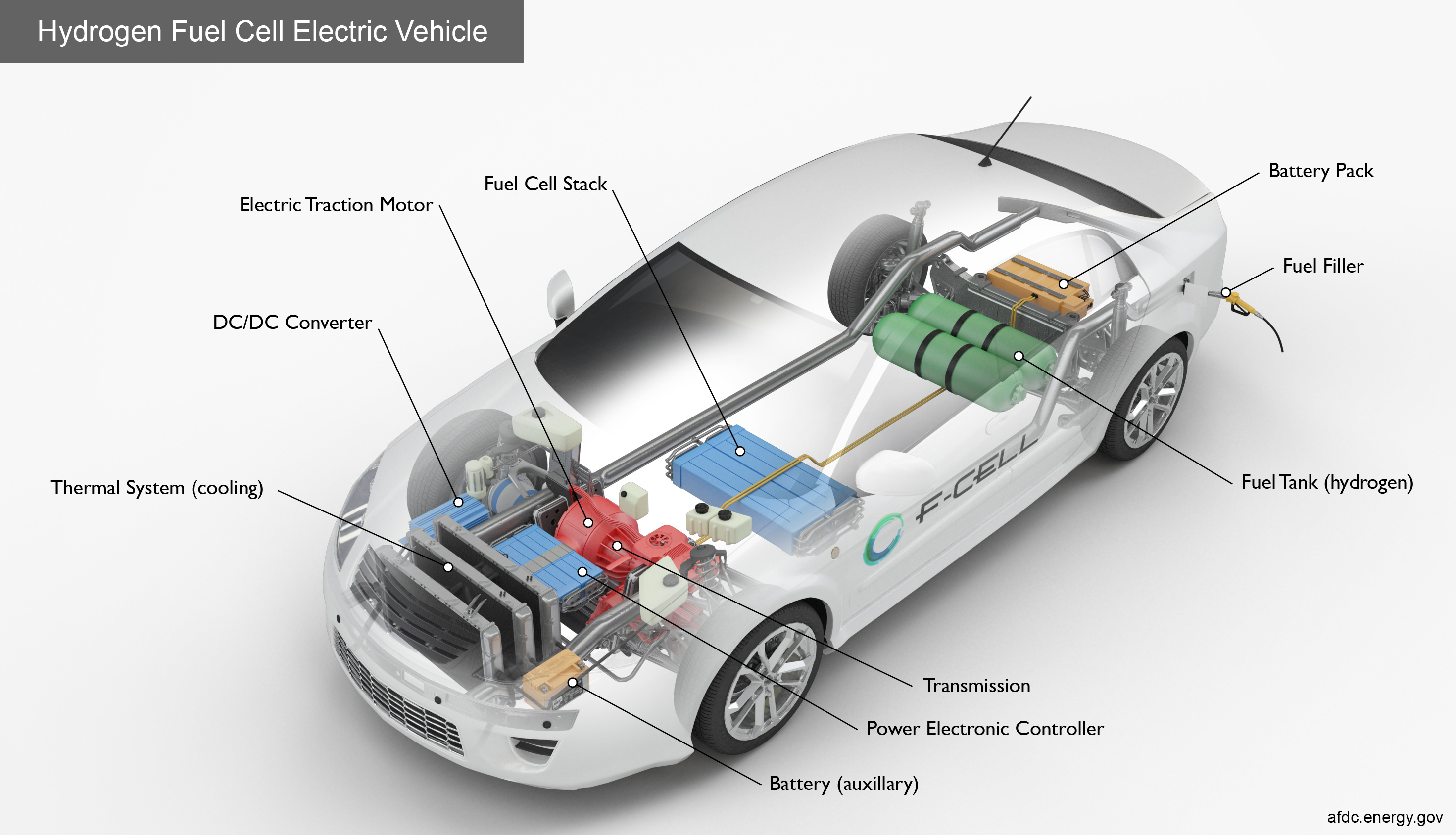
| Automotive Industry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells have the potential to replace internal combustion engines in vehicles, offering zero-emission transportation. Longer range and faster refueling compared to battery electric vehicles. The automotive industry is investing in fuel cell technology to meet stringent emission standards and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Power Generation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional power generation methods. Fuel cell power plants can provide reliable and continuous electricity supply. High efficiency combined heat and power (CHP) systems can utilize waste heat for heating and cooling purposes. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Telecommunications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells can provide backup power for critical telecommunications infrastructure, ensuring uninterrupted communication during power outages. Compact and lightweight fuel cell systems can be easily deployed in remote locations. Fuel cells offer longer runtime compared to traditional battery backup systems. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Material Handling Equipment | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells are increasingly being used in forklifts and other material handling equipment to replace lead-acid batteries. Quick refueling and longer operating hours improve productivity in warehouses and distribution centers. Fuel cell-powered equipment eliminates the need for battery charging infrastructure and reduces downtime. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Marine Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells have the potential to revolutionize the maritime industry by providing clean and efficient propulsion systems. Reduced emissions and noise pollution compared to traditional combustion engines. Fuel cells can offer longer range and extended operational hours for ships and submarines. | 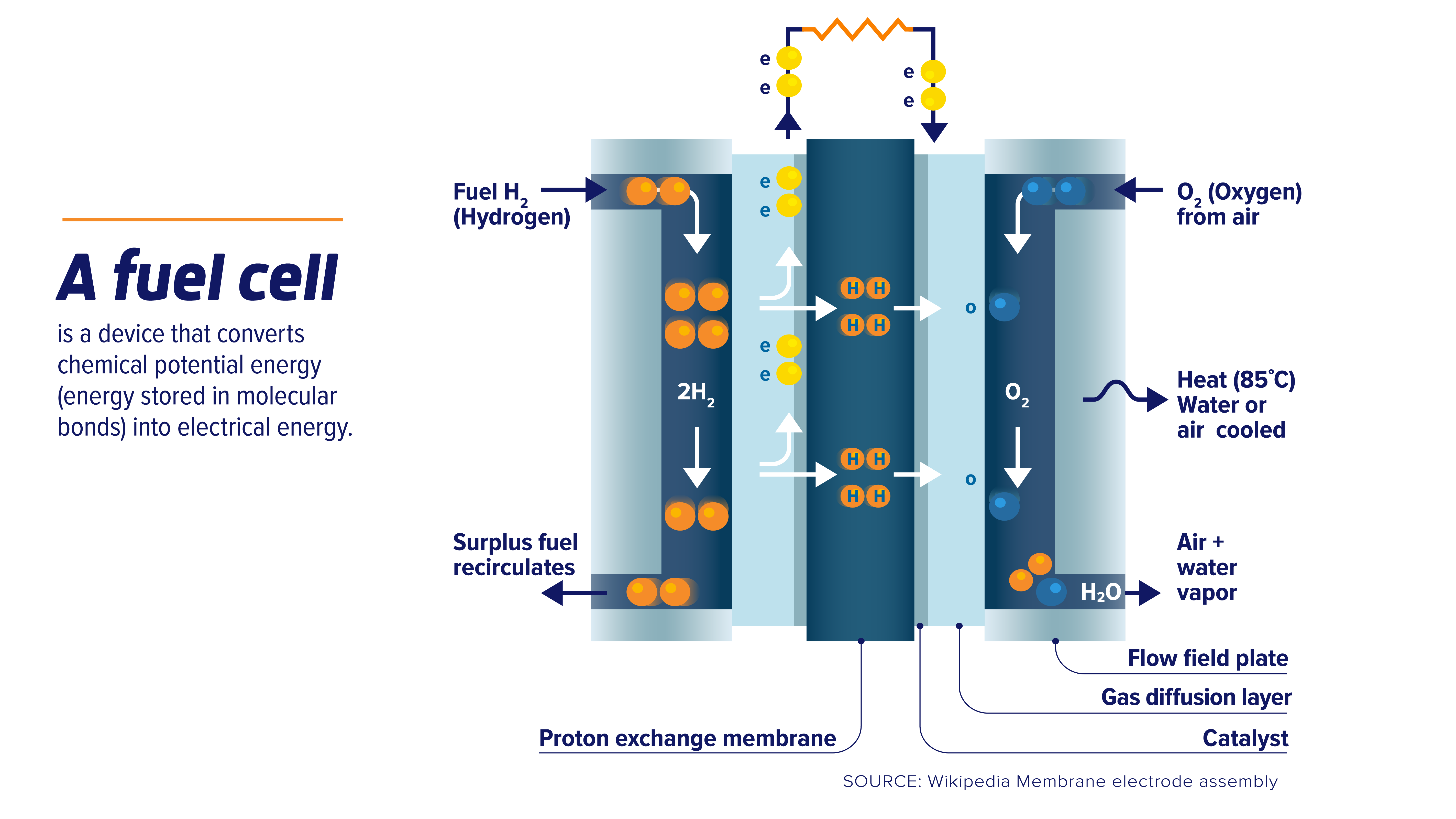 | |
| 6 | ||
| Manufacturing Sector | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells can be integrated into manufacturing processes to provide on-site power and heat, reducing reliance on the grid. Combined with renewable energy sources, fuel cells can support sustainable and decentralized manufacturing operations. Fuel cell-powered equipment can improve energy efficiency and reduce operating costs. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Aerospace Industry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells offer lightweight and compact power solutions for aerospace applications. Longer endurance and reduced emissions compared to traditional combustion engines. NASA and other space agencies are exploring the use of fuel cells for long-duration space missions. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Waste Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells can be used to convert biogas generated from waste treatment plants into electricity and heat. Provides a sustainable and efficient way to harness energy from waste. Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and landfill waste. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The future scope of fuel cells in industrial applications is promising, with potential benefits including reduced emissions, improved energy efficiency, and increased energy independence. Continued research and development, along with supportive policies and investments, will drive the widespread adoption of fuel cells in various industrial sectors. Fuel cells have the potential to play a crucial role in the transition towards a sustainable and low-carbon future. | ||
| 10 | ||