Fungi Presentation
| Introduction to Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that belong to the kingdom Fungi. They are eukaryotic, meaning their cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Fungi play crucial roles in ecosystems as decomposers, symbionts, and pathogens. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Fungal Structure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi have a unique body structure composed of thread-like structures called hyphae. The hyphae form a network called mycelium, which is responsible for nutrient absorption. Fungal cells are surrounded by a rigid cell wall made of chitin, a tough substance also found in the exoskeleton of insects. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|
| There are several major groups of fungi, including yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. Yeasts are single-celled fungi that reproduce by budding or fission. Molds are multicellular fungi that grow as a tangled mass of hyphae. | ||
| 3 | ||
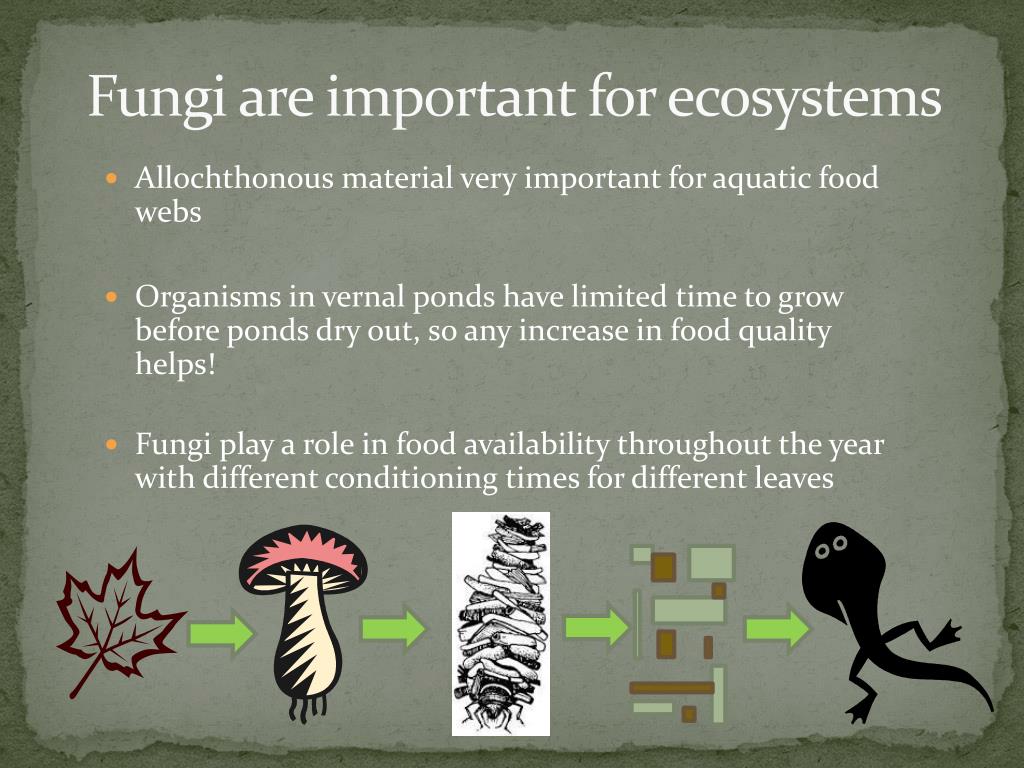
| Ecological Roles of Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi are essential decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Many fungi form mutualistic relationships with plants, helping them absorb nutrients from the soil. Some fungi are pathogens, causing diseases in plants, animals, and humans. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Importance in Food and Medicine | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi are used in the production of various food products, such as bread, cheese, and soy sauce. Certain fungi, like Penicillium, produce antibiotics that are used to treat bacterial infections. Fungi also have potential in the development of new drugs, including anticancer agents. | ||
| 5 | ||
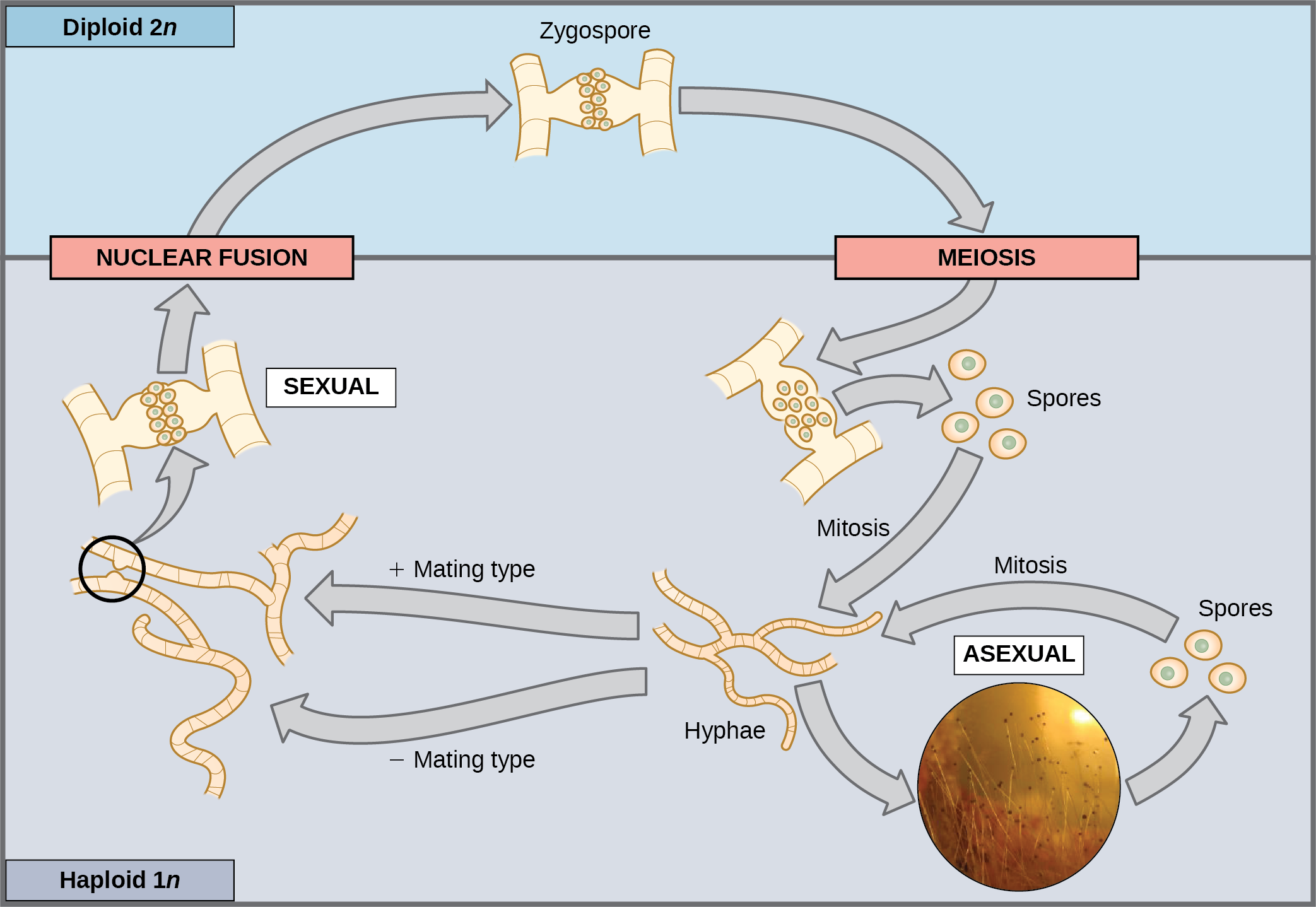
| Reproduction in Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction in fungi involves the fusion of two compatible hyphae and the formation of spores. Asexual reproduction occurs through the production and dispersal of spores without the involvement of mating. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Fungi and Human Health | ||
|---|---|---|
| While some fungi are beneficial, others can cause diseases in humans, such as athlete's foot and ringworm. Fungal infections can occur in various body parts, including the skin, nails, lungs, and digestive system. Immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/ AIDS, are particularly susceptible to severe fungal infections. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Economic Importance of Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi have significant economic importance in industries such as agriculture, biotechnology, and pharmaceuticals. They are used in the production of enzymes, biofuels, and biofertilizers. Fungi also have potential in bioremediation, helping clean up environmental pollutants. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fungi are diverse organisms that play crucial roles in ecosystems and have significant economic and medical importance. Understanding fungi is essential for managing fungal diseases, harnessing their beneficial properties, and preserving biodiversity. Your third bullet | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Alexopoulos CJ, Mims CW, Blackwell M. Introdu... Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA. D... Tortora GJ, Funke BR, Case CL. Microbiology: ... |  | |
| 10 | ||