Fuel Cells All Presentation
| Introduction to Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. They are highly efficient and produce electricity without combustion. Fuel cells have various applications, including transportation, power generation, and portable electronics. | ||
| 1 | ||
| How Fuel Cells Work | ||
|---|---|---|
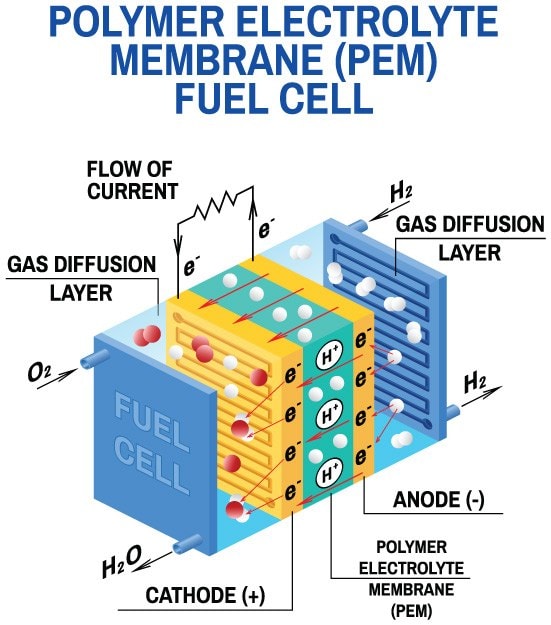
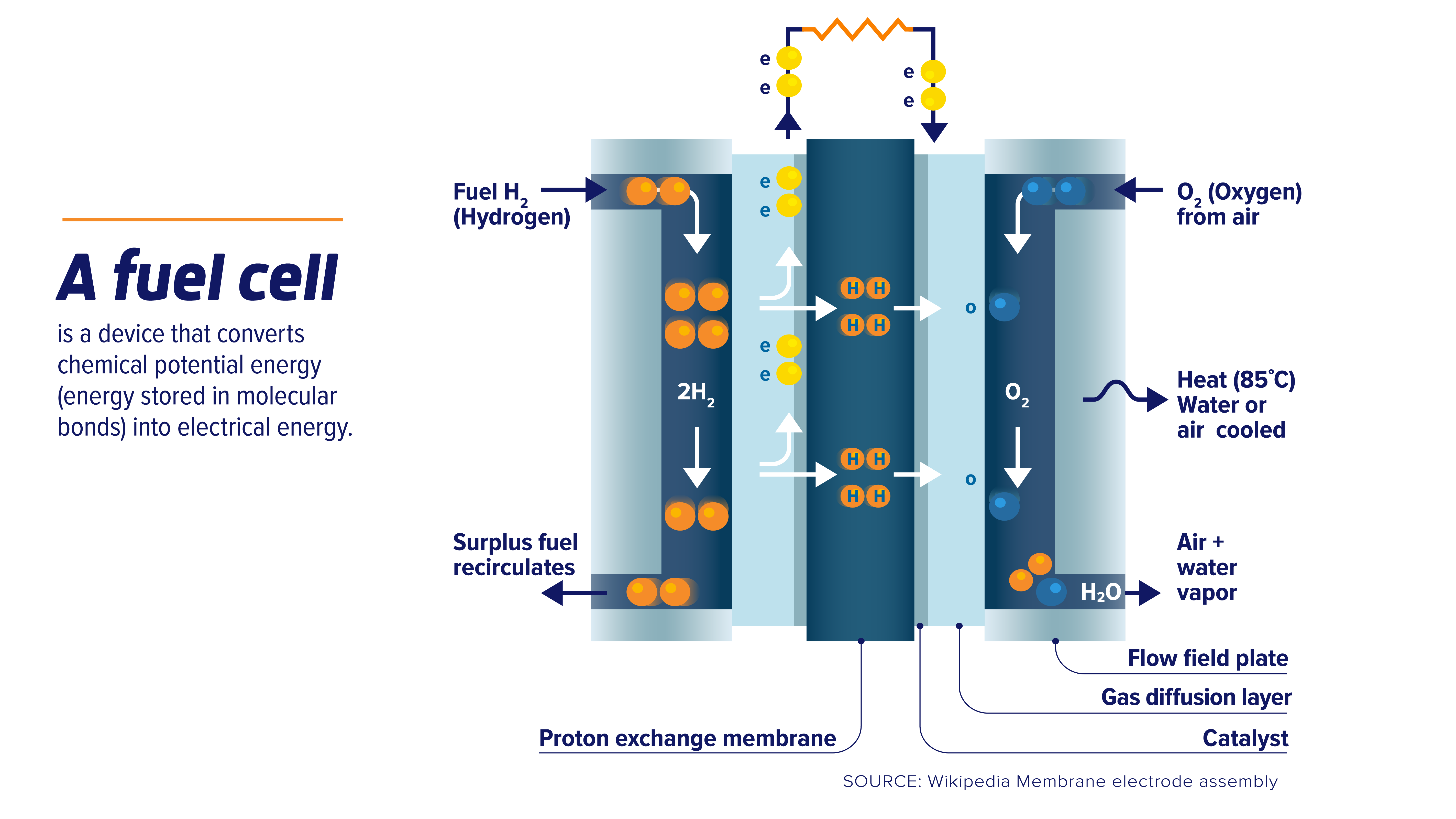
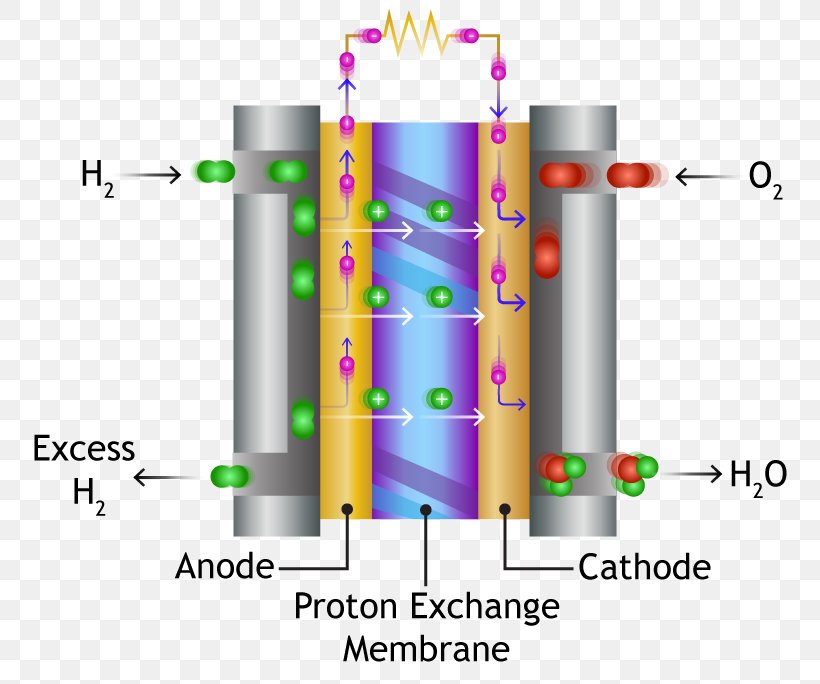
| Fuel cells work by passing hydrogen or other fuels through an anode and oxygen through a cathode. The fuel reacts with the anode catalyst, producing electrons and hydrogen ions. The hydrogen ions travel through an electrolyte and combine with oxygen and electrons at the cathode, generating water and releasing electrical energy. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells: Use a polymer membrane as an electrolyte and operate at low temperatures. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC): Operate at high temperatures and use a solid ceramic electrolyte. Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC): Use a molten carbonate electrolyte and operate at high temperatures. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Advantages of Fuel Cells | ||
|---|---|---|
| High efficiency: Fuel cells can reach efficiencies of up to 60%, compared to 20-30% for combustion-based power sources. Low emissions: Fuel cells produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions and no pollutants if hydrogen is used as fuel. Versatility: Fuel cells can be used in various sizes and applications, from small portable devices to large-scale power plants. |  | |
| 4 | ||
| Challenges in Fuel Cell Adoption | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cost: Fuel cell technology is currently more expensive than traditional power sources. Infrastructure: The lack of hydrogen infrastructure is a barrier to widespread fuel cell adoption. Fuel Source: Hydrogen production requires energy-intensive processes and currently relies on fossil fuels. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Fuel Cell Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transportation: Fuel cells can power electric vehicles providing longer range and shorter refueling times compared to batteries. Backup Power: Fuel cells can provide reliable and clean backup power for critical infrastructure. Portable Electronics: Fuel cells can extend the battery life of smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Current Developments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Research is focused on improving fuel cell efficiency and durability. Advances in hydrogen production methods, such as electrolysis using renewable energy sources. Integration of fuel cells with renewable energy systems to enable energy storage and grid stabilization. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cells offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional power sources. Despite challenges, ongoing research and development are driving progress in fuel cell technology. The widespread adoption of fuel cells has the potential to transform various industries and contribute to a sustainable future. | ||
| 8 | ||