Frequency Modulation Presentation
| Introduction to Frequency Modulation | ||
|---|---|---|
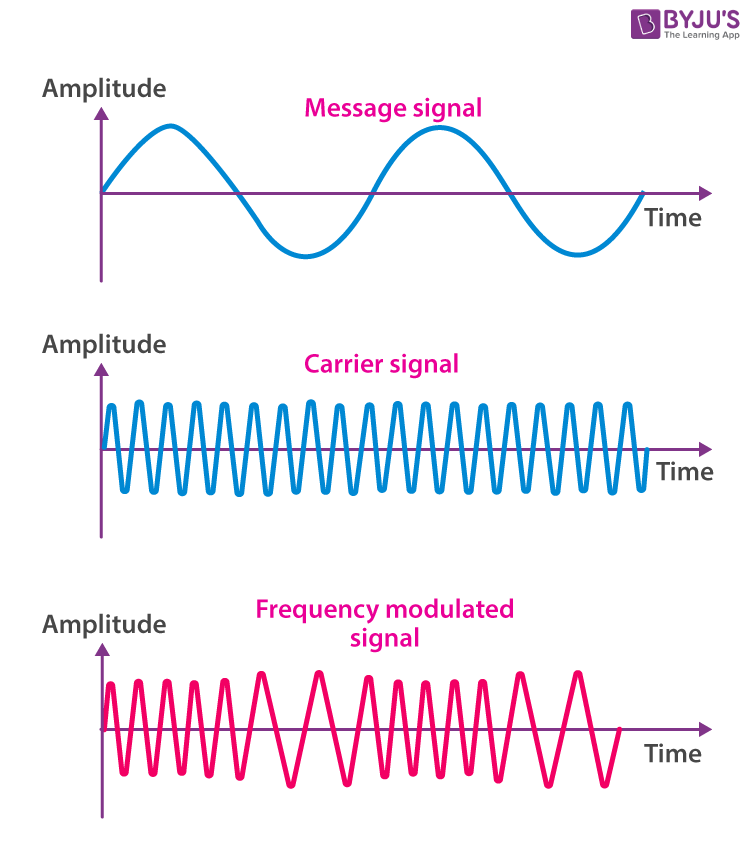
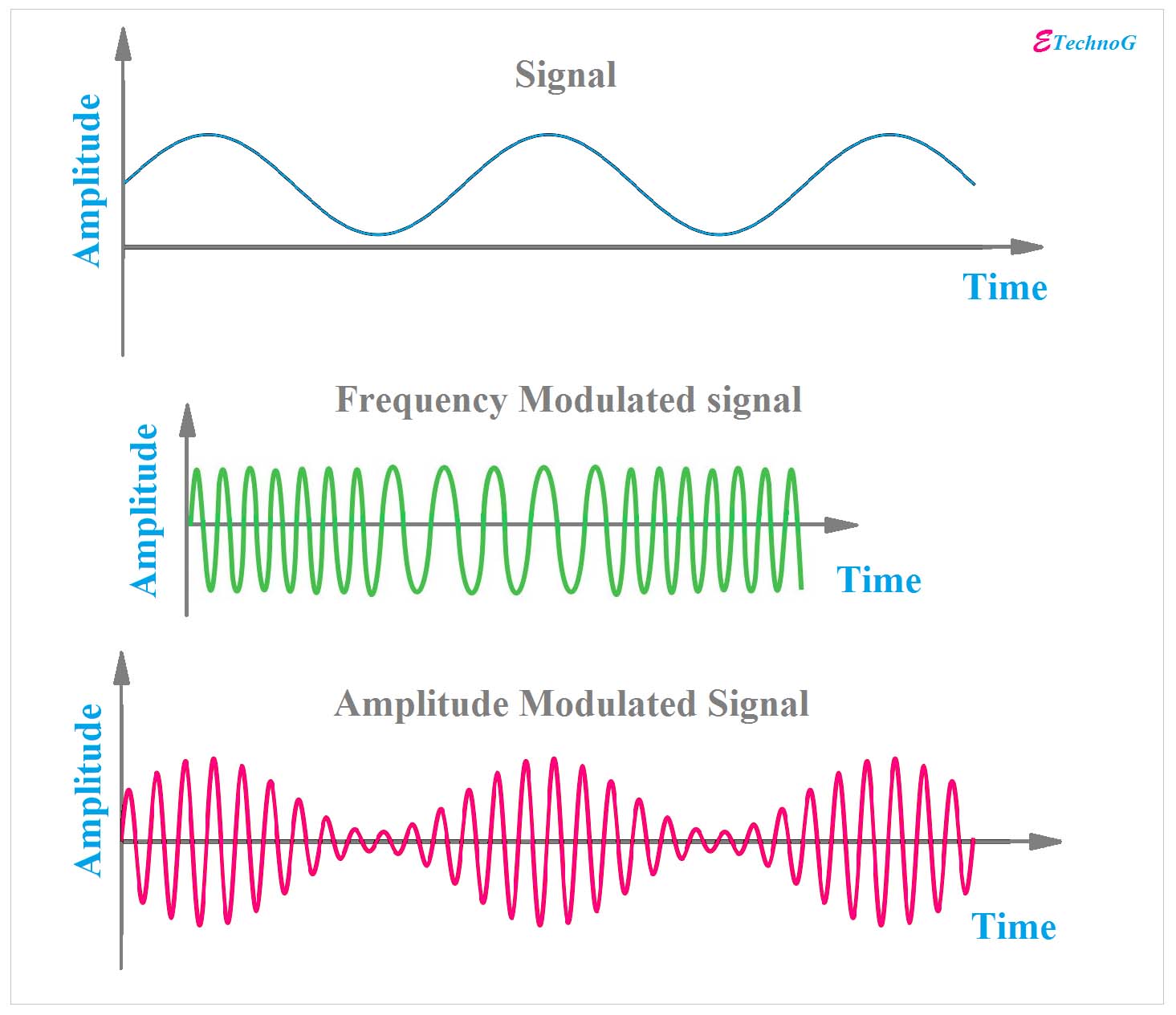
| Frequency Modulation (FM) is a method of encoding information onto a carrier wave by varying its frequency. FM is widely used in radio broadcasting due to its resistance to noise and interference. It was first patented by Edwin Armstrong in 1933 and has since become a fundamental technique in telecommunications. | ||
| 1 | ||
| How Frequency Modulation Works | ||
|---|---|---|
| In FM, the frequency of the carrier wave is changed in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. The modulating signal can be an audio signal, such as voice or music, or any other form of data. The frequency deviation of the carrier wave determines the amount of information that can be transmitted. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Advantages of Frequency Modulation | ||
|---|---|---|
| FM provides better signal quality compared to other modulation techniques, such as amplitude modulation (AM). It has a higher signal-to-noise ratio, making it less susceptible to noise and interference. FM is less affected by atmospheric conditions, making it suitable for long-distance transmission. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Applications of Frequency Modulation | ||
|---|---|---|
| FM is primarily used in radio broadcasting, enabling high-fidelity sound reproduction. It is also used in two-way radio communication systems, such as walkie-talkies and mobile phones. Frequency modulation is employed in various wireless communication standards, including Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Frequency modulation is a versatile and reliable modulation technique widely used in telecommunications. Its resistance to noise, high-quality signal reproduction, and compatibility with various applications make it a preferred choice. Understanding the principles and applications of FM is essential for anyone interested in the field of telecommunications. | ||
| 5 | ||