Four Stroke Engine And Two' Stroke Engine Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
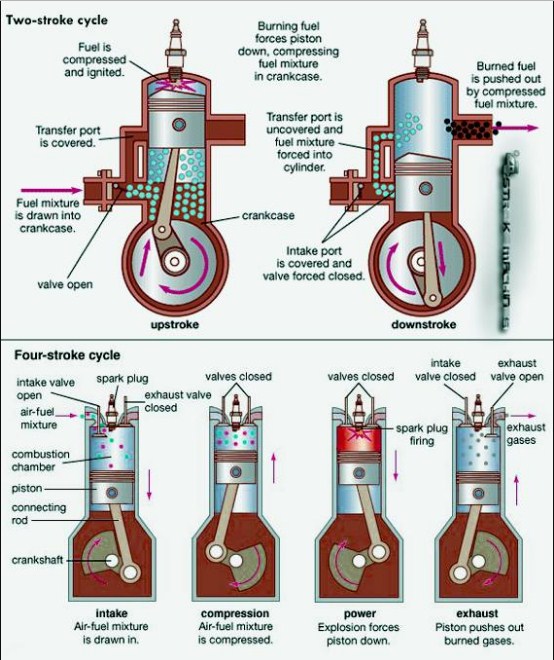
| The difference between a four-stroke engine and a two-stroke engine lies in the number of strokes required to complete a full cycle. A four-stroke engine completes a cycle in four strokes: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. A two-stroke engine completes a cycle in two strokes: compression and combustion. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Four-Stroke Engine - Intake Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
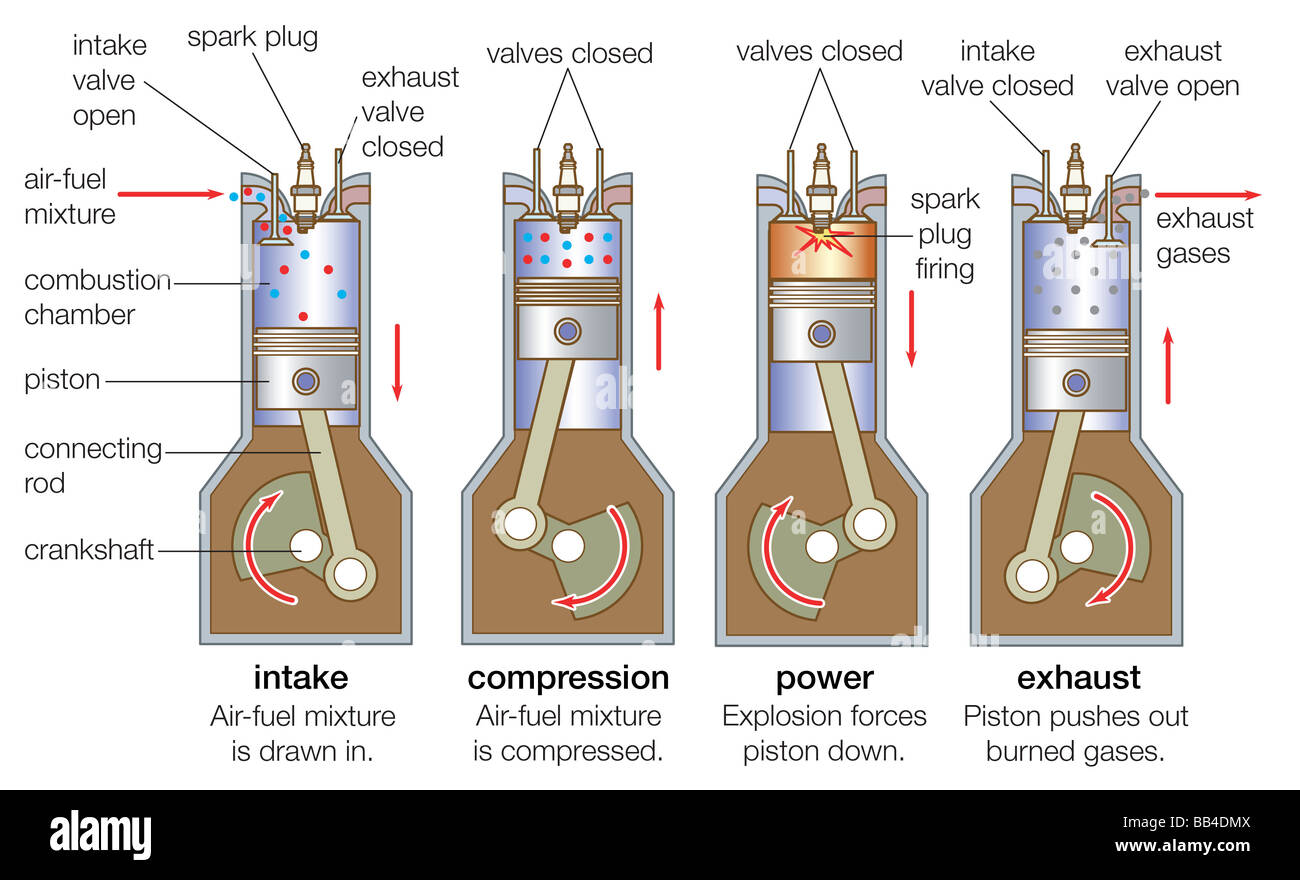
| During the intake stroke, the piston moves downward, drawing in a mixture of air and fuel into the combustion chamber. The intake valve opens, and the fuel-air mixture is pulled in as the piston moves down. At the end of the intake stroke, the intake valve closes. | ||
| 2 | ||
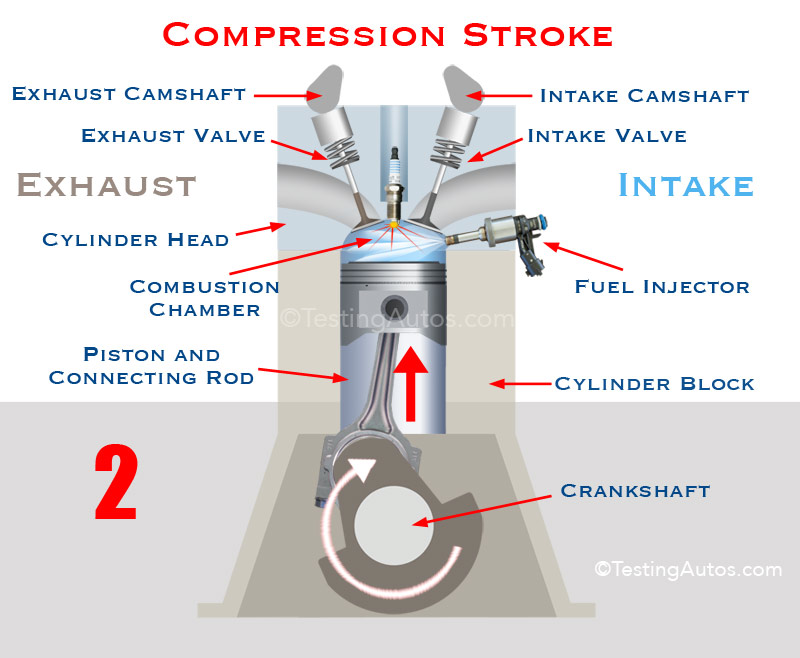
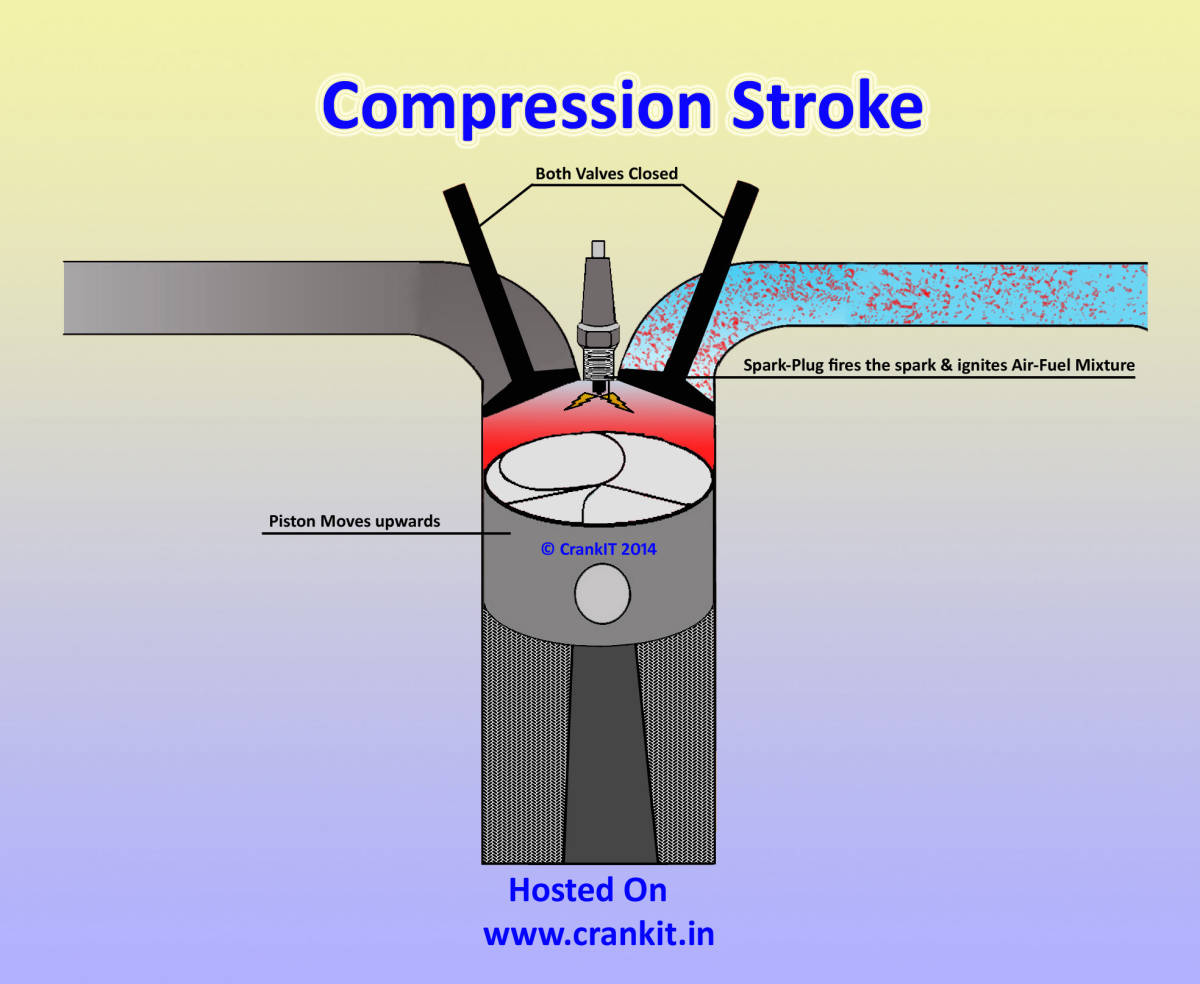
| Four-Stroke Engine - Compression Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
| In the compression stroke, the piston moves upward, compressing the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. Both the intake and exhaust valves remain closed during this stroke. The compression stroke increases the air-fuel mixture's pressure and temperature, preparing it for combustion. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Four-Stroke Engine - Combustion Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
| The combustion stroke is when the spark plug ignites the compressed fuel-air mixture. The burning mixture expands rapidly, creating high pressure that pushes the piston downward. This downward motion generates the engine's power output. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Four-Stroke Engine - Exhaust Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
| During the exhaust stroke, the piston moves upward, pushing the burned gases out of the combustion chamber. The exhaust valve opens, allowing the gases to escape into the exhaust system. The piston's upward motion pushes the gases out through the open exhaust valve. | ||
| 5 | ||
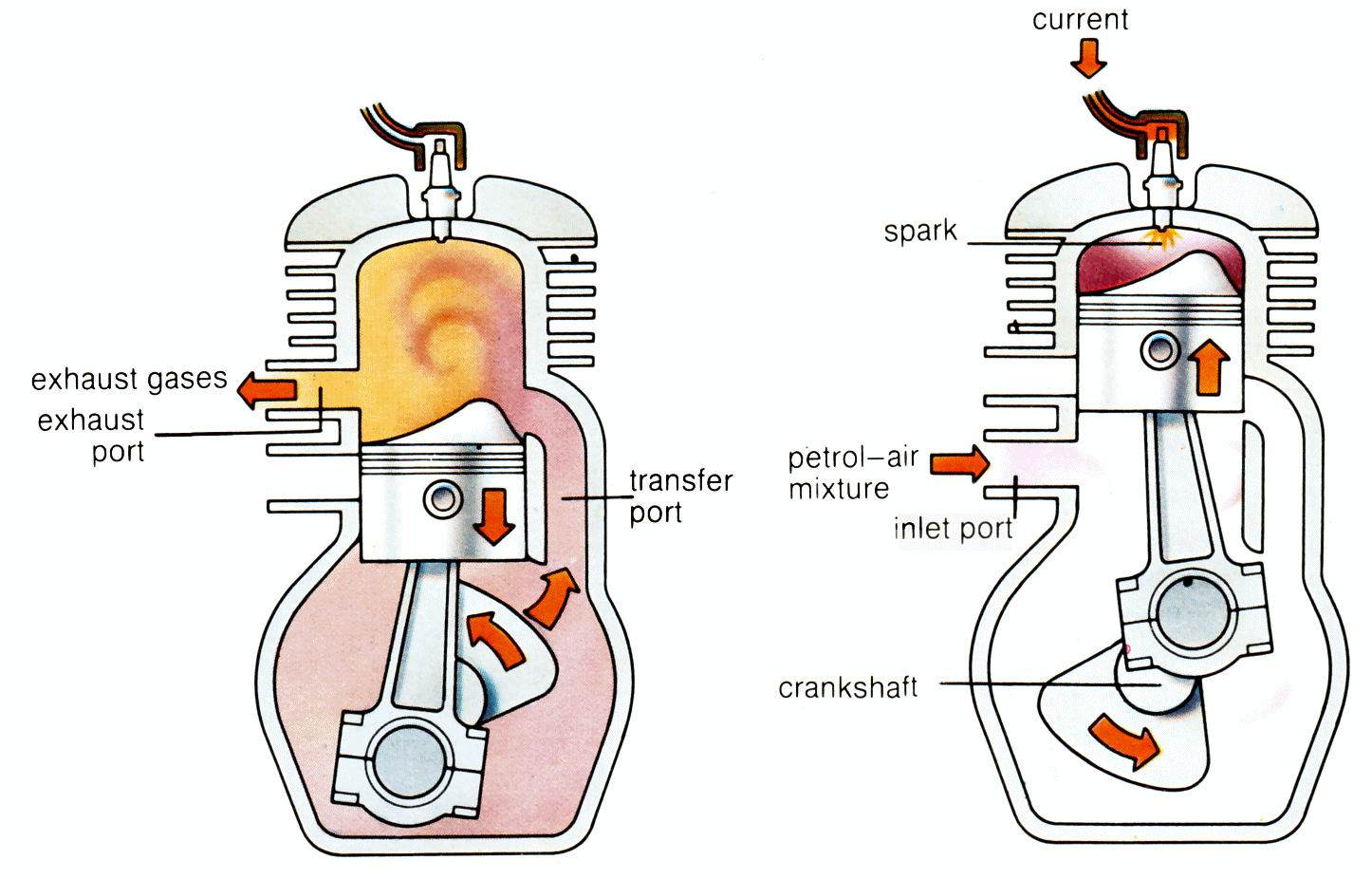
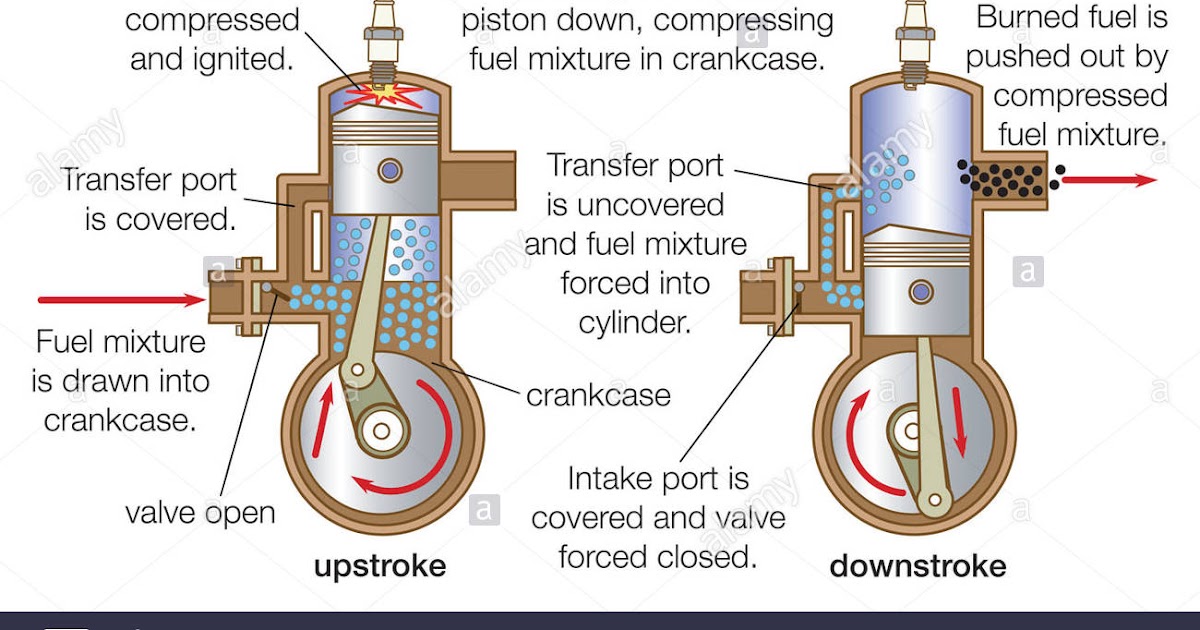
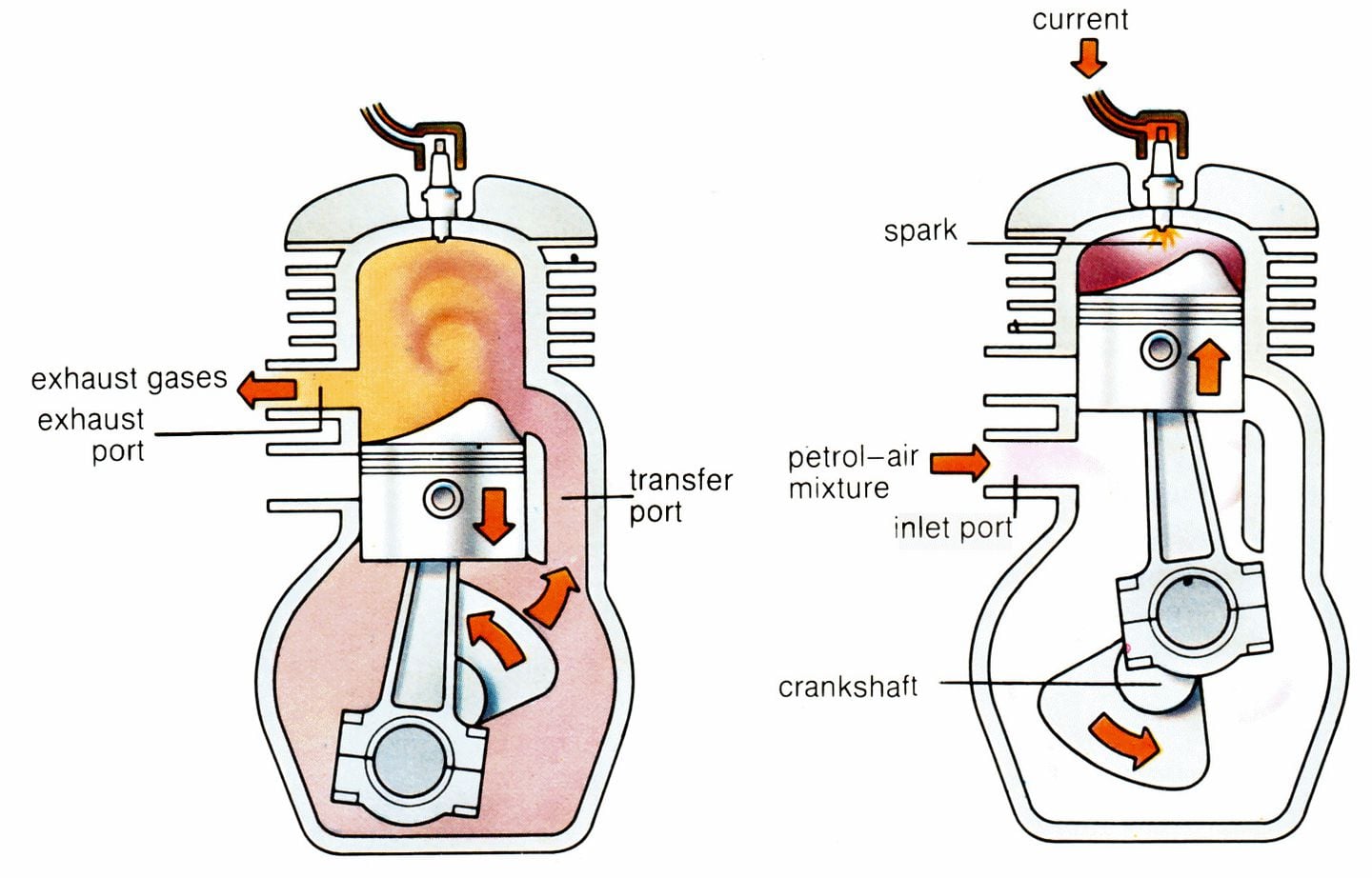
| Two-Stroke Engine - Combustion Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
| In a two-stroke engine, the combustion stroke combines both the combustion and exhaust strokes of a four-stroke engine. The piston moves upward, compressing the fuel-air mixture and closing the exhaust port. Simultaneously, the spark plug ignites the mixture, driving the piston downward and expelling the exhaust gases. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Two-Stroke Engine - Scavenging Stroke | ||
|---|---|---|
| The scavenging stroke is unique to two-stroke engines and occurs simultaneously with the combustion stroke. As the piston moves upward, it uncovers the intake port, allowing fresh fuel-air mixture to enter the combustion chamber. The incoming mixture pushes out the remaining exhaust gases through the open exhaust port. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Two-Stroke Engine - Advantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Two-stroke engines are simpler in design and have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. They are generally lighter and more compact, making them popular for handheld tools and small vehicles. Two-stroke engines have a higher power-to-weight ratio and can deliver more power for their size. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Four-Stroke Engine - Advantages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Four-stroke engines are more fuel-efficient than two-stroke engines. They produce lower emissions due to their more controlled combustion process. Four-stroke engines have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance compared to two-stroke engines. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Both four-stroke and two-stroke engines have their advantages and applications. Four-stroke engines are widely used in automobiles, motorcycles, and larger vehicles, prioritizing fuel efficiency and low emissions. Two-stroke engines are popular in small tools, recreational vehicles, and applications requiring high power-to-weight ratios. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smith, J. (2018). How Two-stroke Engines Work... Davis, M. (2021). Four-Stroke Engine. Britann... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||