Formulation And Evaluation Of Nanoparticles For Anti Cancer Therapy Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles in cancer therapy have gained significant attention. Nanoparticles offer targeted drug delivery and improved therapeutic efficacy. Formulation and evaluation of nanoparticles are crucial for successful anti-cancer therapy. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Nanoparticles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles can enhance drug solubility and stability. Improved drug bioavailability leads to better treatment outcomes. Targeted delivery reduces off-target effects and minimizes toxicity. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Formulation of Nanoparticles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Selection of appropriate materials for nanoparticle synthesis is essential. Various techniques such as emulsion, nanoprecipitation, and self-assembly can be used. Optimization of formulation parameters like drug loading, particle size, and surface charge is crucial. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Types of Nanoparticles | ||
|---|---|---|
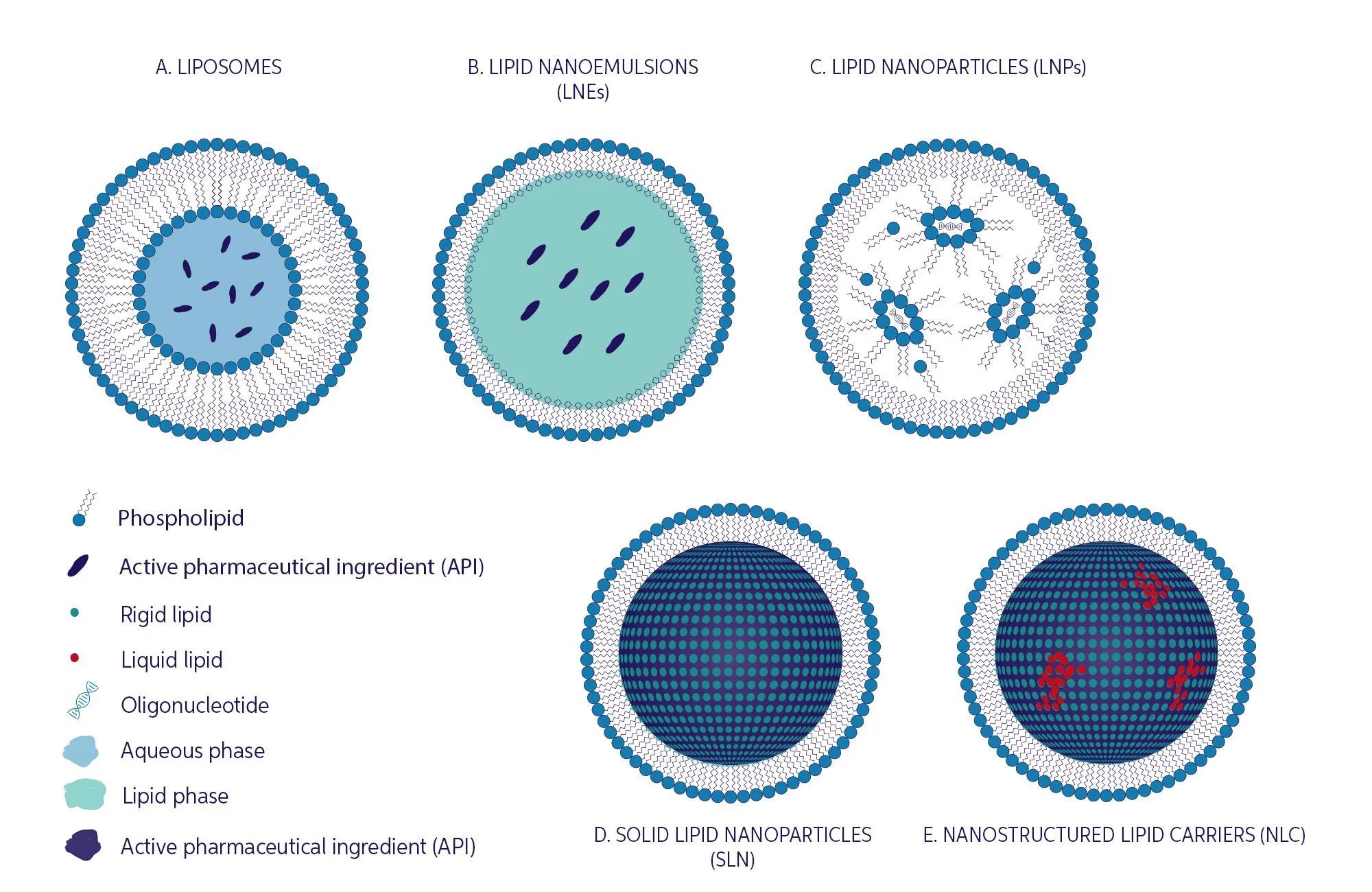
| Lipid-based nanoparticles, such as liposomes and solid lipid nanoparticles, offer controlled release and stability. Polymeric nanoparticles, like poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), provide sustained drug release. Inorganic nanoparticles, such as gold and silver nanoparticles, have unique physicochemical properties. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Characterization of Nanoparticles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Particle size and size distribution determine their bioavailability and cellular uptake. Surface charge affects nanoparticle stability and interaction with biological systems. Encapsulation efficiency and drug release kinetics are evaluated to assess nanoparticle performance. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Targeted Drug Delivery | ||
|---|---|---|
| Functionalization of nanoparticles with ligands enables specific targeting of cancer cells. Ligands can recognize overexpressed receptors on cancer cells. Targeted drug delivery enhances drug accumulation at the tumor site, improving therapeutic outcomes. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Evaluation of Nanoparticle Efficacy | ||
|---|---|---|
| In vitro studies assess cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and drug release kinetics. In vivo animal studies evaluate biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and anti-tumor activity. Combining in vitro and in vivo data provides a comprehensive evaluation of nanoparticle efficacy. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Challenges and Future Directions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Scaling up nanoparticle production for clinical applications is a challenge. Long-term safety and potential toxicity of nanoparticles require further investigation. Integration of nanotechnology with other treatment modalities, such as immunotherapy, holds promise. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Clinical Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Several nanoparticle-based therapies have entered clinical trials. Examples include Abraxane® (albumin-bound paclitaxel) and Doxil® (liposomal doxorubicin). Nanoparticles have shown promise in treating various cancers, including breast, lung, and prostate cancer. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Formulation and evaluation of nanoparticles play a critical role in anti-cancer therapy. Nanoparticles offer targeted drug delivery, improved drug stability, and enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Further research is needed to overcome challenges and optimize the clinical translation of nanoparticle-based therapies. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peer D, et al. Nanocarriers as an emerging pl... Bobo D, et al. Nanoparticle-based medicines: ... Jain RK, Stylianopoulos T. Delivering nanomed... |  | |
| 11 | ||