Electronic Business Presentation
| Introduction to Electronic Business | ||
|---|---|---|
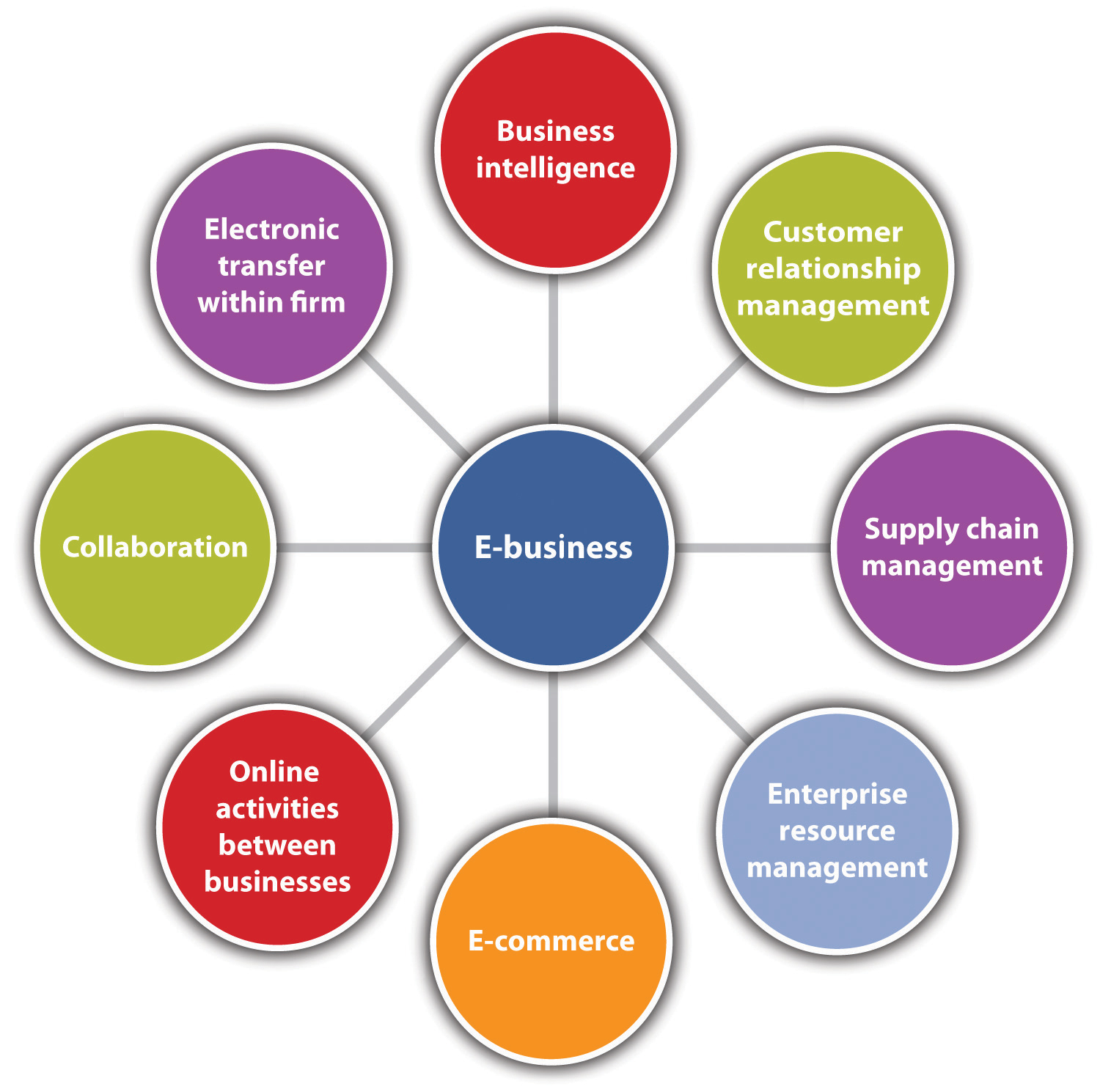
| Electronic business, also known as e-business, refers to the use of electronic means to conduct business activities. It involves the buying and selling of goods and services, as well as the exchange of information, through electronic channels. E-business has revolutionized the way businesses operate and has opened up new opportunities for growth and innovation. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Benefits of Electronic Business | ||
|---|---|---|
| Increased reach and accessibility: E-business allows businesses to reach a global audience and operate 24/ 7, breaking geographical barriers. Cost savings: By eliminating the need for physical stores and reducing manual processes, e-business can significantly reduce operational costs. Improved customer experience: E-business enables businesses to provide convenient and personalized services to customers, enhancing their overall experience. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Key Components of E-business | ||
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce: The online buying and selling of goods and services, including activities such as online shopping, online payments, and digital delivery. E-marketing: The use of digital channels, such as social media and email marketing, to promote products and services and engage with customers. E-commerce infrastructure: The technological systems and platforms, including websites, payment gateways, and inventory management systems, that enable e-business operations. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Types of E-commerce | ||
|---|---|---|
| Business-to-Consumer (B2C): In B2C e-commerce, businesses sell products and services directly to individual consumers through online platforms. Business-to-Business (B2B): B2B e-commerce involves the buying and selling of products and services between businesses through online platforms. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): C2C e-commerce enables individuals to sell products or services directly to other individuals through online marketplaces. | ||
| 4 | ||
| E-business Security | ||
|---|---|---|
| Secure transactions: E-business relies on secure protocols and encryption to protect sensitive customer information during online transactions. Data protection: E-businesses must comply with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, to safeguard customer data and prevent unauthorized access. Cybersecurity measures: E-businesses implement measures like firewalls and antivirus software to protect against cyber threats and ensure the security of their systems. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Mobile E-commerce | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mobile e-commerce, or m-commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services through mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. The widespread use of mobile devices has made m-commerce a crucial aspect of e-business, allowing businesses to reach customers on the go. Mobile apps and optimized websites are key tools for businesses to provide a seamless and user-friendly mobile shopping experience. | ||
| 6 | ||
| E-business Challenges | ||
|---|---|---|
| Security risks: With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, e-businesses must constantly stay updated on security measures to protect customer data. Competition: The ease of setting up an online business has led to intense competition, requiring e-businesses to differentiate themselves and offer unique value propositions. Technological advancements: E-businesses must keep up with evolving technologies and trends to stay relevant and provide innovative solutions to customers. |  | |
| 7 | ||
| E-business Success Factors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Strong online presence: E-businesses need a well-designed and user-friendly website or online platform to attract and engage customers. Effective digital marketing strategies: E-businesses must utilize various digital marketing channels to reach their target audience and drive traffic to their online platforms. Focus on customer experience: Providing exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, and easy navigation are essential for e-business success. | ||
| 8 | ||
| E-business Future Trends | ||
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants will enhance customer service and streamline e-business operations. Personalization: E-businesses will focus on delivering personalized experiences based on customer preferences and behavior. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices will enable seamless integration between physical and online shopping experiences, enhancing convenience for customers. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electronic business has transformed the way businesses operate, offering numerous benefits such as increased reach, cost savings, and improved customer experience. E-business encompasses various components, including e-commerce and e-marketing, and involves ensuring security and staying up to date with technological advancements. With the future trends of AI, personalization, and IoT, e-business will continue to evolve and shape the business landscape. | ||
| 10 | ||