Electrical Conductor Presentation
| Introduction to Electrical Conductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductors are materials that allow the flow of electric current. They are essential components in electrical systems and devices. Conductors have low resistance and high conductivity, enabling the efficient transmission of electricity. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Characteristics of Electrical Conductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conductors have a high density of free electrons, allowing them to easily conduct electricity. They possess low resistivity, meaning they offer minimal obstruction to the flow of electrons. Conductors typically have high thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat dissipation. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Electrical Conductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Copper is one of the most commonly used conductors due to its excellent conductivity and affordability. Aluminum is another widely used conductor, especially in power transmission lines due to its lower cost and lighter weight. Other conductive materials include silver, gold, and various alloys, each with their own unique properties and applications. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Factors Affecting Conductivity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Temperature: Conductivity decreases with increasing temperature due to increased atomic vibrations that impede electron flow. Impurities: Presence of impurities in a conductor can decrease its conductivity by interrupting electron movement. Cross-sectional area: Conductivity is directly proportional to the cross-sectional area of a conductor. A larger area allows for more electron flow. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Electrical Conductor Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wiring: Conductors, particularly copper wires, are extensively used in electrical wiring for buildings, appliances, and electronic devices. Power transmission: High-voltage overhead transmission lines utilize conductors to efficiently transport electricity over long distances. Electronics: Conductors are essential components in circuit boards and connectors, facilitating the flow of electricity between components. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Conductivity vs. Resistivity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity is the measure of a material's ability to conduct electricity and is the reciprocal of resistivity. Resistivity is the measure of a material's resistance to the flow of electric current. Conductivity and resistivity are related through the equation: Conductivity = 1 / Resistivity. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Insulators vs. Conductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Insulators are materials that impede the flow of electric current. Unlike conductors, insulators have high resistivity and low conductivity. Examples of insulators include rubber, plastic, and glass. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Superconductivity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Superconductors are materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance at extremely low temperatures. Superconductivity allows for the efficient transmission of electric current without any energy loss due to resistance. Potential applications of superconductors include advanced power transmission, magnetic levitation, and high-speed computing. | ||
| 8 | ||
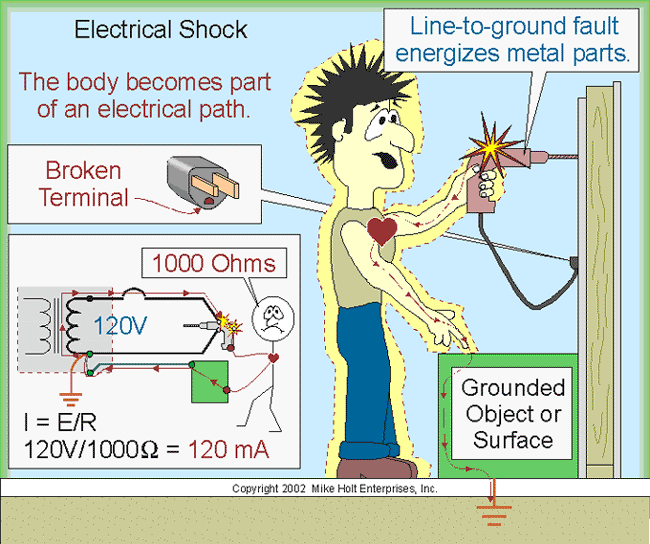
| Safety Considerations with Electrical Conductors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Proper insulation is crucial when using conductors to prevent electrical shocks and short circuits. Adequate grounding is necessary to redirect excess electrical currents safely to the ground. Regular maintenance and inspections should be carried out to ensure the integrity of conductors and prevent potential hazards. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductors play a vital role in modern electrical systems, facilitating the flow of electric current. Understanding the characteristics, types, and applications of conductors is crucial for designing and implementing efficient and safe electrical systems. Ongoing research and advancements in materials continue to expand the possibilities and potential applications of electrical conductors. | ||
| 10 | ||


/examples-of-electrical-conductors-and-insulators-608315_v3-5b609152c9e77c004f6e8892.png)