Electric Vehicles Presentation
| Introduction to Electric Vehicles | ||
|---|---|---|
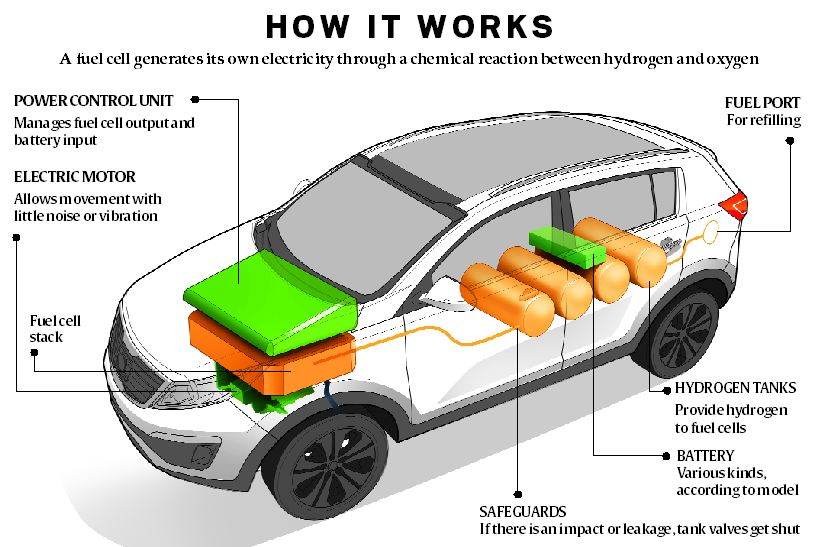
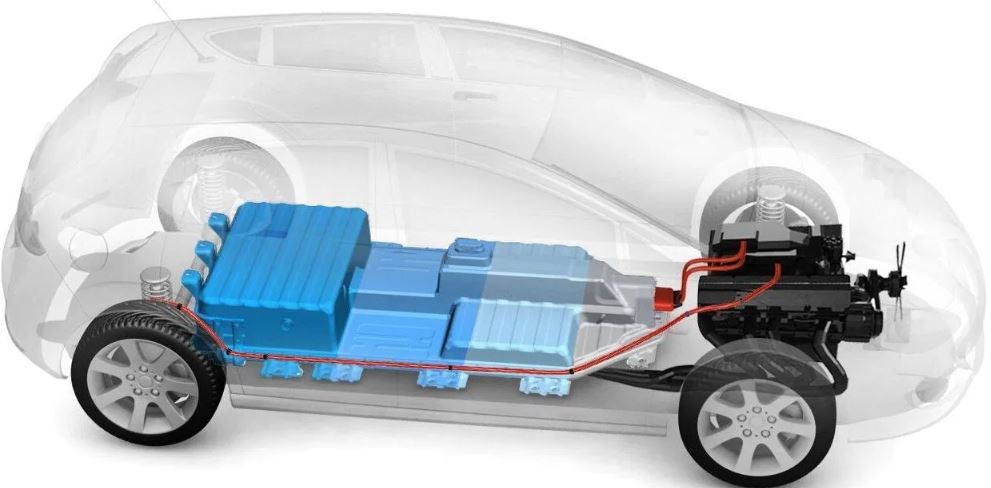
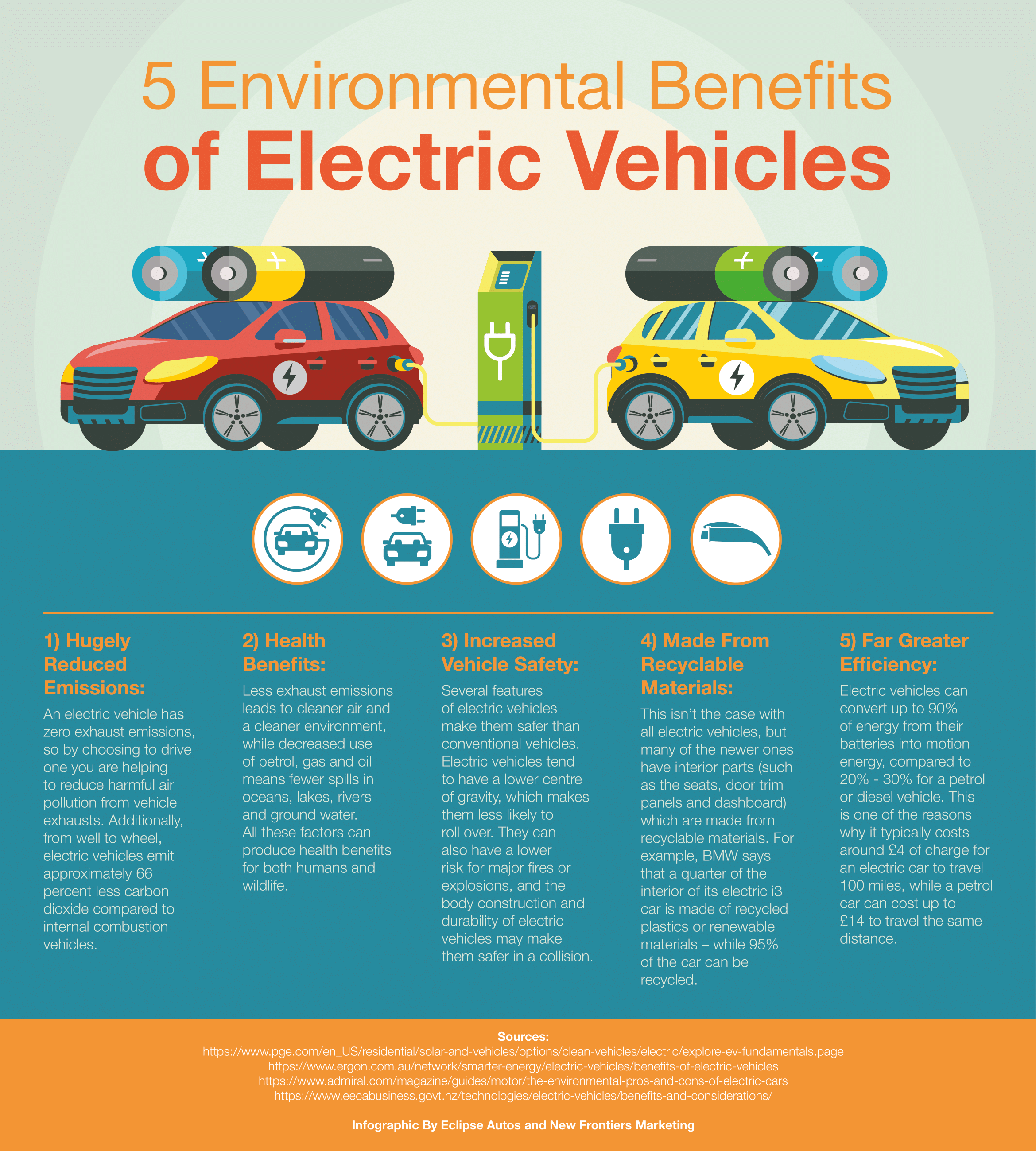
| Electric vehicles (EVs) are automobiles that run on electricity instead of gasoline or diesel. EVs use rechargeable batteries to store and provide power to the electric motor. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them environmentally friendly. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Electric Vehicles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are fully electric and solely rely on battery power. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor and can be charged via a power outlet. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) use both a gasoline engine and an electric motor, but the electric motor cannot be charged externally. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Benefits of Electric Vehicles | ||
|---|---|---|
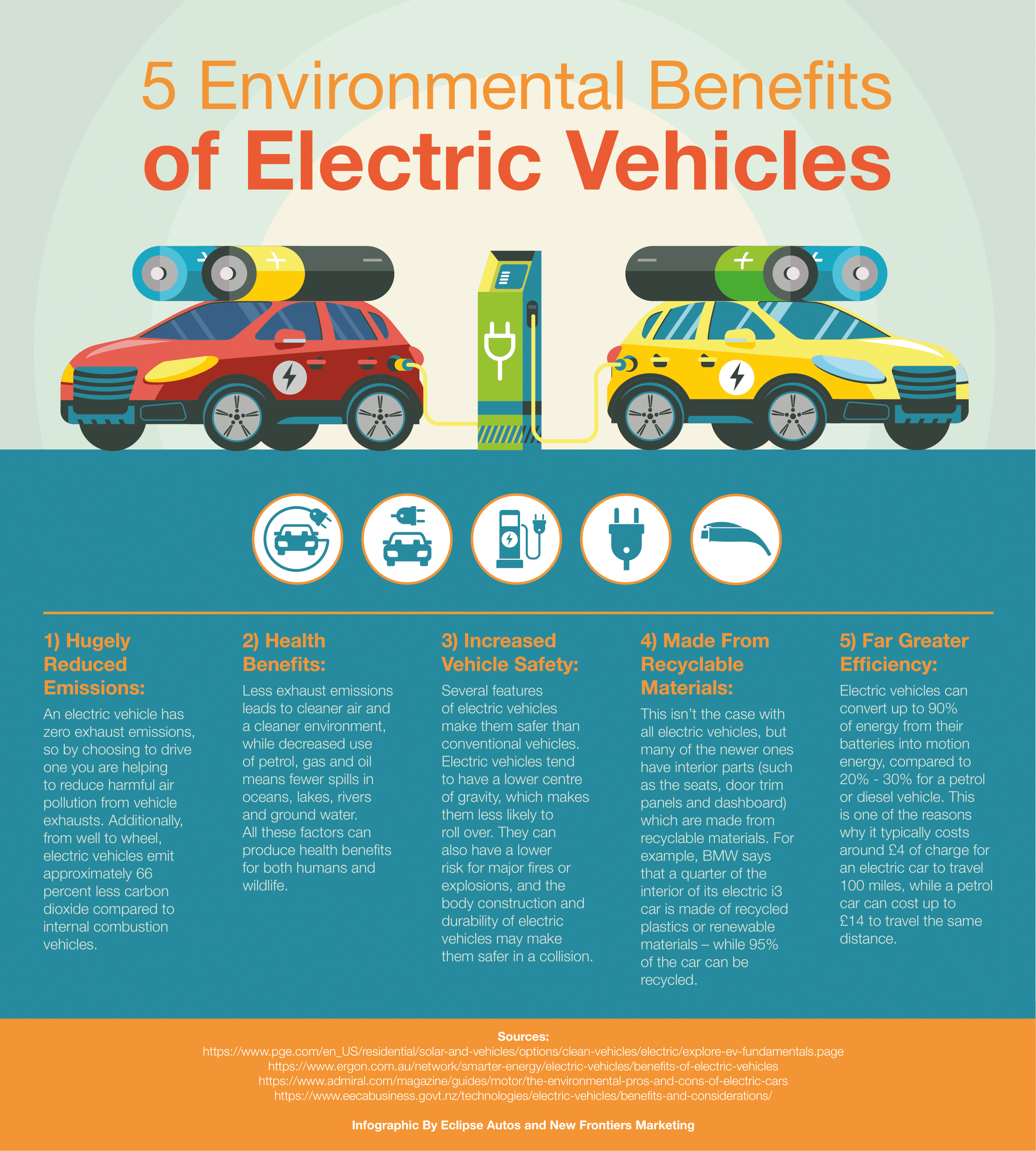
| Lower running costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, resulting in lower fuel costs for EV owners. Reduced emissions: EVs produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced pollution. Lower maintenance: EVs have fewer moving parts compared to internal combustion engine vehicles, resulting in lower maintenance costs. | ||
| 3 | ||
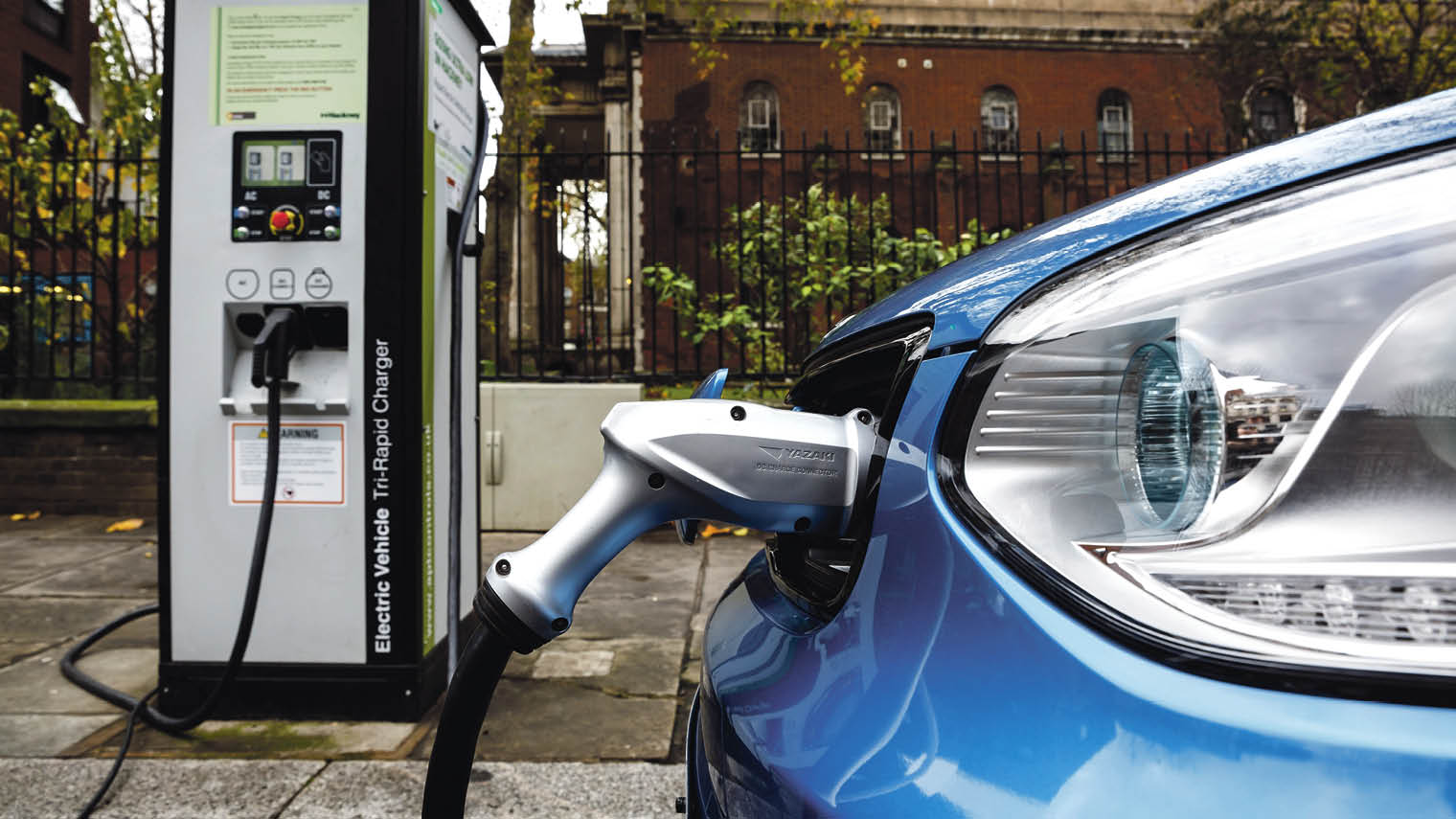
| Charging Infrastructure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Public charging stations are available in various locations, such as shopping centers, parking lots, and public streets. Home charging stations allow EV owners to conveniently charge their vehicles overnight. Rapid charging stations can provide a significant amount of charge in a short period, enabling long-distance travel. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Range and Battery Technology | ||
|---|---|---|
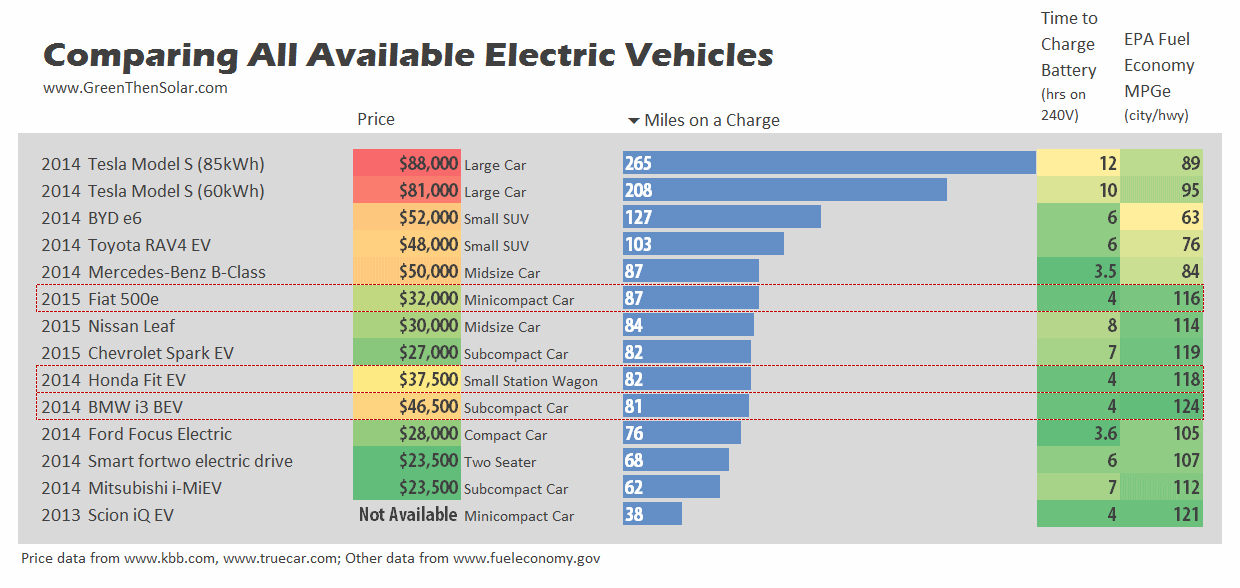
| EV range varies depending on the model and battery capacity, typically ranging from 100 to 300 miles. Battery technology is improving rapidly, leading to increased energy density and longer range capabilities. Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery, is diminishing as EVs provide longer ranges and improved charging infrastructure. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Government Incentives and Support | ||
|---|---|---|
| Many governments provide financial incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. Some countries have implemented regulations to phase out internal combustion engine vehicles in the coming years. Governments are investing in charging infrastructure development to support the growth of electric vehicles. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges of Electric Vehicles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Limited charging infrastructure in certain areas may hinder long-distance travel for some EV owners. The initial cost of purchasing an EV can be higher compared to traditional vehicles, although this is gradually decreasing. Battery technology is still evolving, and concerns about battery degradation and disposal need to be addressed. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Future Outlook for Electric Vehicles | ||
|---|---|---|
| The electric vehicle market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and environmental concerns. Automakers are investing heavily in electric vehicle development to meet the increasing demand and regulatory requirements. The adoption of electric vehicles will contribute to a more sustainable transportation sector and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. | ||
| 8 | ||
| EVs and Renewable Energy | ||
|---|---|---|
| EVs can be charged using electricity generated from renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. The combination of EVs and renewable energy promotes a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system. Smart grid technologies can optimize the charging and discharging of EVs, improving overall energy efficiency. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electric vehicles offer numerous benefits, including lower running costs, reduced emissions, and lower maintenance. Government incentives and support are driving the adoption of electric vehicles. With technological advancements and increasing environmental awareness, the future of electric vehicles looks promising. | ||
| 10 | ||