ELISA Principle And Procedure Presentation
| Introduction to ELISA Principle and Procedure | ||
|---|---|---|
| ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is a widely used technique in the field of immunology and biochemistry. ELISA is used to detect and quantify specific proteins or antibodies in a sample. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Basic Principle of ELISA | ||
|---|---|---|
| ELISA is based on the specific binding of an antigen and an antibody. The antigen of interest is immobilized on a solid surface, such as a microplate. The immobilized antigen will bind to specific antibodies present in the sample. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of ELISA | ||
|---|---|---|
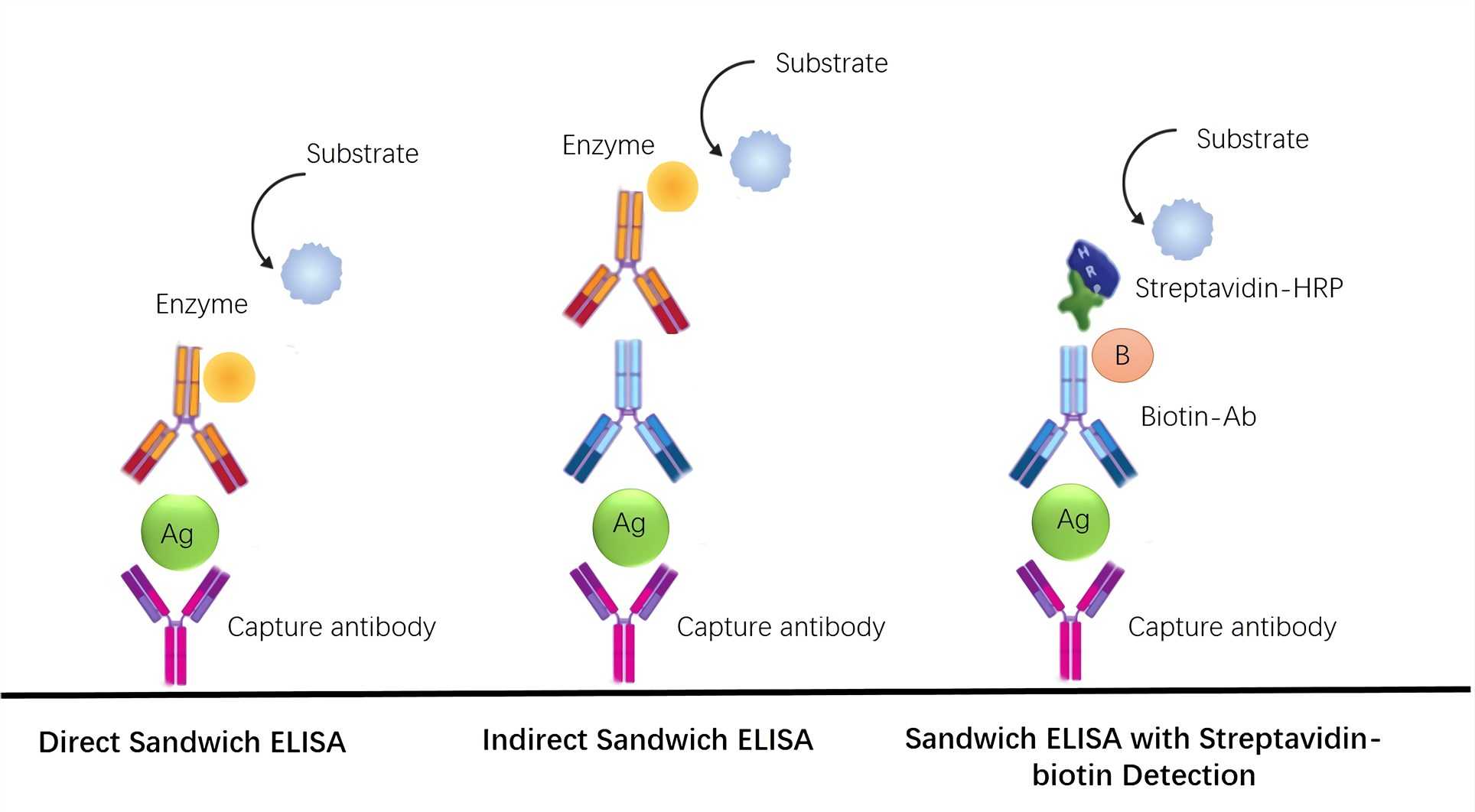
| Direct ELISA: The antigen is immobilized, and a labeled antibody directly detects it. Indirect ELISA: The antigen is immobilized, and a primary antibody binds to it. A secondary labeled antibody then detects the primary antibody. Sandwich ELISA: The antigen is captured between two antibodies - a capture antibody and a detection antibody - both specific to the antigen. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Steps of ELISA - Coating | ||
|---|---|---|
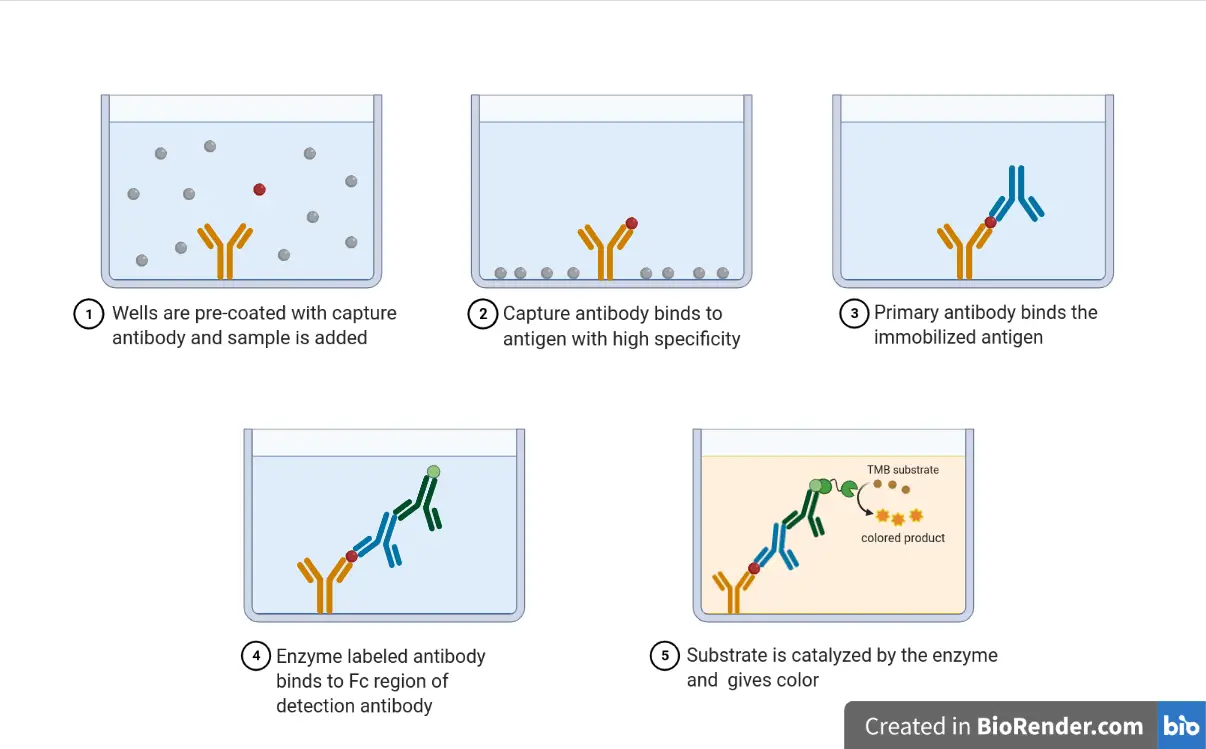
| The first step is to immobilize the antigen on a solid surface, typically a microplate well. The antigen is diluted in a buffer and added to the well. The plate is then incubated to allow the antigen to bind to the surface. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Steps of ELISA - Blocking | ||
|---|---|---|
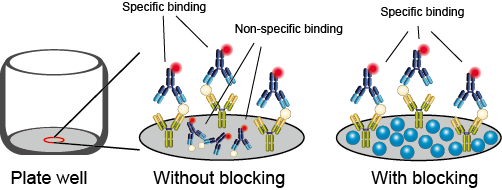
| After coating, the plate is washed to remove any unbound antigen. The next step is to block any remaining uncoated surface to prevent nonspecific binding. A blocking agent, such as BSA or milk, is added to the wells and incubated. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Steps of ELISA - Primary Antibody | ||
|---|---|---|
| The primary antibody, specific to the antigen, is added to the wells. The primary antibody will bind to the antigen present on the coated surface. Incubation allows for the formation of antibody-antigen complexes. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Steps of ELISA - Secondary Antibody | ||
|---|---|---|
| If using an indirect or sandwich ELISA, a secondary antibody is added. The secondary antibody is specific to the primary antibody and is labeled with an enzyme. The secondary antibody will bind to the primary antibody-antigen complex. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Steps of ELISA - Enzyme Substrate | ||
|---|---|---|
| After incubation with the secondary antibody, the plate is washed again. A substrate specific to the enzyme label is added. The enzyme catalyzes a reaction, producing a detectable signal, such as a color change. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Steps of ELISA - Signal Detection | ||
|---|---|---|
| The signal generated by the enzyme-substrate reaction is measured using a spectrophotometer. The intensity of the signal is proportional to the amount of antigen or antibody present in the sample. A standard curve is used to quantify the unknown sample based on the signal intensity. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Applications of ELISA | ||
|---|---|---|
| ELISA is used in medical diagnostics to detect diseases, such as HIV or COVID-19. It is also used in research to study protein-protein interactions and antibody production. ELISA has applications in agriculture, environmental monitoring, and food safety testing. | ||
| 10 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| ELISA is a versatile and widely used technique to detect and quantify proteins or antibodies. Understanding the principle and following the procedure are crucial for accurate results. The development of ELISA has revolutionized various fields, enabling rapid and sensitive detection of target molecules. | ||
| 11 | ||