E Governance Presentation
| Introduction to E Governance | ||
|---|---|---|
| E Governance is the implementation of digital technology in government processes to improve efficiency and transparency. It encompasses various aspects such as online services, digital communication, and electronic record keeping. E Governance aims to enhance citizen participation and improve government service delivery. | ||
| 1 | ||
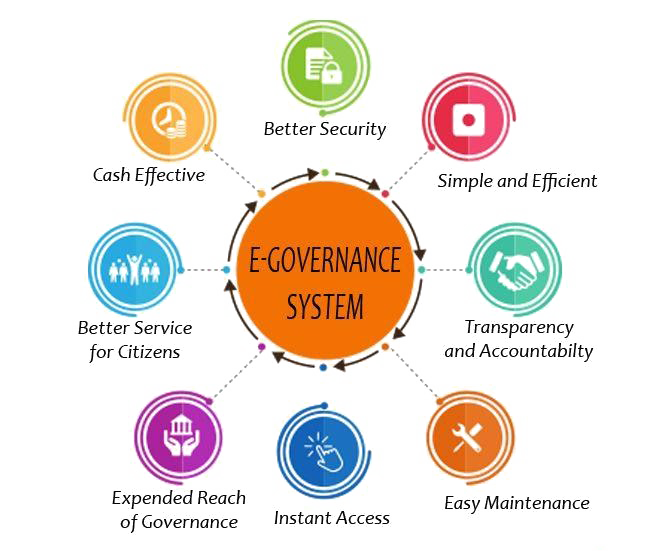
| Benefits of E Governance | ||
|---|---|---|
| E Governance improves accessibility by providing online services that can be accessed anytime, anywhere. It increases transparency by enabling public access to government information and decision-making processes. E Governance reduces bureaucracy and improves efficiency by automating processes and reducing paperwork. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Key Components of E Governance | ||
|---|---|---|
| E Services: Provision of government services online, such as tax filing, license application, and bill payments. E Participation: Involving citizens in decision-making processes through online consultations and feedback mechanisms. E Records: Digitization and management of government records and documents for easy access and retrieval. | ||
| 3 | ||
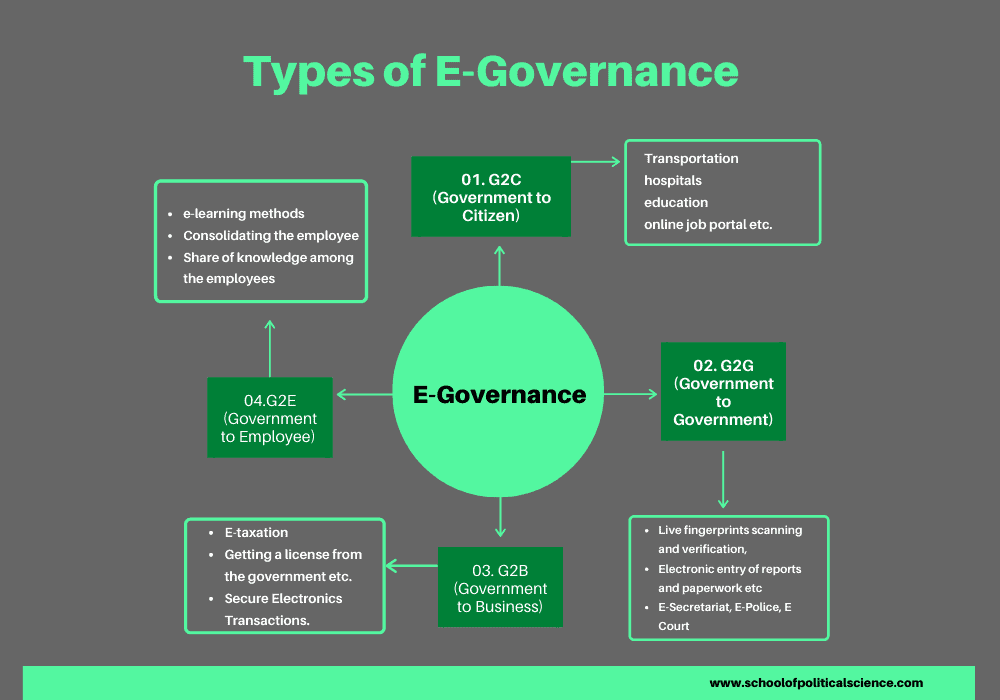
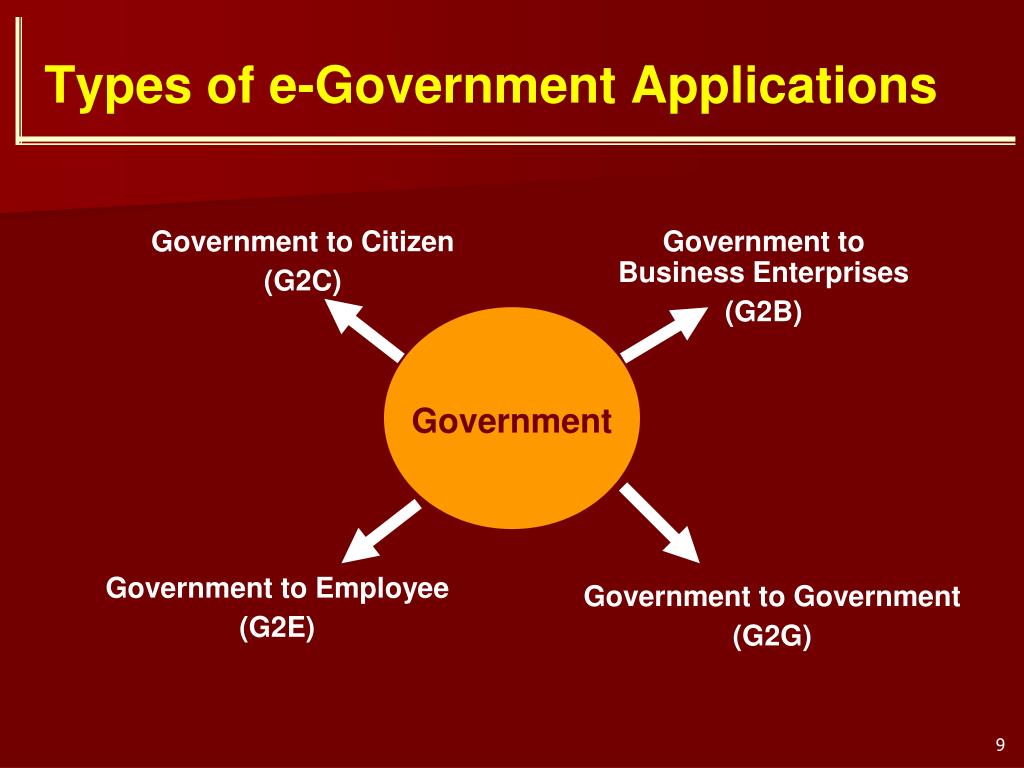
| Types of E Governance | ||
|---|---|---|
| G2C (Government-to-Citizen): Online services provided by the government to citizens, such as e-voting and online forms. G2B (Government-to-Business): Online services provided by the government to businesses, such as online registration and licensing. G2G (Government-to-Government): Digital interactions between government agencies, such as data sharing and collaboration. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Challenges in Implementing E Governance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology and internet infrastructure, limiting citizen participation. Privacy and Security: Ensuring the protection of personal data and preventing unauthorized access. Resistance to Change: Overcoming resistance from government officials and employees accustomed to traditional processes. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Examples of Successful E Governance Initiatives | ||
|---|---|---|
| Estonia: Known for its advanced digital infrastructure, offering e-Residency and e-Government services. Singapore: Implements e-Government initiatives to provide seamless services to citizens and businesses. India: Introduces initiatives like Aadhaar for biometric identification and Digital India for digital empowerment. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Case Study: Digital Transformation in Rwanda | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rwanda implemented e-Government initiatives to improve service delivery and reduce corruption. Online services like e-Government portal and Irembo enable citizens to access various government services. The digital transformation in Rwanda has led to increased efficiency, transparency, and citizen satisfaction. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Future Trends in E Governance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Governance: Expanding e-Government services through mobile applications for increased accessibility. Blockchain Technology: Utilizing blockchain for secure and transparent digital transactions and record-keeping. Artificial Intelligence: Integration of AI to automate processes and improve decision-making in government services. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Key Considerations in E Governance Implementation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure: Developing robust internet connectivity and digital infrastructure for seamless service delivery. Capacity Building: Training government officials and employees to adapt to digital technologies and processes. Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships between government, private sector, and civil society for effective implementation. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| E Governance plays a vital role in modernizing government processes and improving citizen satisfaction. It has the potential to increase efficiency, transparency, and citizen participation in government affairs. However, successful implementation requires addressing challenges, considering future trends, and ensuring collaboration among stakeholders. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| World Bank. (2020). E-Government. Retrieved f... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||