Domestic Waste Management Presentation
| Introduction to Domestic Waste Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Domestic waste management refers to the process of collecting, treating, and disposing of waste generated by households. It plays a crucial role in maintaining environmental sustainability and public health. Effective waste management practices can minimize pollution, conserve resources, and promote recycling. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Domestic Waste | ||
|---|---|---|
| Domestic waste can be categorized into organic and inorganic waste. Organic waste includes food scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials. Inorganic waste comprises plastics, metals, glass, paper, and other non-biodegradable materials. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Importance of Segregation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Segregation is a key aspect of domestic waste management. Proper segregation helps in separating different types of waste for efficient recycling and disposal. It reduces the burden on landfill sites and allows for the recovery of valuable resources. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Recycling and Composting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Recycling involves converting waste materials into new products to conserve resources. Composting is the process of decomposing organic waste to produce nutrient-rich compost for gardening and agriculture. Encouraging recycling and composting at the household level can significantly reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Waste Reduction Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waste reduction strategies include reducing consumption, reusing items, and minimizing packaging. Adopting a "zero waste" mindset can help households reduce their overall waste generation. By choosing durable products, repairing instead of replacing, and using reusable containers, individuals can make a significant impact. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Waste Collection and Segregation at Source | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waste collection services should be provided regularly to ensure timely disposal. Source segregation at the household level should be encouraged to simplify waste management processes. Properly labeled and color-coded bins can aid in the segregation of different types of waste. | ||
| 6 | ||
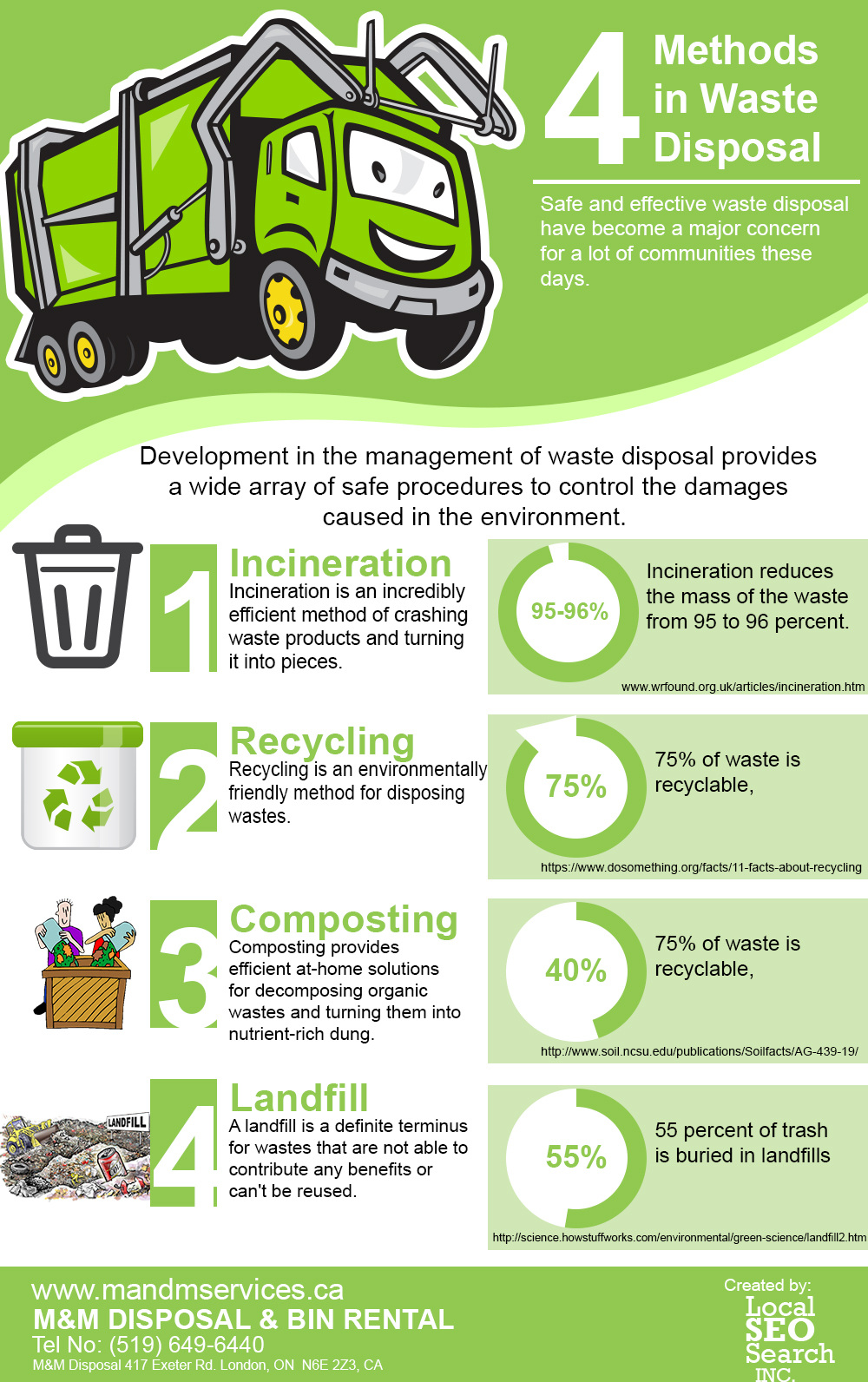
| Waste Treatment Methods | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waste treatment methods include incineration, landfilling, and biological treatment. Incineration involves burning waste at high temperatures to produce energy. Landfilling is the most common method but should be used as a last resort due to environmental concerns. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Promoting Awareness and Education | ||
|---|---|---|
| Educating households about the importance of waste management is crucial for behavior change. Awareness campaigns can encourage individuals to adopt sustainable waste management practices. Providing information on the environmental impact of waste and the benefits of recycling can motivate community participation. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Government Regulations and Policies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Governments play a vital role in implementing waste management regulations and policies. Strict enforcement of waste disposal guidelines can ensure compliance. Governments should also incentivize recycling and composting initiatives to promote sustainable waste management. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Domestic waste management is essential for environmental sustainability and public health. Effective waste management practices include segregation, recycling, composting, and waste reduction. With collective efforts from households, governments, and communities, we can achieve a cleaner and greener future. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Protection Agency. (2021). Mana... United Nations Environment Programme. (2020).... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||