Dissolution Of Tablets Presentation
| Introduction to Dissolution of Tablets | ||
|---|---|---|
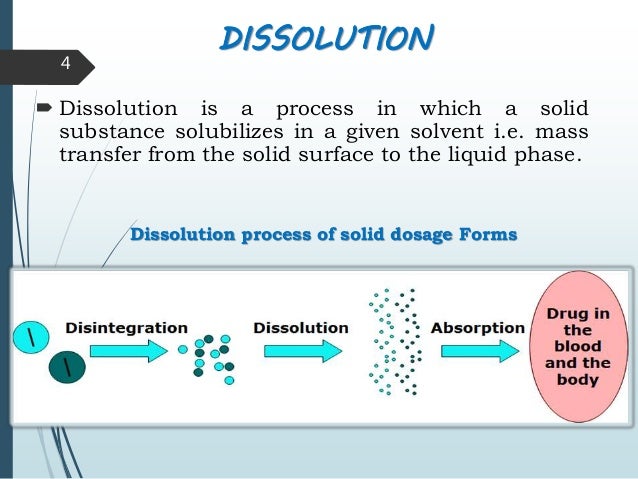
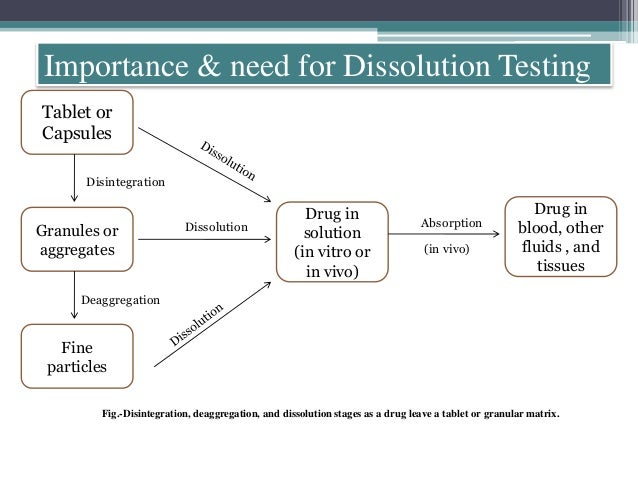
| Dissolution is the process by which a solid tablet disintegrates and dissolves in a liquid medium. It is an essential step in drug absorption and bioavailability. Factors such as tablet composition, size, and formulation affect the dissolution process. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Dissolution Testing | ||
|---|---|---|
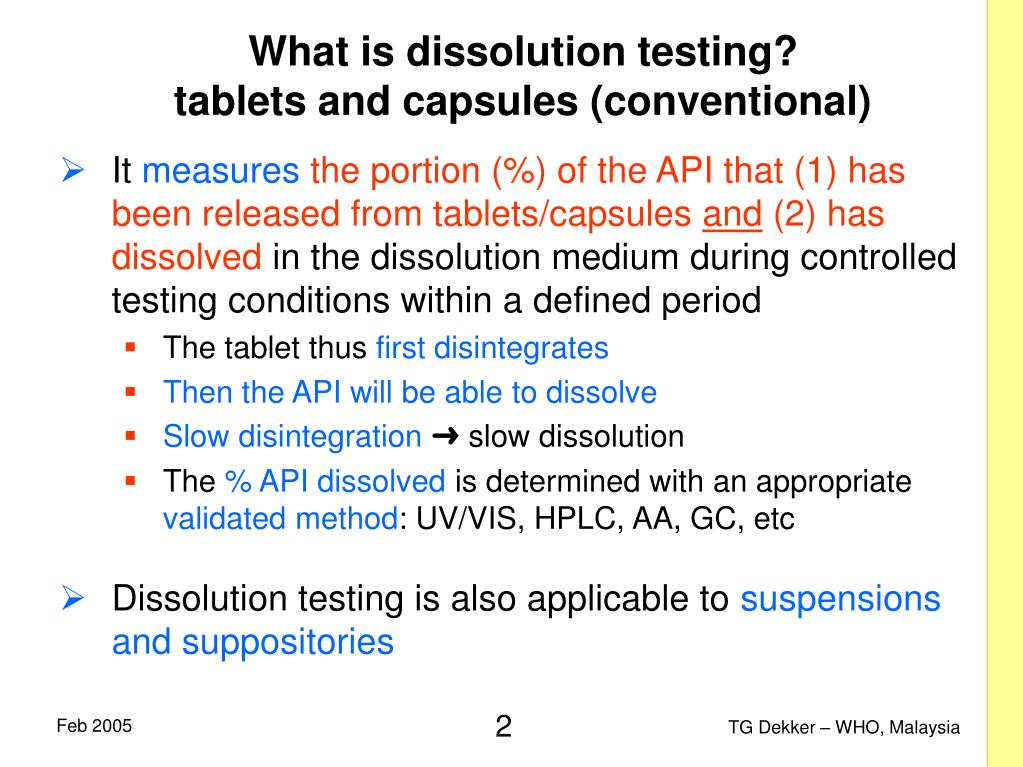
| Dissolution testing helps determine the rate and extent of drug release from a tablet. It ensures consistency and quality control of the product. Dissolution data is crucial for establishing bioequivalence between generic and branded drugs. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Dissolution Apparatus | ||
|---|---|---|
| The US Pharmacopeia (USP) defines several dissolution apparatus types (e.g., USP I, II, IV). Each apparatus simulates a specific physiological condition or drug delivery system. The choice of apparatus depends on the drug properties and intended release profile. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Dissolution Media | ||
|---|---|---|
| The dissolution medium should mimic physiological conditions (pH, temperature, and ionic strength). Common media include simulated gastric fluid (SGF) and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF). Additional media variations may be required for specialized drug formulations. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Factors Affecting Dissolution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tablet formulation, including excipients, binders, and disintegrants, affects dissolution. Particle size and surface area of the tablet influence the rate of dissolution. pH, temperature, and agitation speed of the dissolution medium impact the dissolution process. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Dissolution Testing Procedure | ||
|---|---|---|
| The tablet is placed in the dissolution apparatus, which is filled with the dissolution medium. The tablet is agitated under controlled conditions, ensuring uniformity. Samples are withdrawn at specific time intervals and analyzed for drug concentration. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Dissolution Profiles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dissolution profiles provide information about the drug release pattern over time. They are often represented graphically, showing the percentage of drug released versus time. Comparison of dissolution profiles allows the assessment of product quality and batch-to-batch consistency. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Regulatory Requirements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dissolution testing is a mandatory requirement for drug approval by regulatory authorities. The US FDA and other agencies specify dissolution testing protocols. Dissolution specifications are established based on the drug's therapeutic effect and pharmacokinetics. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Challenges and Future Trends | ||
|---|---|---|
| Poorly soluble drugs pose challenges in dissolution testing. Advanced techniques such as biorelevant media and in vitro-in vivo correlation (IVIVC) are being developed. Continuous flow systems and real-time monitoring may improve dissolution testing accuracy. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dissolution testing is a critical step in evaluating tablet performance and drug release. Understanding the factors affecting dissolution is crucial for ensuring drug efficacy and patient safety. Ongoing advancements in dissolution testing methods will continue to enhance pharmaceutical development. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| USP General Chapter <711> Dissolution. United... Shah VP et al. Pharmaceutical dissolution tes... Jain DK. Handbook of dissolution testing. CRC... |  | |
| 11 | ||