Dictionary In Python Presentation
| Introduction to Dictionaries | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dictionaries in Python are unordered collections of key-value pairs. They are mutable and can hold any data type, including other dictionaries. Dictionaries are created using curly brackets {} or the dict() constructor. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Accessing and Modifying Dictionary Elements | ||
|---|---|---|
| To access a value in a dictionary, use its corresponding key inside square brackets. Values can be modified by assigning a new value to a specific key. If a key is not found, a KeyError will be raised. | ||
| 2 | ||
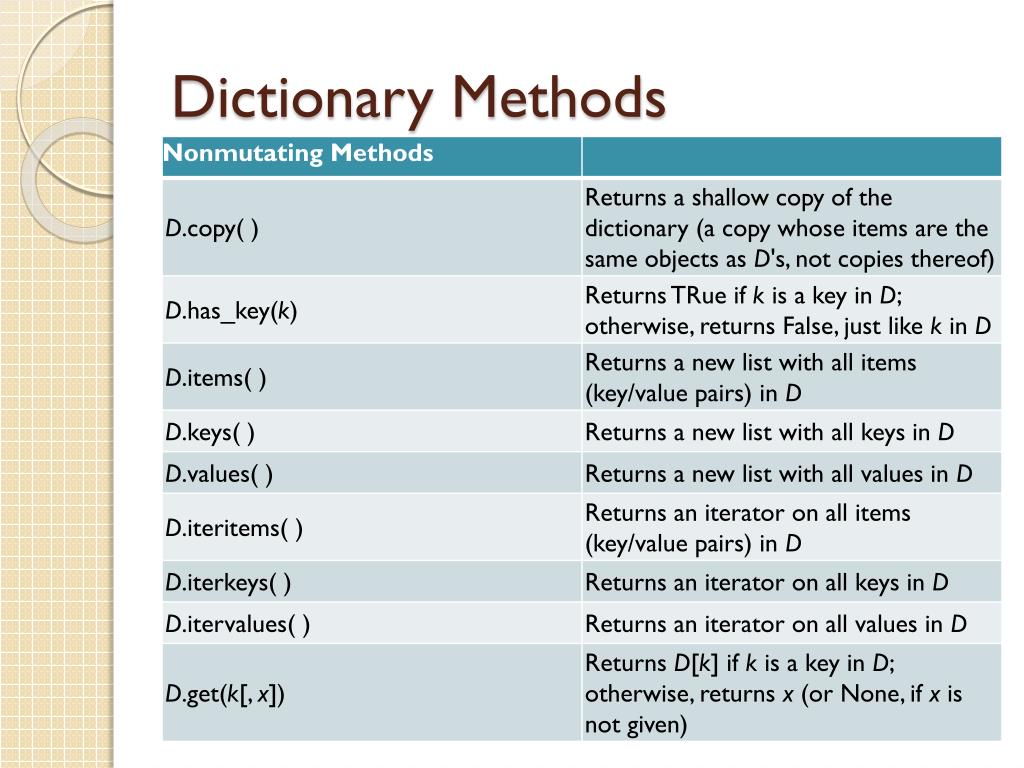
| Dictionary Methods and Operations | ||
|---|---|---|
| The len() function returns the number of key-value pairs in a dictionary. The keys() method returns a list of all the keys in the dictionary. The values() method returns a list of all the values in the dictionary. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Adding and Removing Elements in Dictionaries | ||
|---|---|---|
| To add a new key-value pair, simply assign a value to a new key. The update() method can be used to add multiple key-value pairs at once. Use the del keyword to remove a specific key-value pair from the dictionary. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Useful Dictionary Techniques and Tips | ||
|---|---|---|
| The get() method allows you to retrieve a value for a specific key, with a default value if the key is not found. The items() method returns a list of tuples, where each tuple contains a key-value pair. Dictionaries can be sorted using the sorted() function based on keys or values. Note: Please feel free to customize the content and design of the slides as per your requirements. |  | |
| 5 | ||