Defination Of Solid Waste , Solid Waste Management, Elements Of Solid Waste Management Presentation
| Definition of Solid Waste | ||
|---|---|---|
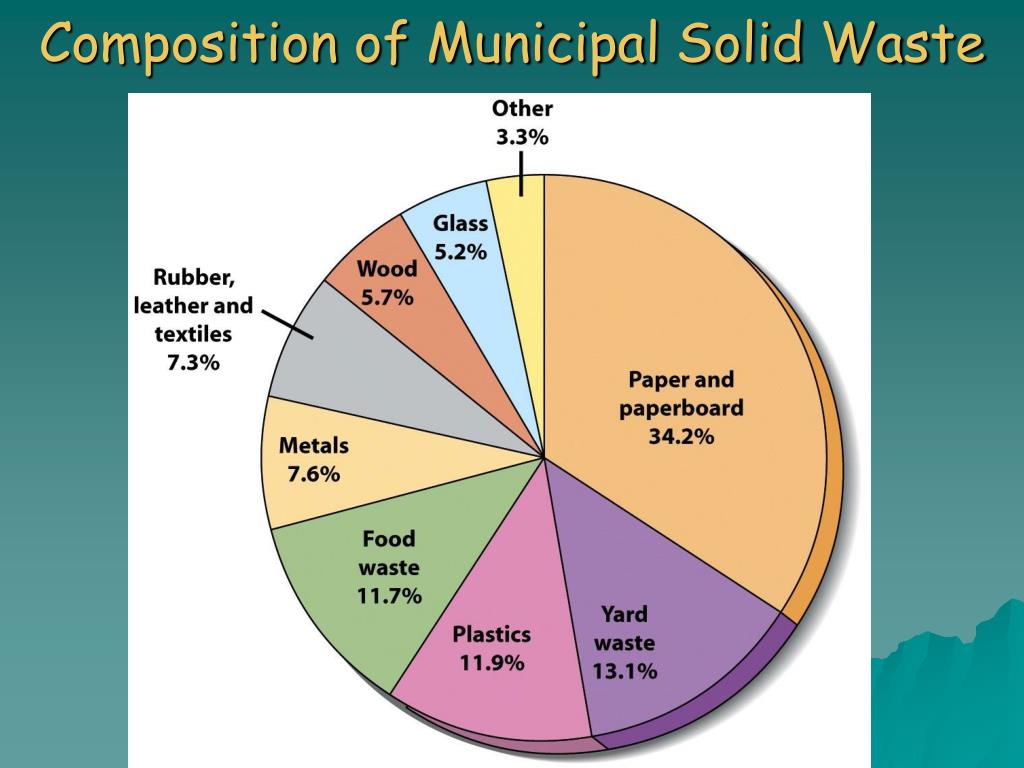
| Solid waste refers to any discarded materials that are no longer needed or are no longer useful. These materials can be in the form of household garbage, industrial waste, construction debris, or even hazardous waste. Solid waste can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid in nature. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Solid Waste Management | ||
|---|---|---|
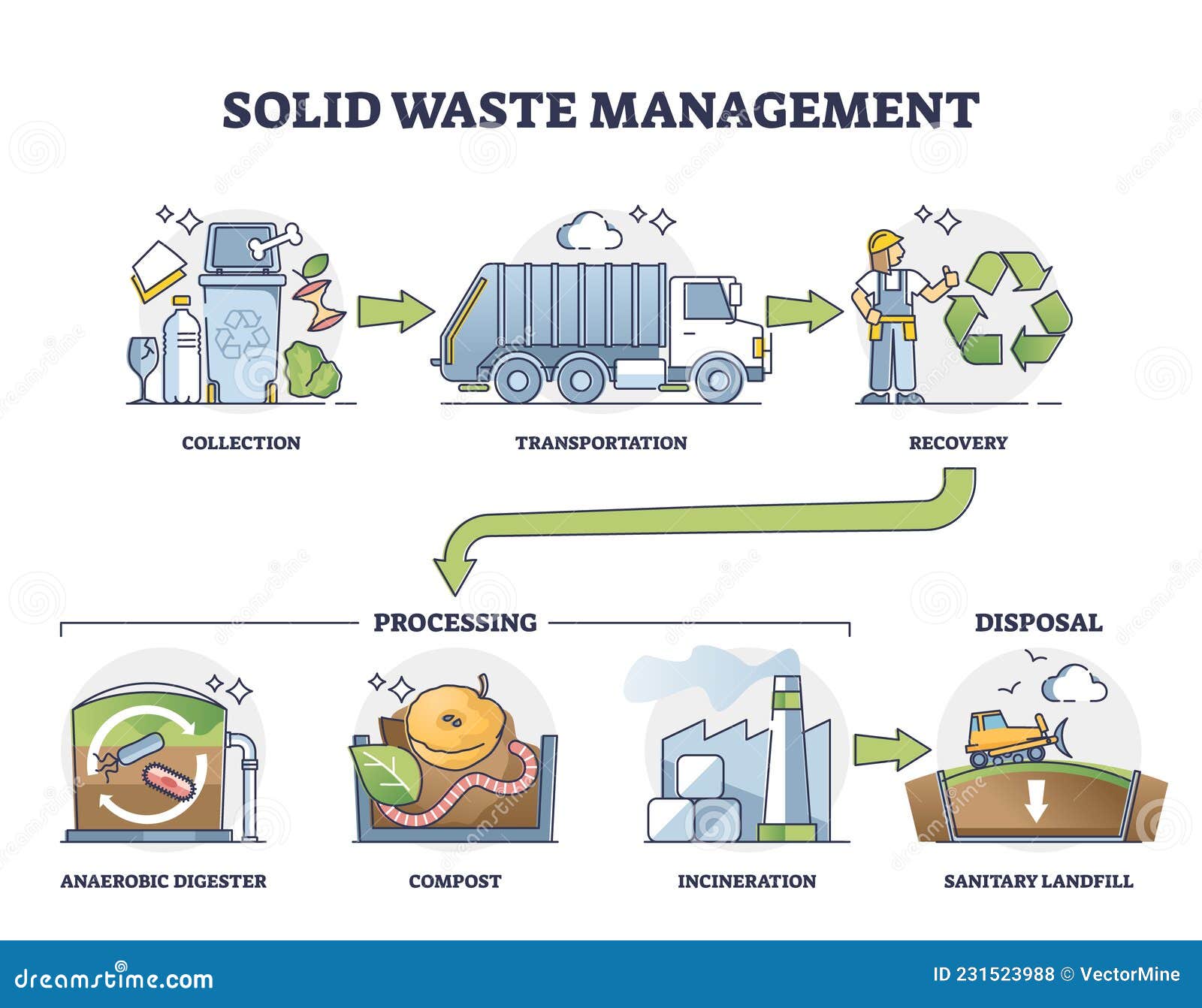
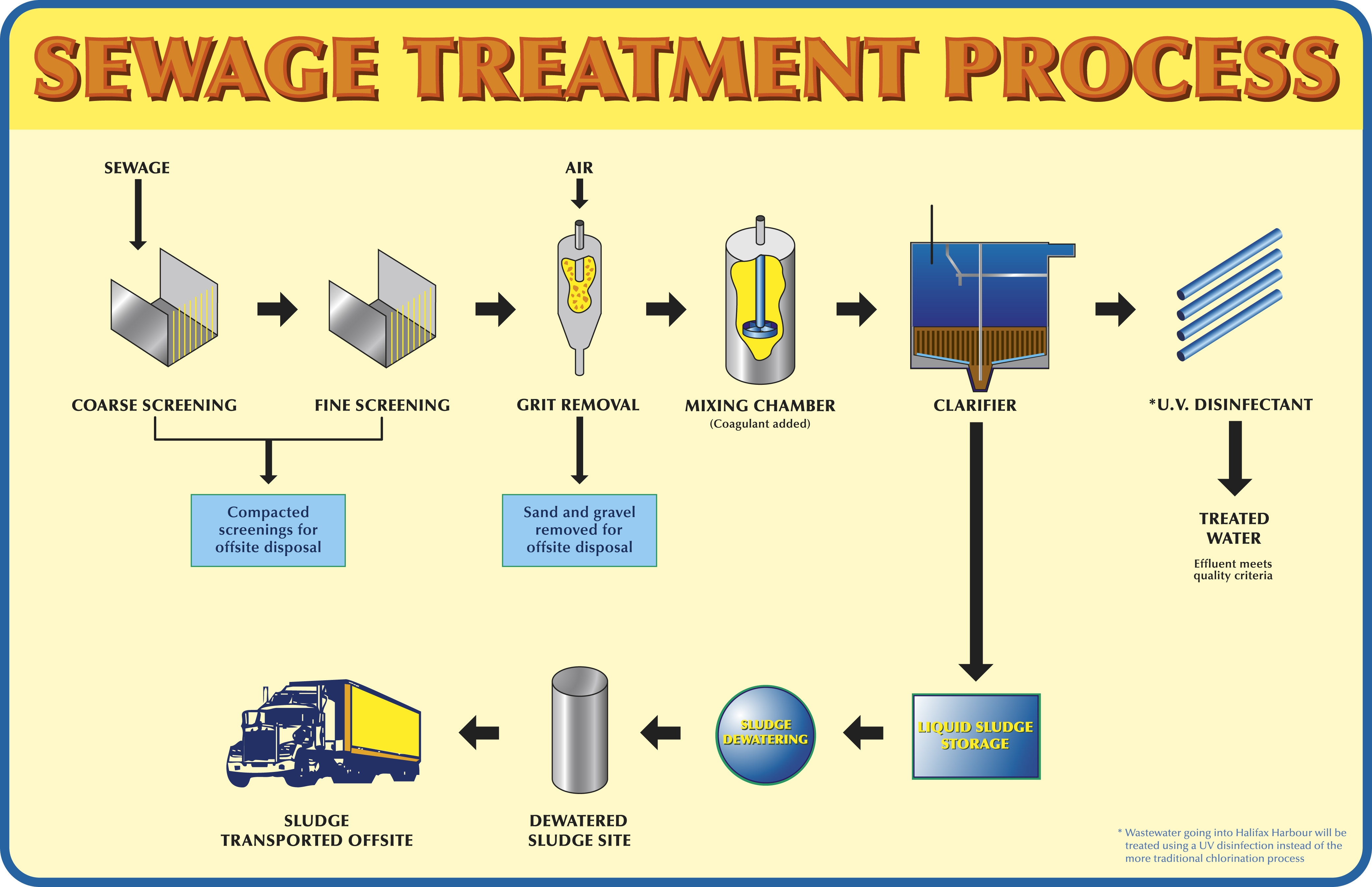
| Solid waste management is the process of collecting, treating, and disposing of solid waste in an environmentally friendly and sustainable manner. It involves various activities such as waste segregation, recycling, composting, and landfills. Effective solid waste management helps minimize the impact of waste on the environment and public health. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Elements of Solid Waste Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waste Segregation: The separation of different types of waste at the source, such as organic waste, recyclables, and non-recyclables. Recycling: The process of converting waste materials into new products to prevent the need for raw material extraction and reduce waste volume. Composting: The decomposition of organic waste into nutrient-rich compost that can be used as soil conditioner. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Elements of Solid Waste Management (continued) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waste Treatment: The process of treating hazardous or non-biodegradable waste to make it less harmful or easier to handle. Landfills: The disposal of solid waste in designated areas where it is compacted and buried under layers of soil to minimize environmental impact. Waste-to-Energy: The conversion of solid waste into energy through processes like incineration or anaerobic digestion. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Elements of Solid Waste Management (continued) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Public Awareness and Education: The promotion of responsible waste management practices through campaigns, workshops, and educational programs. Policy and Regulation: The development and enforcement of laws and regulations to govern waste management practices and ensure compliance. Monitoring and Enforcement: The regular monitoring of waste management activities and enforcement of regulations to maintain environmental standards. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Elements of Solid Waste Management (continued) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Resource Recovery: The extraction of valuable materials from waste through techniques like waste-to-energy, recycling, and upcycling. Waste Minimization: The reduction of waste generation through sustainable consumption and production practices. Circular Economy: The concept of designing waste out of the system by promoting the reuse, repair, and recycling of materials. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Elements of Solid Waste Management (continued) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Technology and Innovation: The use of advanced technologies and innovative solutions to improve waste management processes. Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: The involvement of various stakeholders, including government, industries, communities, and NGOs, to collectively address solid waste management challenges. Continuous Improvement: The ongoing evaluation and enhancement of solid waste management strategies to adapt to changing needs and advancements. |  | |
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Solid waste management plays a crucial role in preserving our environment and safeguarding public health. By implementing effective waste management practices and embracing the principles of sustainability, we can minimize waste generation, promote resource recovery, and create a cleaner and healthier future. It is essential for individuals, communities, industries, and governments to work together towards sustainable solid waste management solutions. | ||
| 8 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Insert references here (APA or any preferred ... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 9 | ||
| Questions? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Open the floor for any questions or discussions regarding solid waste management and its elements. Your second bullet Your third bullet | ||
| 10 | ||