Cybersecurity Presentation
| Introduction to Cybersecurity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage. It is crucial in today's digital age to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. Cybersecurity includes various technologies, processes, and measures to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Cybersecurity | ||
|---|---|---|
| With the increasing reliance on technology and the rise of cybercrime, cybersecurity is essential to safeguard sensitive information. A successful cyber attack can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal implications. Cybersecurity is vital for individuals, businesses, governments, and organizations to protect their assets and maintain trust. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Cyber Threats | ||
|---|---|---|
| Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems or networks. Phishing: Social engineering technique that tricks individuals into revealing sensitive information through deceptive emails or fraudulent websites. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Overloading a network or website to make it inaccessible to legitimate users. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Cybersecurity Best Practices | ||
|---|---|---|
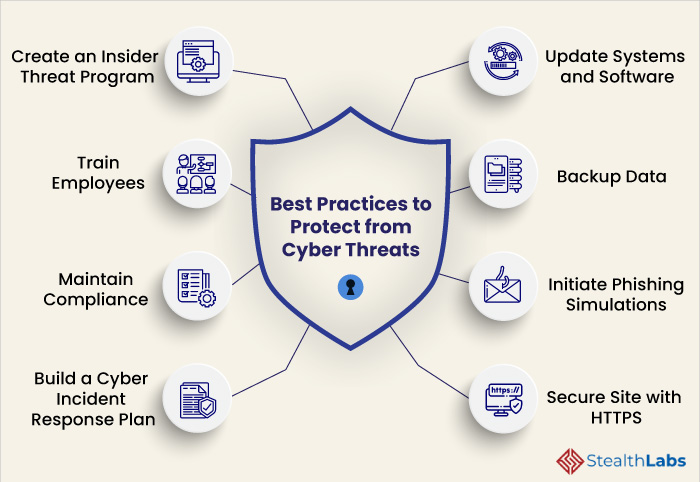
| Strong Passwords: Use unique, complex passwords for each online account and enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible. Regular Software Updates: Keep operating systems, applications, and security software up to date to patch vulnerabilities. Employee Training: Educate employees about cybersecurity risks, safe browsing habits, and how to identify and report suspicious activities. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Network Security Measures | ||
|---|---|---|
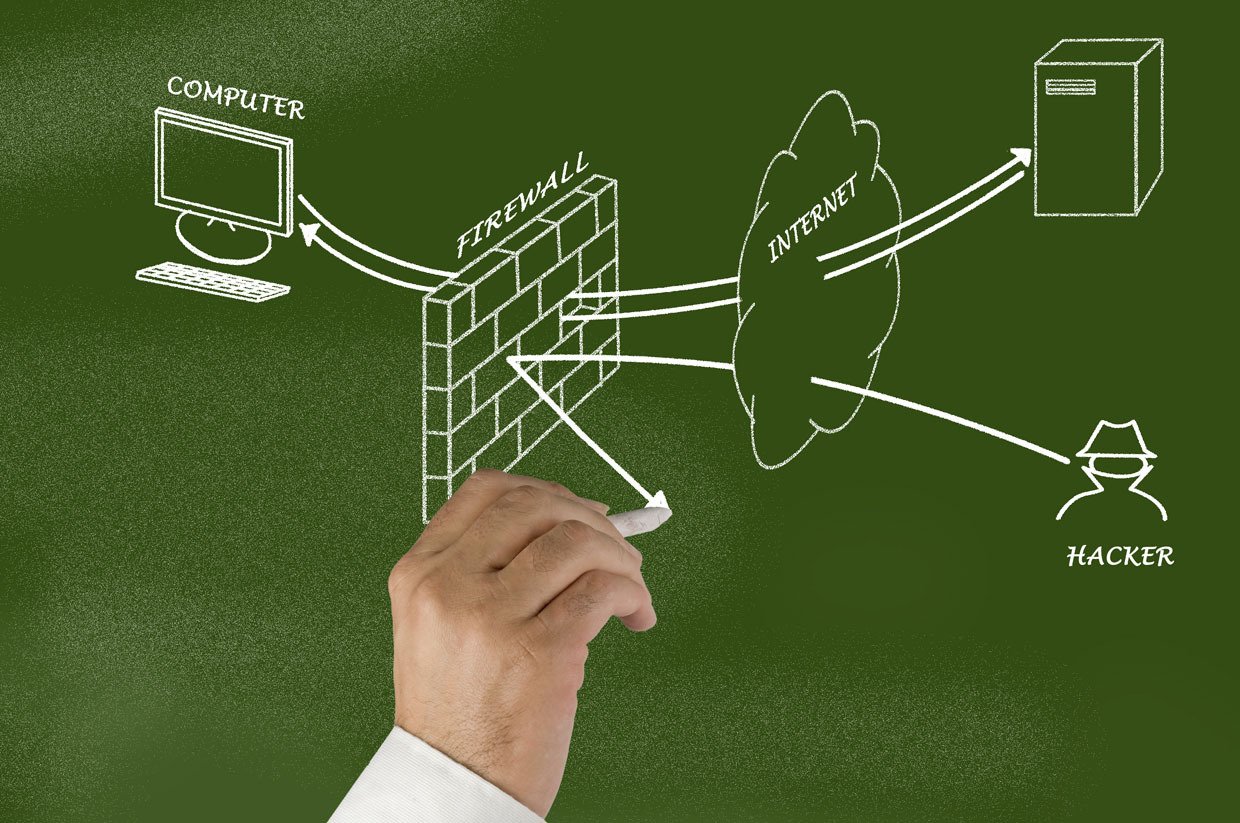
| Firewalls: Hardware or software-based security systems that monitor and control network traffic to prevent unauthorized access. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Detect and prevent malicious activities and attacks on a network. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Encrypted connections that allow secure remote access to a private network over the internet. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Data Protection Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Encryption: Transforming data into unreadable format to prevent unauthorized access or data theft. Regular Backups: Creating copies of important data and storing them securely to recover in case of data loss or ransomware attacks. Data Classification: Identifying and categorizing data based on its sensitivity level to implement appropriate security measures. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Incident Response and Recovery | ||
|---|---|---|
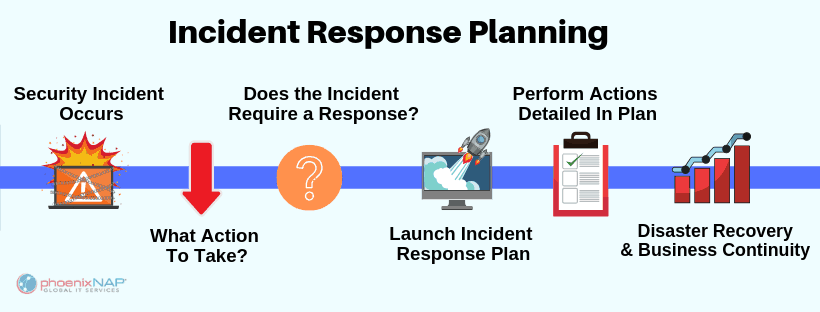
| Incident Response Plan: Establishing a documented process to handle cybersecurity incidents promptly and efficiently. Incident Detection and Analysis: Monitoring systems for suspicious activities, investigating incidents, and identifying their root causes. Recovery and Remediation: Restoring affected systems, removing malware, and implementing measures to prevent future incidents. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Emerging Cybersecurity Trends | ||
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity: AI-powered tools and algorithms to detect and respond to threats more effectively. Internet of Things (IoT) Security: Ensuring the security of interconnected devices and networks to prevent unauthorized access. Cloud Security: Protecting data stored in cloud environments and ensuring secure access and data transmission. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Cybersecurity Challenges | ||
|---|---|---|
| Skills Gap: The shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals to meet the growing demand for cybersecurity expertise. Sophisticated Threats: Cybercriminals constantly evolve their techniques, making it challenging to stay ahead of emerging threats. Insider Threats: Security risks posed by employees or individuals with authorized access to systems who misuse their privileges. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity is crucial to protect systems, networks, and data from cyber threats in today's digital landscape. By implementing best practices, staying updated, and investing in robust security measures, individuals and organizations can mitigate risks. Continuous monitoring, education, and collaboration are key to ensuring a safe and secure cyber environment. | ||
| 10 | ||