Cybercrime On Banking Presentation
| Introduction to Cybercrime on Banking | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cybercrime on banking refers to illegal activities targeting financial institutions and their customers. Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in online banking systems to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. The rise of technology and digitalization has made cybercrime a significant threat to the banking industry. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Cybercrime on Banking | ||
|---|---|---|
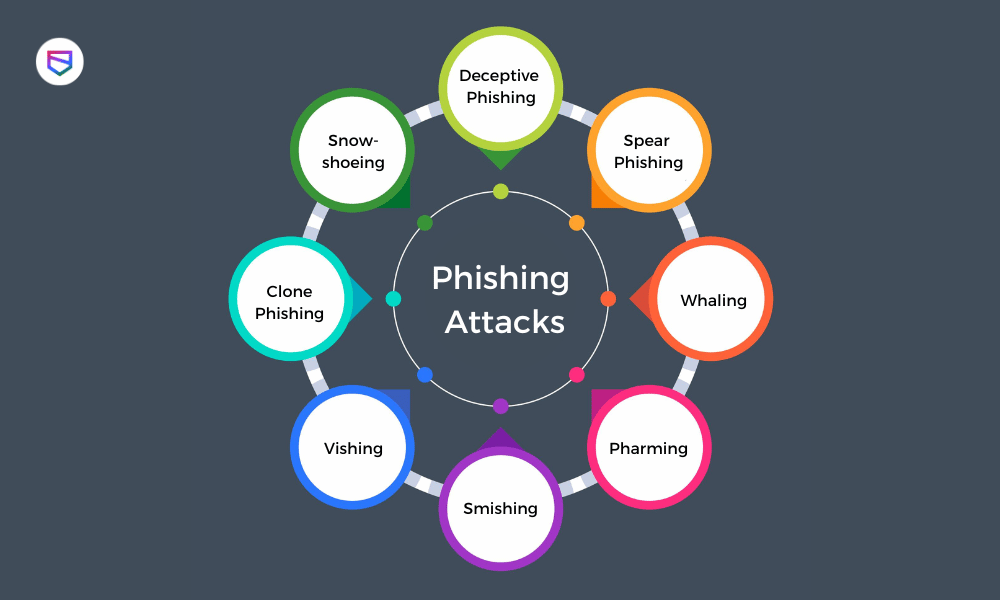
| Phishing attacks: Cybercriminals send deceptive emails or messages to trick users into revealing their login credentials or personal information. Malware attacks: Cybercriminals use malicious software to gain unauthorized access to banking systems, steal data, or initiate fraudulent transactions. Social engineering attacks: Cybercriminals manipulate individuals through psychological tactics to gain access to their financial accounts or personal information. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Impact of Cybercrime on Banking | ||
|---|---|---|
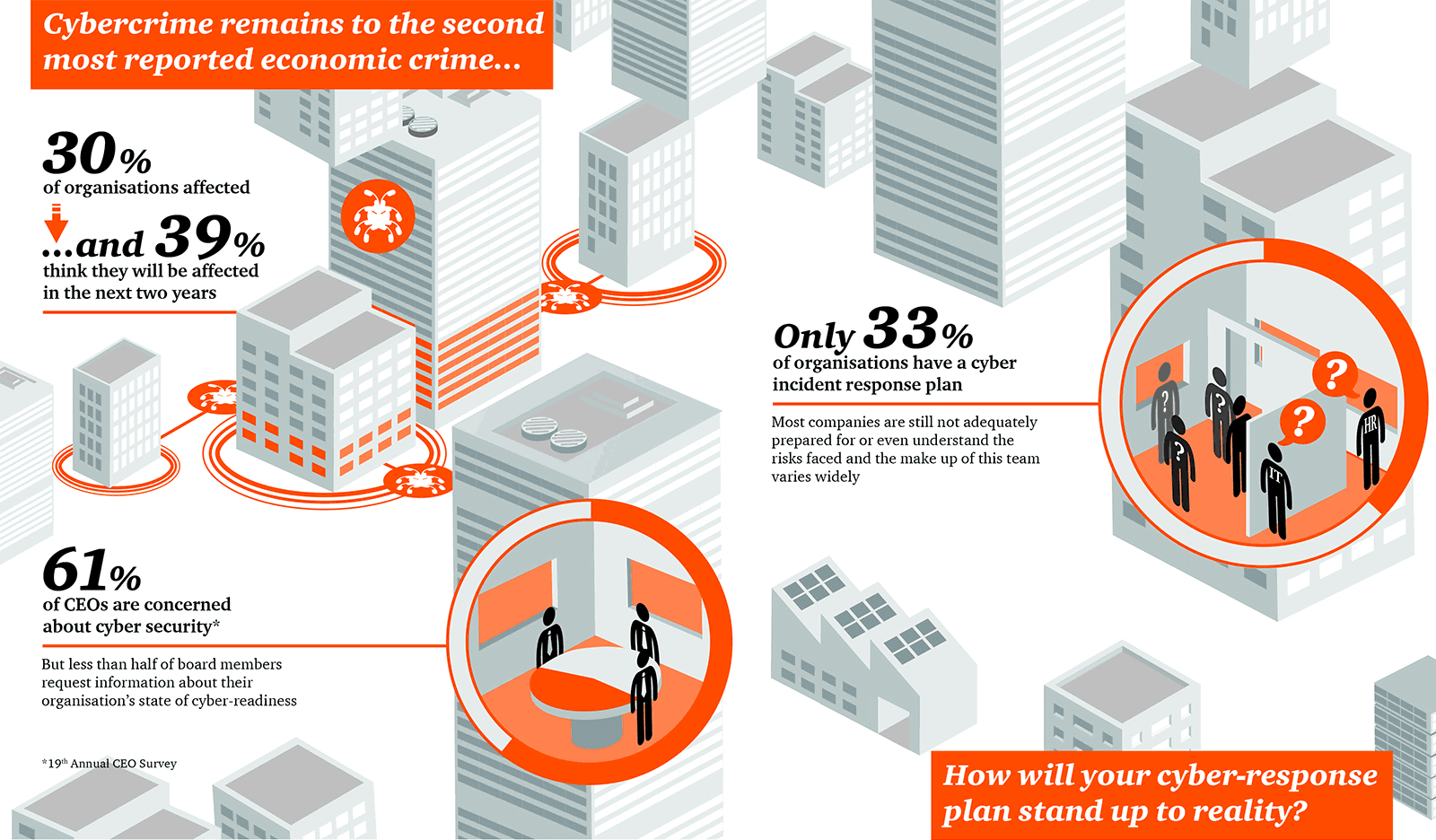
| Financial losses: Cybercrime on banking can result in significant financial losses for both financial institutions and customers. Reputation damage: Incidents of cybercrime can severely damage the reputation of banks, leading to a loss of trust from customers and investors. Legal and regulatory consequences: Banks may face legal and regulatory consequences for failing to protect customer data and prevent cybercrime. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Common Vulnerabilities in Online Banking | ||
|---|---|---|
| Weak authentication: Inadequate security measures such as weak passwords or lack of multi-factor authentication can make it easier for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access. Software vulnerabilities: Unpatched or outdated software can have security flaws that cybercriminals exploit to infiltrate banking systems. Insider threats: Employees with access to sensitive information can pose a risk if they engage in malicious activities or fall victim to social engineering attacks. |  | |
| 4 | ||
| Preventive Measures for Banks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Implement strong security measures: Banks should use robust authentication methods, encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to protect their systems and customer data. Educate customers: Banks should provide regular cybersecurity awareness training to customers to help them identify and avoid common cyber threats. Collaborate with law enforcement: Establishing strong partnerships with law enforcement agencies can help banks respond effectively to cybercrime incidents. |  | |
| 5 | ||
| Preventive Measures for Customers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Use strong passwords: Customers should create unique and complex passwords for their online banking accounts and regularly update them. Enable multi-factor authentication: By enabling multi-factor authentication, customers add an extra layer of security to their online banking accounts. Be cautious of phishing attempts: Customers should be vigilant when receiving emails or messages requesting personal or financial information and avoid clicking on suspicious links. |  | |
| 6 | ||
| Incident Response for Banks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Develop an incident response plan: Banks should have a well-defined plan in place to respond promptly and effectively to cybercrime incidents. Conduct regular security assessments: Regular security assessments help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in banking systems, allowing banks to address them proactively. Collaborate with cybersecurity experts: Engaging with cybersecurity experts can provide banks with valuable insights and guidance in responding to cybercrime incidents. |  | |
| 7 | ||
| Legal and Regulatory Framework | ||
|---|---|---|
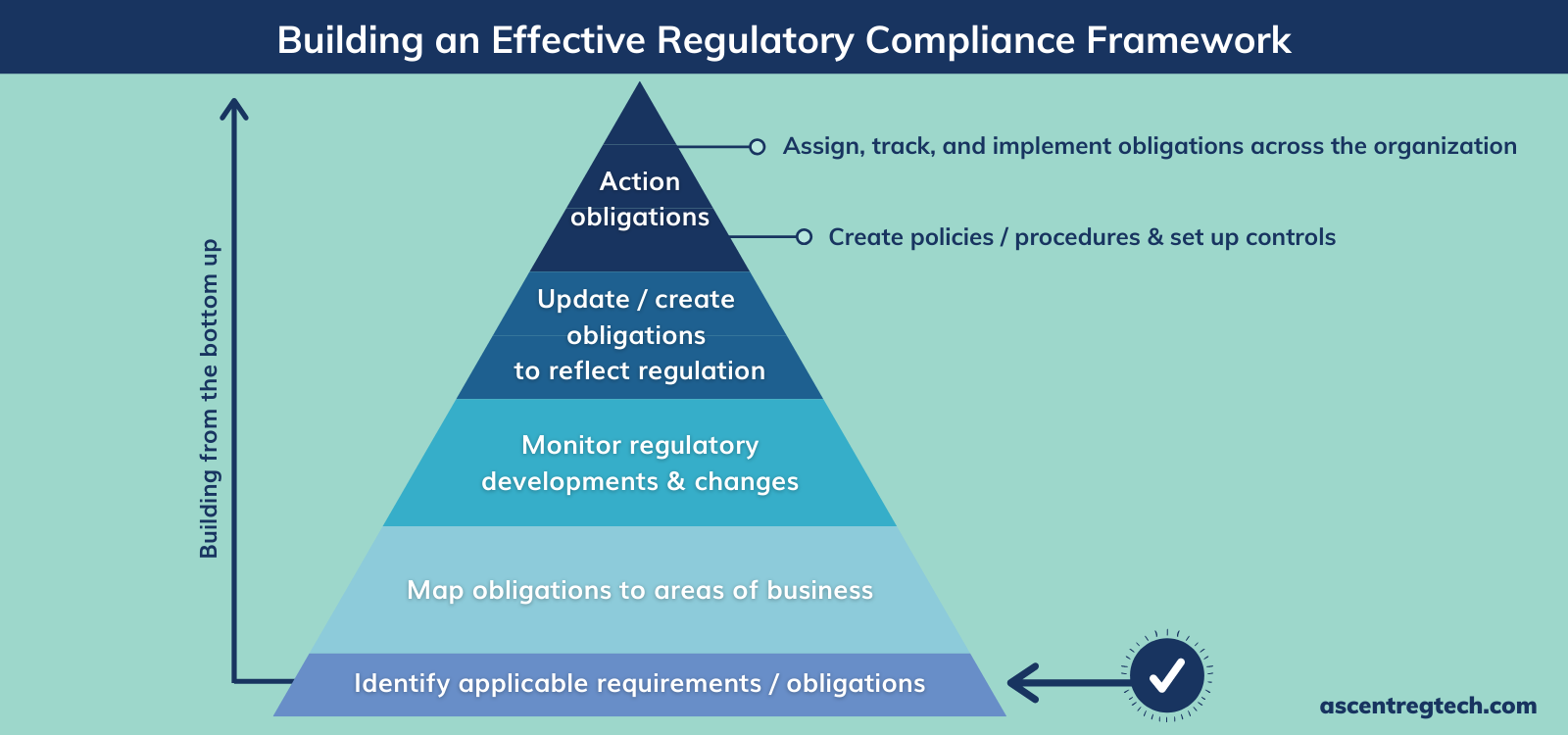
| Compliance with regulations: Banks must comply with relevant legal and regulatory requirements regarding data protection and cybersecurity. Reporting obligations: Banks should have processes in place to report cybercrime incidents to the appropriate authorities promptly. Collaboration with regulators: Establishing a collaborative relationship with regulators can help banks stay updated on emerging threats and best practices. | ||
| 8 | ||
| International Cooperation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cybercrime is a global issue, requiring international cooperation and collaboration among governments, law enforcement agencies, and financial institutions. Sharing threat intelligence: Banks should participate in information-sharing initiatives to exchange cybersecurity threat intelligence and enhance collective defense against cybercrime. Joint investigations and prosecutions: International cooperation enables joint investigations and prosecutions of cybercriminals, increasing the chances of successful apprehension and prosecution. |  | |
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cybercrime on banking is a growing threat that poses significant challenges to financial institutions and their customers. Banks must implement robust security measures, educate customers, and collaborate with law enforcement to combat cybercrime effectively. By taking preventive measures, developing incident response plans, and complying with legal and regulatory frameworks, banks can mitigate the risks associated with cybercrime on banking. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| [Insert references here]... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||