Cyber Security Presentation
| Introduction to Cyber Security | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cyber security is the practice of protecting electronic systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. It involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of information. Cyber security is essential in today's digital world to safeguard personal, organizational, and national security. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Cyber Security | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cyber threats are evolving and becoming more sophisticated, posing a significant risk to individuals and organizations. A successful cyber attack can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Implementing robust cyber security measures ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, protecting against potential threats. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Common Cyber Security Threats | ||
|---|---|---|
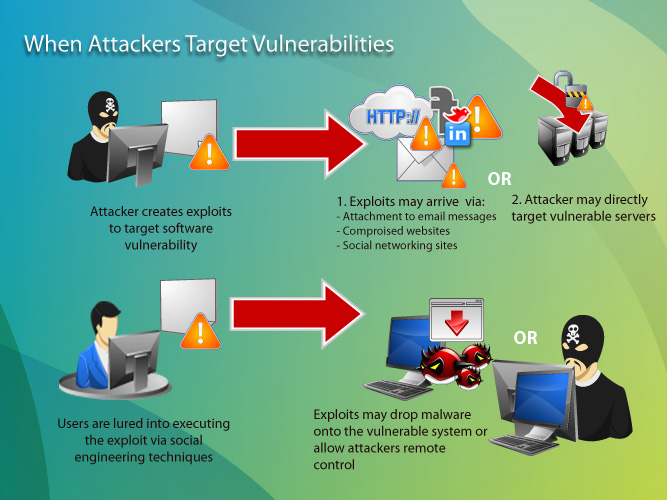
| Malware: Software designed to harm or exploit computer systems, including viruses, ransomware, and spyware. Phishing: Deceptive emails or messages aimed at tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious attachments. Social Engineering: Manipulating human behavior to gain unauthorized access, often through impersonation or trust exploitation. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Cyber Security Best Practices for Individuals | ||
|---|---|---|
| Use strong, unique passwords for each online account and consider using a password manager. Regularly update software and operating systems to patch vulnerabilities. Be cautious when clicking on links or opening attachments, especially from unknown or suspicious sources. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Cyber Security Best Practices for Organizations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conduct regular employee training on cyber security awareness and safe online practices. Implement a robust firewall and secure network infrastructure to protect against unauthorized access. Regularly backup crucial data and develop an incident response plan to quickly address and mitigate cyber attacks. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Cyber Security Technologies and Tools | ||
|---|---|---|
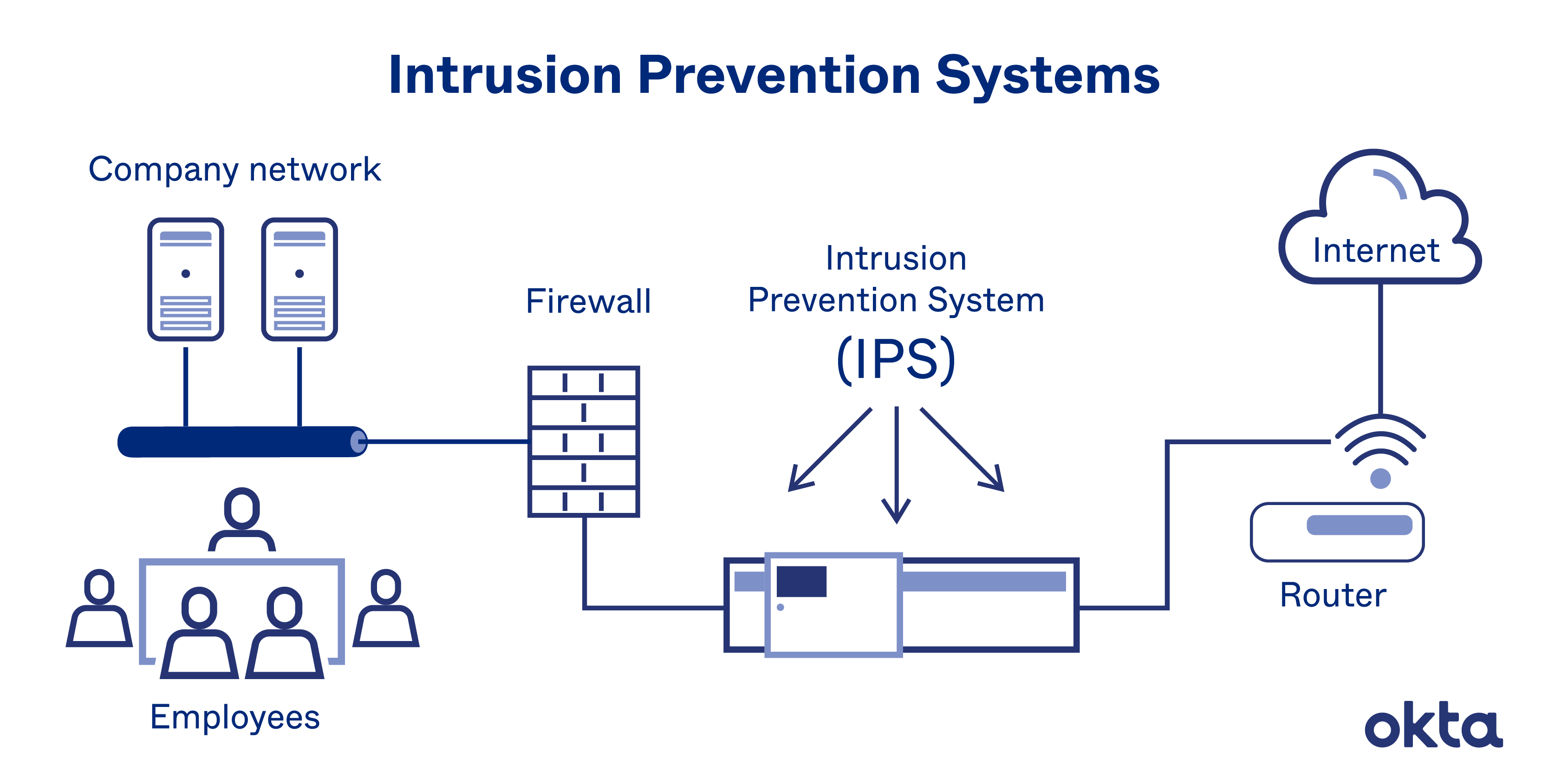
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) help monitor and detect potential threats in real-time. Antivirus and antimalware software scan and protect devices from malicious software. Encryption tools ensure data confidentiality by converting information into unreadable code. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Cyber Security and Cloud Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cloud computing offers flexibility and scalability but introduces new security challenges. Implementing strong access controls and encryption protocols is critical when storing sensitive data in the cloud. Regularly monitoring and auditing cloud service providers is essential to ensure compliance with security standards. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Cyber Security Regulations and Compliance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Many countries have enacted cyber security laws and regulations to protect individuals and organizations. Compliance frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS provide guidelines for data protection and privacy. Organizations must understand and adhere to these regulations to avoid legal consequences and reputational damage. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Cyber Security in the Future | ||
|---|---|---|
| As technology evolves, cyber threats will continue to advance, requiring ongoing innovation in cyber security. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in detecting and preventing cyber attacks. Collaboration between governments, organizations, and individuals is crucial to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cyber security is a critical aspect of protecting personal and organizational information from cyber threats. By implementing best practices, utilizing advanced technologies, and complying with regulations, individuals and organizations can effectively mitigate cyber risks. Continuous education, awareness, and proactive measures are key to maintaining a secure digital environment. | ||
| 10 | ||