Culling Of Livestock Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
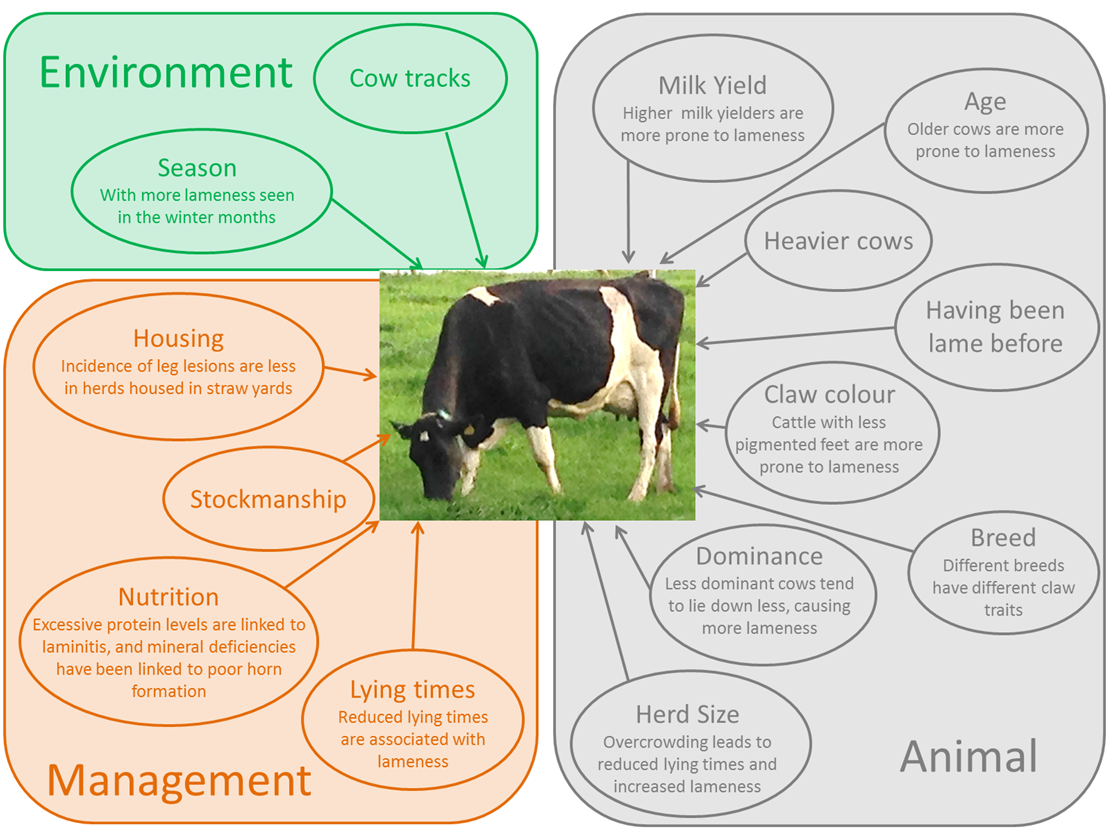
| Culling of livestock refers to the process of selectively removing animals from a herd or flock. Culling is often done to improve overall productivity, health, and genetic quality of the remaining animals. The decision to cull is based on various factors such as age, performance, health, and genetic traits. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Reasons for Culling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Poor reproductive performance: Animals that fail to conceive or have repeated breeding issues may be culled to maintain herd/ flock fertility. Low productivity: Animals that show consistently low milk production, egg production, or weight gain may be culled to improve overall productivity. Health issues: Animals with chronic or contagious diseases that pose a risk to the rest of the herd/ flock may be culled to prevent further spread. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Genetic Improvement | ||
|---|---|---|
| Culling allows for the removal of animals with undesirable genetic traits, such as poor conformation or temperament. By culling animals with undesirable traits, breeders can improve the genetic quality of the remaining herd/ flock. Genetic selection through culling contributes to the development of more productive and disease-resistant livestock. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Age-related Culling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Aging animals may experience declining productivity, increased health issues, and decreased fertility. Older animals may be culled to make room for younger, more productive individuals in the herd/ flock. Age-related culling can help maintain a healthy and productive population. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Economic Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Culling allows farmers to optimize their resources by focusing on the most productive animals. Removing unproductive or unhealthy animals reduces feed and healthcare costs. Selling culled animals can generate additional income for the farmer. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Ethical Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Culling should be carried out with proper animal welfare considerations, ensuring minimal stress and pain for the animals. Humane euthanasia methods should be employed when necessary. Regular monitoring and assessment of animal welfare during culling processes are essential. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges in Culling | ||
|---|---|---|
| Determining the optimal time for culling can be challenging, as it requires balancing productivity, health, and genetics. Limited market demand for culled animals may pose challenges for farmers looking to sell them. Proper record-keeping and documentation are crucial to facilitate informed decision-making during culling. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Culling Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular performance monitoring and health checks can help identify animals that need to be culled. Genetic selection programs can be implemented to identify animals with desirable traits for breeding purposes. Consultation with veterinarians and industry experts can provide valuable guidance in implementing effective culling strategies. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Culling of livestock plays a vital role in maintaining herd/ flock productivity, health, and genetic quality. Proper culling strategies help farmers optimize their resources and improve overall profitability. Ethical considerations and animal welfare should always be prioritized throughout the culling process. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Insert a list of references and sources used ... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 10 | ||