Corporate Accounting Presentation
| Introduction to Corporate Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Corporate accounting refers to the process of recording, analyzing, and reporting financial transactions and information of a corporation. It involves the preparation of financial statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Corporate accounting plays a crucial role in providing stakeholders with accurate and reliable financial information. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Corporate Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
| Corporate accounting helps in evaluating the financial performance of a company, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions. It ensures compliance with accounting standards and regulations, promoting transparency and accountability. Accurate corporate accounting facilitates efficient tax planning and management, minimizing tax liabilities. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Key Principles of Corporate Accounting | ||
|---|---|---|
| The principle of consistency ensures that accounting methods and procedures are consistently applied across different reporting periods. The principle of materiality emphasizes the disclosure of information that could potentially impact the decision-making process of stakeholders. The principle of conservatism requires accountants to err on the side of caution when recording financial transactions. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Types of Financial Statements | ||
|---|---|---|
| The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific point in time, showing its assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. The income statement summarizes a company's revenues, expenses, gains, and losses over a specified period, indicating its profitability. The cash flow statement shows the inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents, providing insights into a company's liquidity and cash management. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Accounting Methods | ||
|---|---|---|
| Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. Cash basis accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash is received or paid, disregarding the timing of the actual economic activity. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) guide the selection of the appropriate accounting method. | ||
| 5 | ||
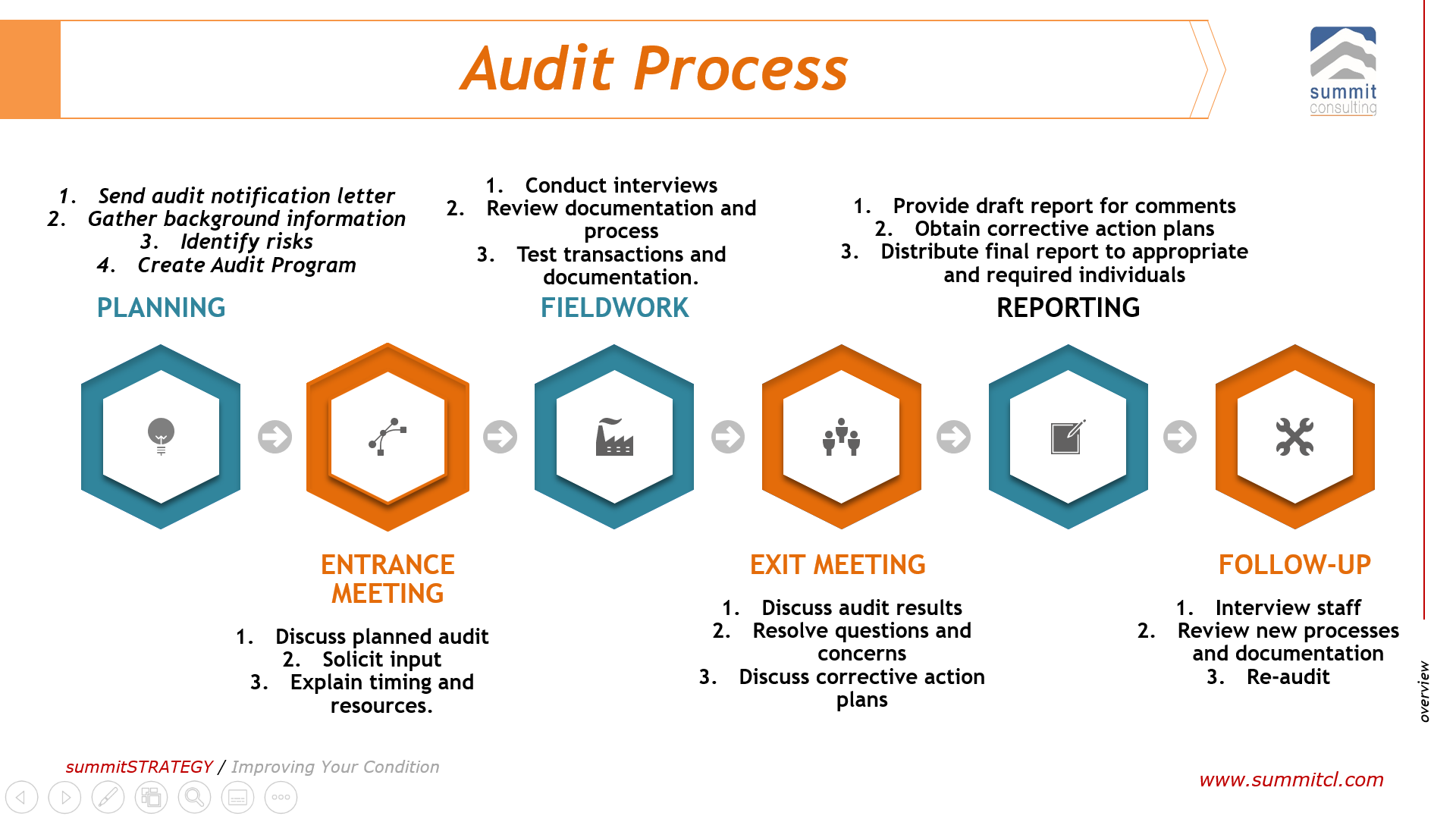
| Corporate Accounting Cycle | ||
|---|---|---|
| The accounting cycle encompasses the steps involved in processing financial transactions, including journalizing, posting, preparing trial balances, and adjusting entries. It culminates in the preparation of financial statements, followed by the closing entries to reset the accounts for the next accounting period. The cycle repeats with each reporting period to maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Auditing and Internal Controls | ||
|---|---|---|
| Auditing is the independent examination of a company's financial records and processes to ensure compliance and accuracy. Internal controls are established to safeguard company assets, prevent fraud, and ensure the reliability of financial reporting. Both auditing and internal controls play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of corporate accounting. | ||
| 7 | ||
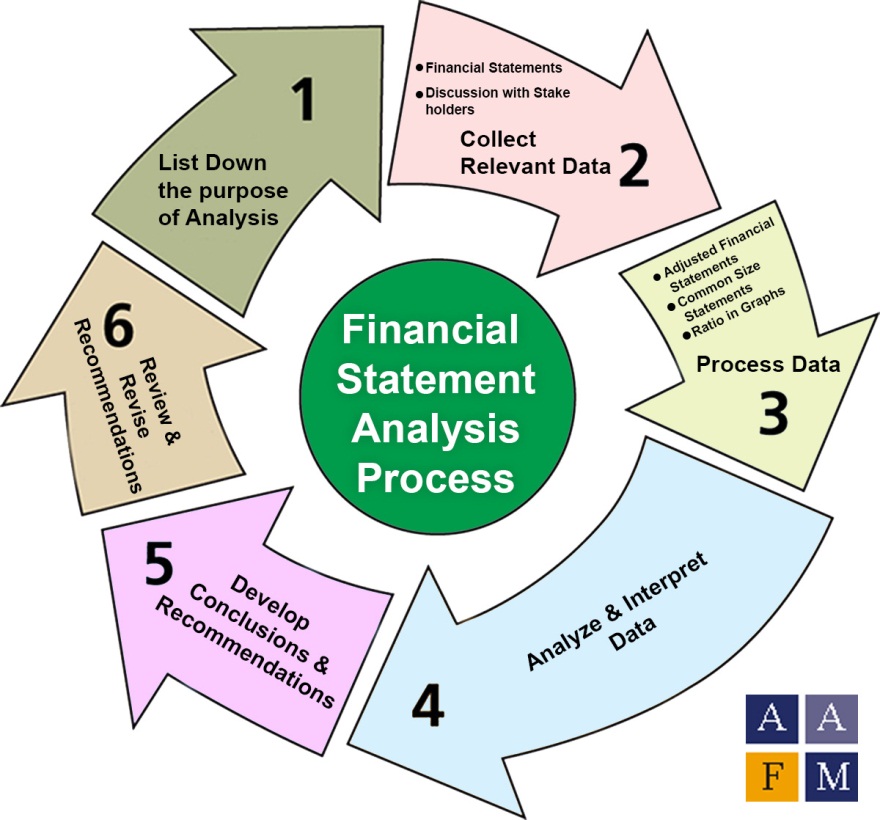
| Importance of Financial Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Financial analysis involves the interpretation and evaluation of financial statements to assess a company's performance, profitability, and financial health. It helps identify trends, strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement within a company's financial operations. Financial analysis is vital for decision-making, investment analysis, and strategic planning. | ||
| 8 | ||
| International Accounting Standards | ||
|---|---|---|
| International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are globally accepted accounting standards that ensure consistency and comparability of financial statements across different countries. IFRS is used by companies operating in countries that have adopted these standards, facilitating international business transactions and investment analysis. IFRS convergence aims to harmonize accounting practices globally, reducing disparities between IFRS and local accounting standards. |  | |
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Corporate accounting is essential for financial reporting, decision-making, and ensuring the transparency and integrity of a company's financial information. It follows key principles, prepares financial statements, and undergoes auditing to provide accurate and reliable financial information to stakeholders. Continuous analysis and adherence to international accounting standards contribute to the effectiveness and efficiency of corporate accounting. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| AccountingTools. (n.d.). Corporate Accounting... Financial Accounting Standards Board. (n.d.).... International Financial Reporting Standards F... |  | |
| 11 | ||



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)