Conventional Machines And Cnc Machines Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
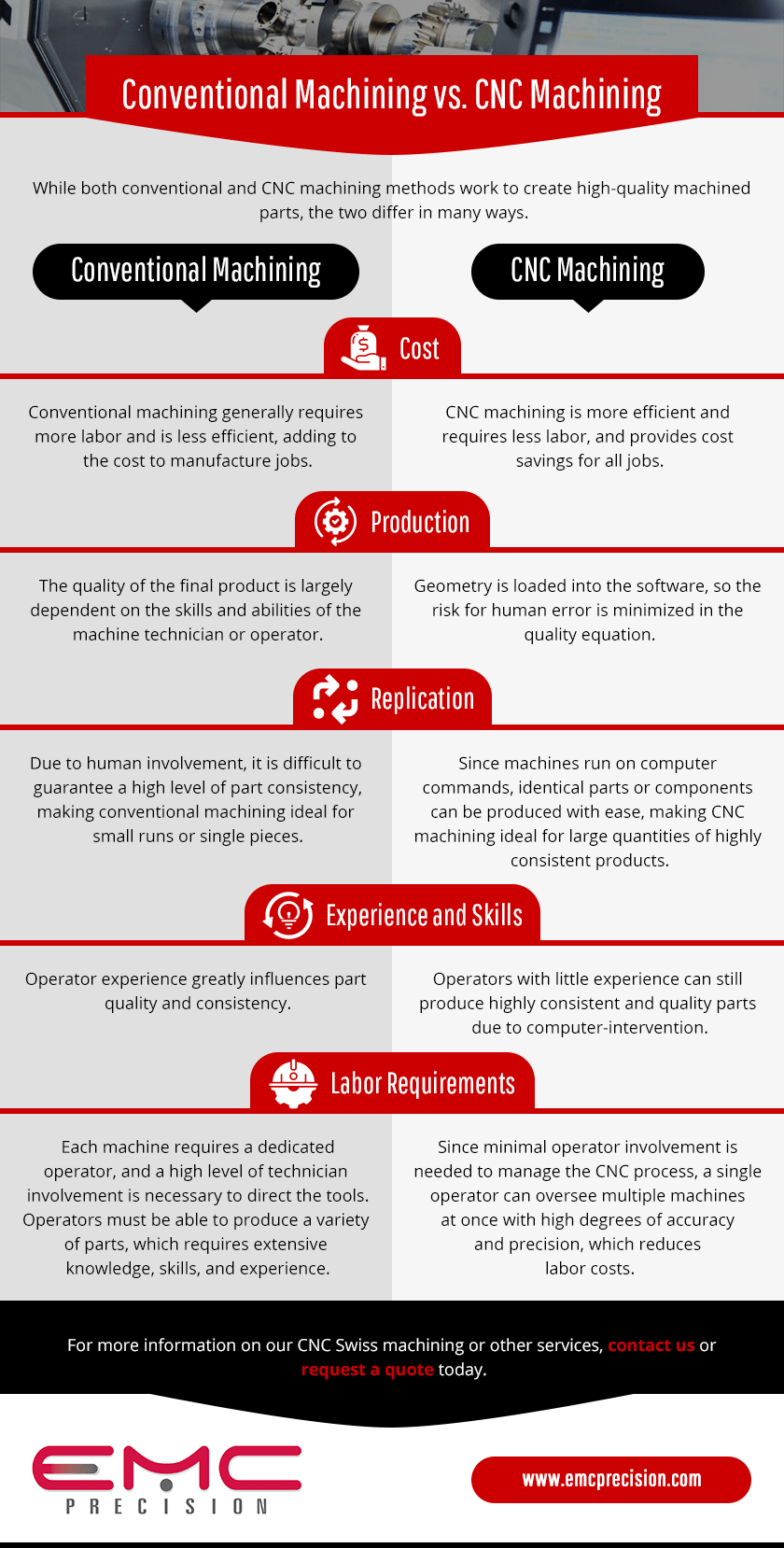
| Conventional machines and CNC machines are two different types of machinery used in manufacturing processes. Conventional machines are manually operated and require human intervention for every task. CNC machines are automated and controlled by computer programs, reducing the need for human intervention. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Definition of Conventional Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
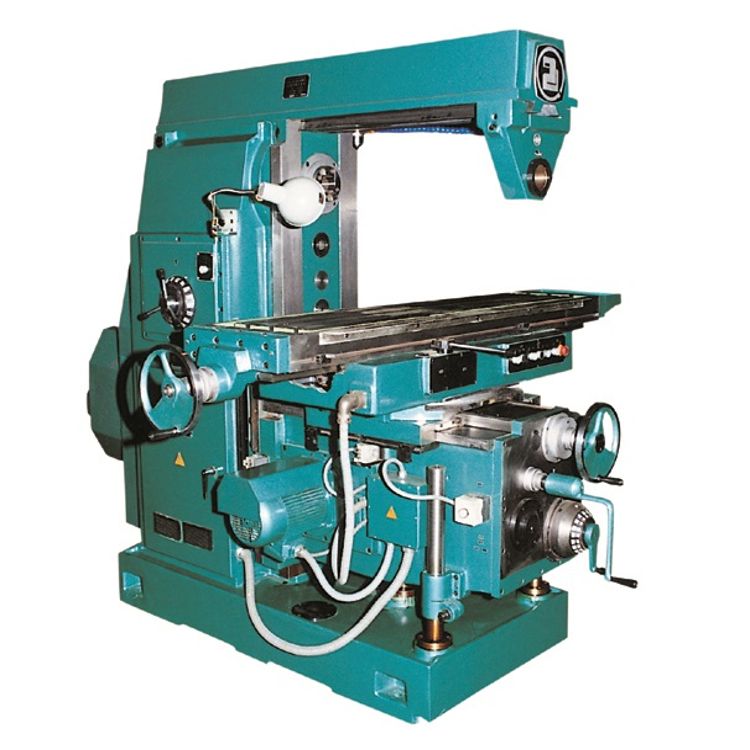
| Conventional machines refer to traditional machinery used in manufacturing. These machines are operated manually by skilled workers. Examples of conventional machines include lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Advantages of Conventional Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conventional machines offer flexibility in terms of customization and adjustments. They are often more affordable compared to CNC machines. Skilled workers can quickly adapt and troubleshoot issues with conventional machines. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Limitations of Conventional Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conventional machines require skilled operators, which can be costly to train and retain. They have lower accuracy and precision compared to CNC machines. Conventional machines are slower in production and have longer setup times. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Definition of CNC Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
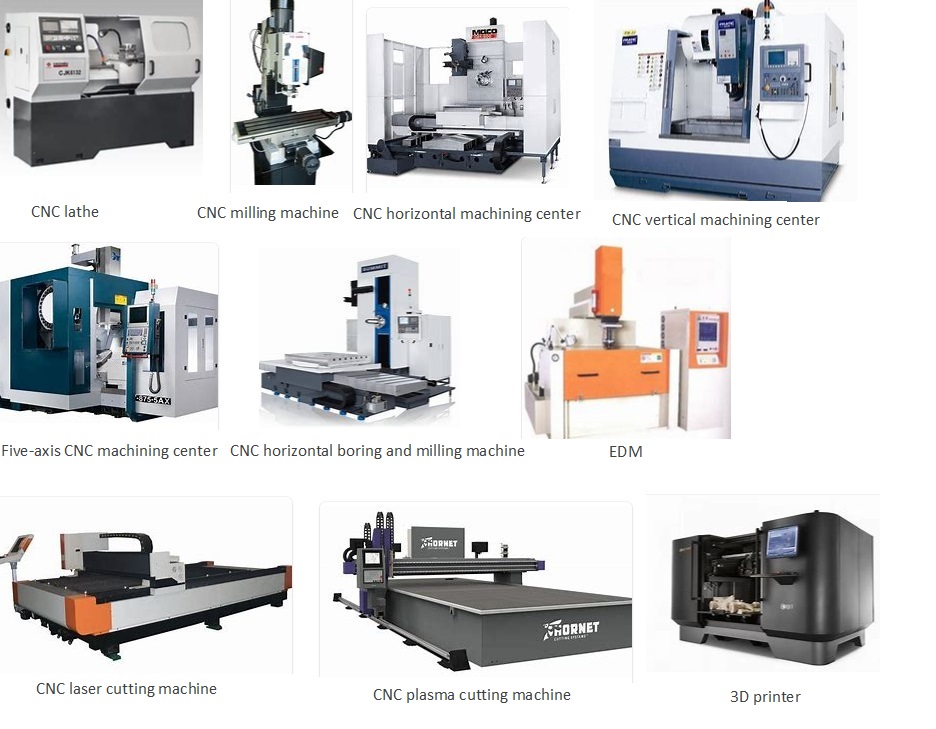
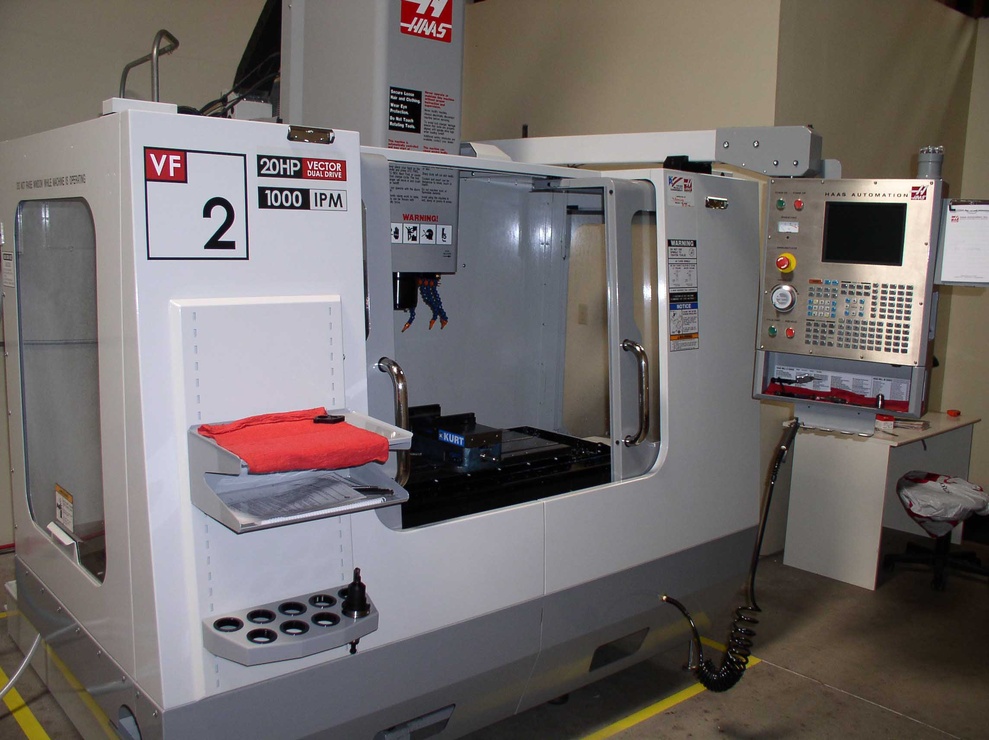
| CNC machines, or Computer Numerical Control machines, are automated manufacturing tools. They are controlled by computer programs and operate with high precision. CNC machines include CNC milling machines, CNC lathes, and CNC routers. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Advantages of CNC Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| CNC machines offer high accuracy and precision in manufacturing processes. They can perform complex tasks and produce intricate designs consistently. CNC machines reduce human error and increase productivity in mass production. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Limitations of CNC Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| CNC machines require skilled programmers to create and modify the computer programs. They have higher initial costs compared to conventional machines. Maintenance and repairs of CNC machines can be more complex and expensive. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Comparison of Conventional and CNC Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conventional machines are suitable for small-scale production and customizations. CNC machines excel in mass production and complex designs. Conventional machines require skilled operators, while CNC machines need skilled programmers. | ||
| 8 | ||
| When to Use Conventional Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conventional machines are preferred when flexibility and customization are essential. They are suitable for small-scale production and prototyping. Conventional machines are commonly used in repair and maintenance shops. | ||
| 9 | ||
| When to Use CNC Machines | ||
|---|---|---|
| CNC machines are ideal for high-volume production and mass manufacturing. They are preferred for complex tasks and intricate designs. CNC machines are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. | ||
| 10 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Conventional machines and CNC machines offer different advantages and limitations. The choice between them depends on the specific manufacturing requirements. Both types of machines play significant roles in various industries, contributing to the overall manufacturing ecosystem. | ||
| 11 | ||


.jpg)




