Constitution Of India Presentation
| Introduction to the Constitution of India | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution of India is the supreme law of the country. It was adopted on 26th November 1949 and came into effect on 26th January 1950. It is the longest written constitution in the world. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Preamble of the Constitution | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Preamble outlines the goals and objectives of the Constitution. It declares India to be a sovereign, socialist, secular, and democratic republic. It emphasizes justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity among citizens. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Fundamental Rights | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution guarantees several fundamental rights to Indian citizens. These include the right to equality, freedom of speech and expression, and the right to education. These rights ensure individual liberty and protect citizens from discrimination. | ||
| 3 | ||
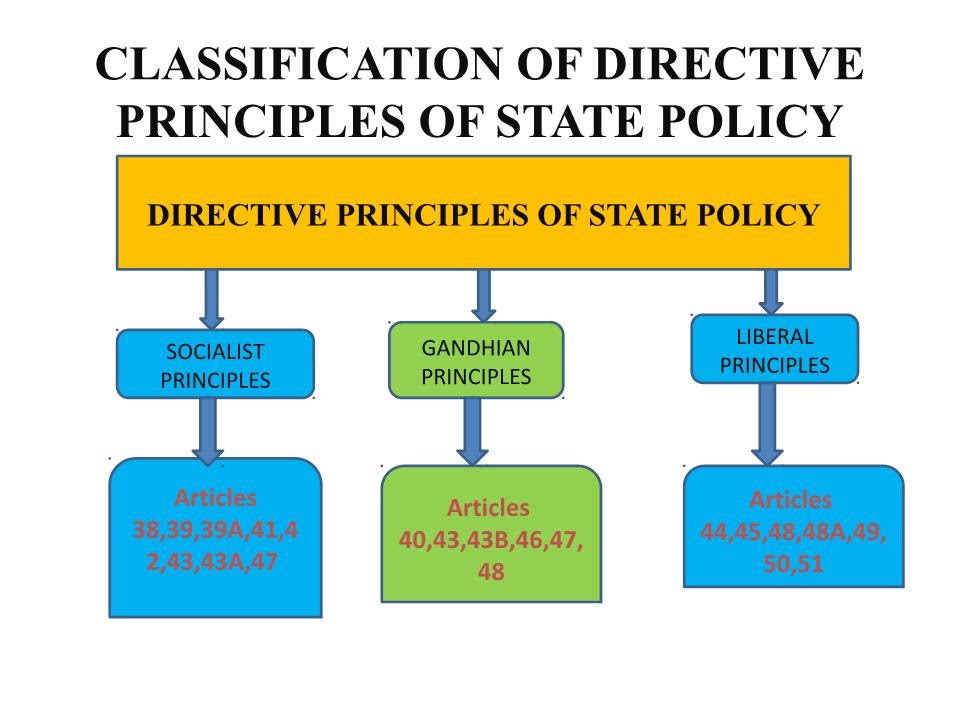
| Directive Principles of State Policy | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Directive Principles of State Policy are guidelines for the government to ensure social justice and welfare. They include provisions for free and compulsory education, protection of the environment, and promotion of equal opportunities. Although not enforceable in court, they serve as a moral compass for governance. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Structure of the Government | ||
|---|---|---|
| India follows a parliamentary system of government. The President is the head of state, and the Prime Minister is the head of government. The government consists of three branches: the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary. | ||
| 5 | ||
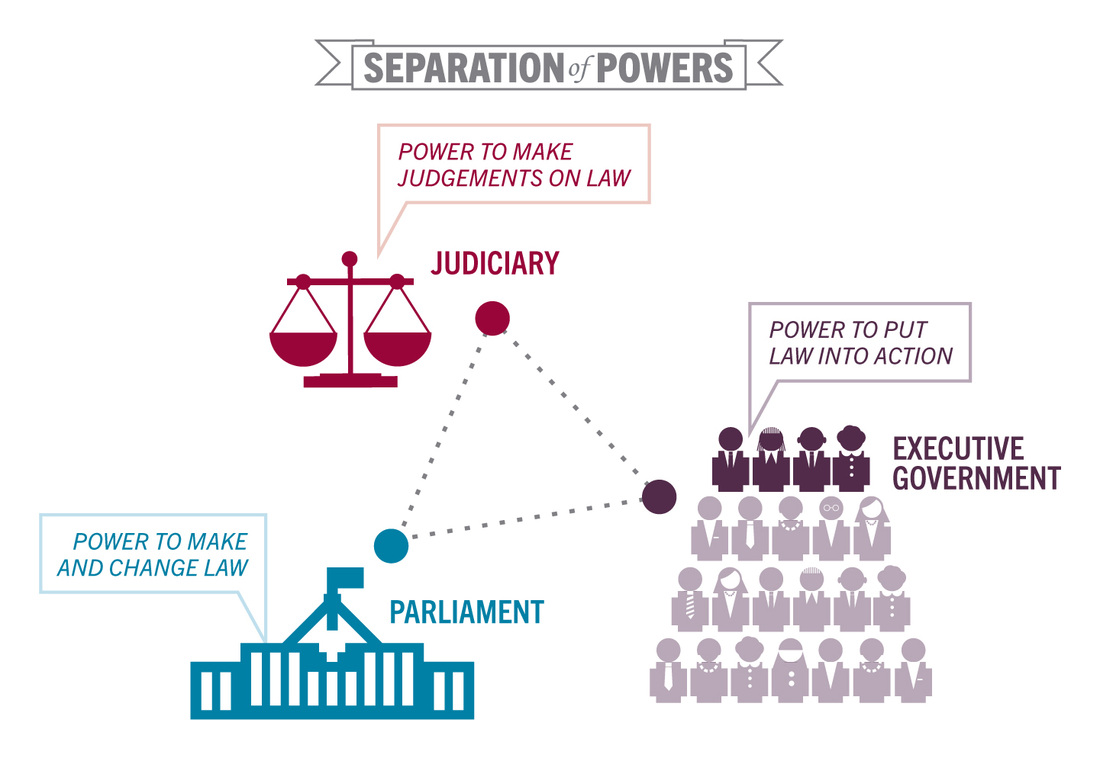
| Separation of Powers | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution provides for separation of powers between the three branches of government. The legislature makes laws, the executive implements them, and the judiciary interprets them. This separation ensures a system of checks and balances to prevent abuse of power. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Amendments to the Constitution | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution of India can be amended to adapt to changing times and needs. Amendments require a two-thirds majority in both houses of Parliament. Some significant amendments have been made to address social issues and improve governance. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Fundamental Duties | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution also outlines fundamental duties for citizens. These include respecting the national flag, promoting harmony, and protecting the environment. Fundamental duties are intended to promote a sense of social responsibility and civic consciousness. | ||
| 8 | ||
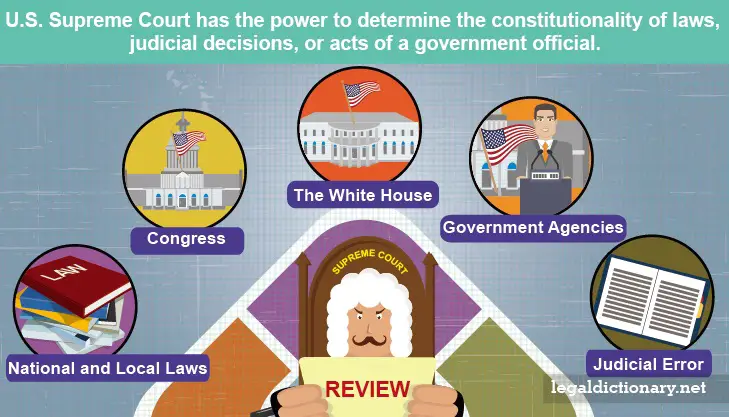
| Judicial Review | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution empowers the judiciary to review the constitutionality of laws and government actions. This ensures that the government operates within the bounds of the Constitution. Judicial review is a crucial mechanism for protecting individual rights and upholding the rule of law. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Constitution of India is the foundation of our democratic system. It provides a framework for governance, protects individual rights, and ensures social justice. It has played a vital role in shaping India's progress and maintaining its unity in diversity. | ||
| 10 | ||