Concept Of Anthropometric Indices Presentation
| Introduction to Anthropometric Indices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric indices are measurements used to assess body composition and health status. These indices provide valuable information about an individual's body size, shape, and fat distribution. Anthropometric indices are widely used in research, clinical practice, and public health interventions. | ||
| 1 | ||
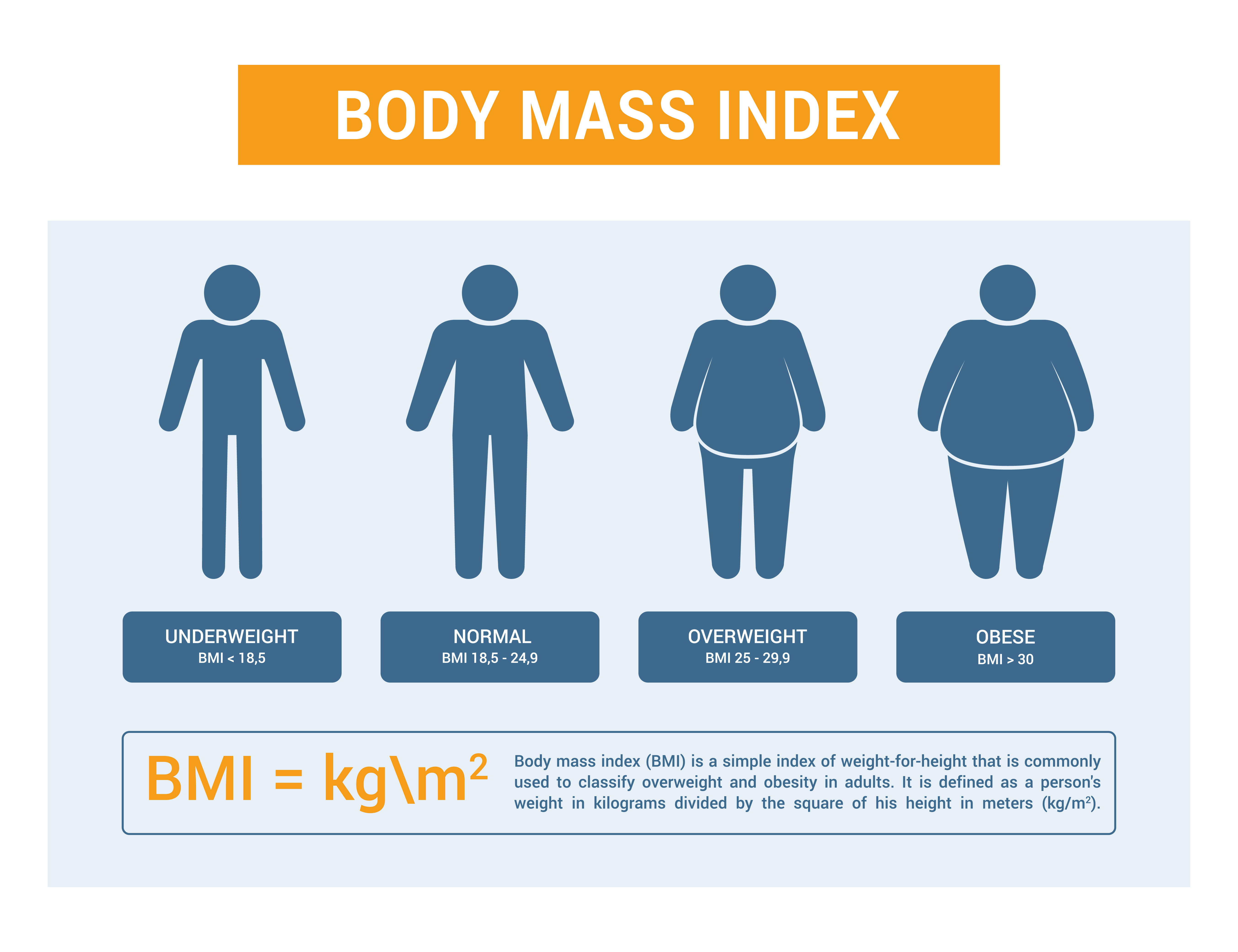
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| BMI is a commonly used anthropometric index calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. It is a simple and cost-effective way to estimate body fatness and assess weight status. BMI is used to classify individuals into categories such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR) | ||
|---|---|---|
| WHR is a measure of fat distribution and is calculated by dividing the circumference of the waist by the circumference of the hips. It provides information about the distribution of body fat, with higher values indicating an increased risk of certain health conditions. WHR is used to assess abdominal obesity and associated health risks. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Waist Circumference (WC) | ||
|---|---|---|
| WC is a direct measurement of the circumference of the waist at the level of the navel. It is a simple and reliable measure of abdominal obesity, which is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and other health problems. WC is used in conjunction with other anthropometric indices to assess overall health and disease risk. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Skinfold Thickness | ||
|---|---|---|
| Skinfold thickness measurements involve pinching a fold of skin and subcutaneous fat at specific sites on the body using calipers. These measurements are used to estimate overall body fatness and distribution. Skinfold thickness measurements are commonly used in research, sports science, and body composition assessments. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Waist-to-Height Ratio (WHtR) | ||
|---|---|---|
| WHtR is calculated by dividing waist circumference by height. It provides a simple and effective measure of central obesity and is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases. WHtR is a useful tool for identifying individuals at risk of metabolic disorders and cardiovascular diseases. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Body Adiposity Index (BAI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| BAI is a recently developed index that estimates body fat percentage based on hip circumference and height. It is a non-invasive alternative to other methods of body fat assessment. BAI is still being evaluated for its accuracy and reliability compared to other established indices. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Limitations of Anthropometric Indices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric indices have limitations, such as not accounting for muscle mass and body composition variations. They may not accurately reflect health risks in certain populations, such as athletes or older adults. Anthropometric indices should be used in conjunction with other clinical assessments for a comprehensive evaluation. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric indices play a crucial role in assessing body composition and health status. They provide valuable information for research, clinical practice, and public health interventions. Understanding the concept of anthropometric indices helps in identifying individuals at risk of various health conditions. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| World Health Organization (WHO). (2020). Wais... Bray, G. A., & Gray, D. S. (1988). Obesity: A... Flegal, K. M., Kit, B. K., Orpana, H., & Grau... |  | |
| 10 | ||