Concept Of AI And History Presentation
| Introduction to AI | ||
|---|---|---|
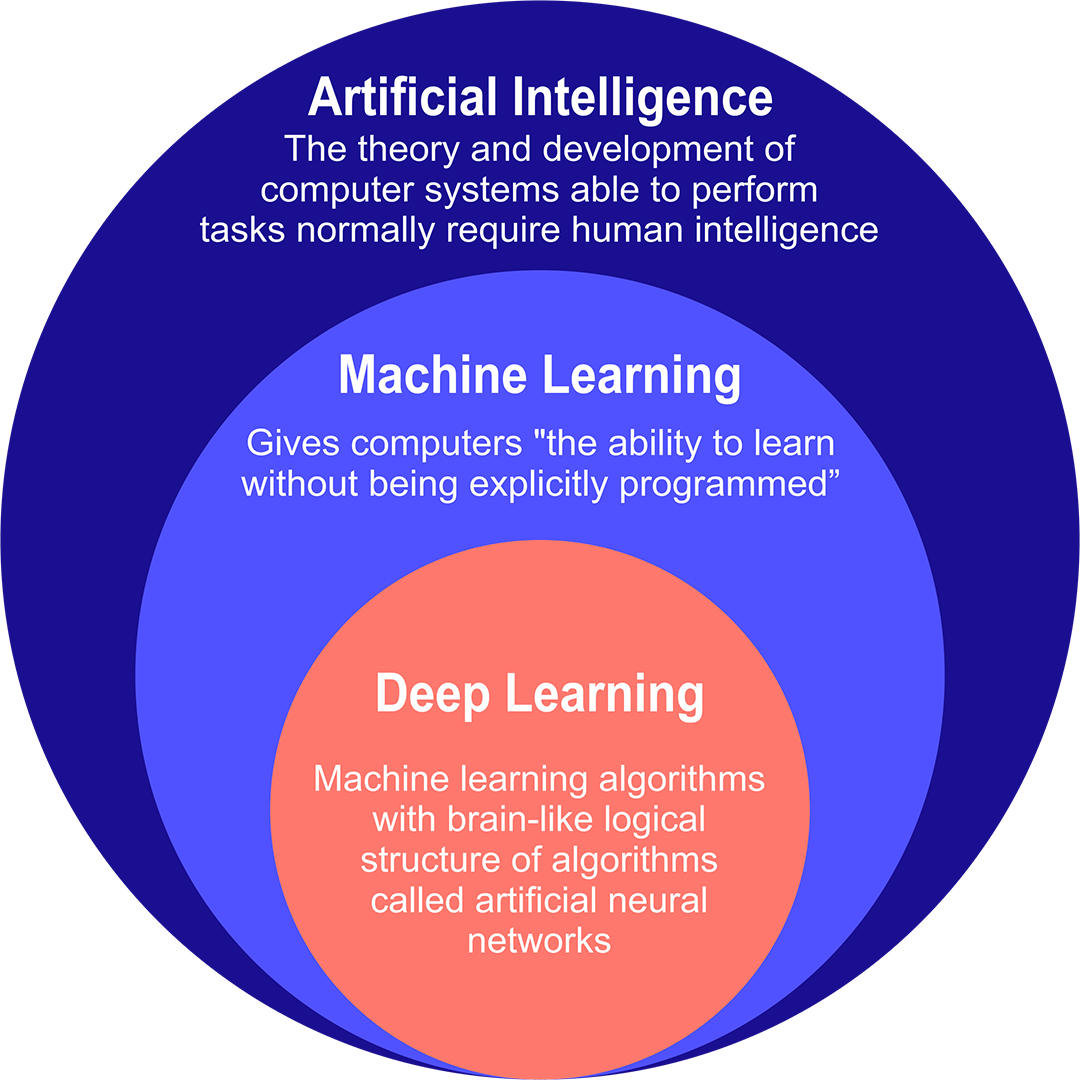
| AI stands for Artificial Intelligence. It is the concept of machines or computer systems that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. AI aims to simulate human intelligence, including abilities such as problem-solving, learning, reasoning, and decision-making. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Early Beginnings of AI | ||
|---|---|---|
| The idea of AI dates back to ancient times, with myths and legends featuring artificial beings. The development of modern AI began in the 1950s. Early AI researchers sought to create machines that could imitate human thinking and behavior. | ||
| 2 | ||
| The Dartmouth Conference | ||
|---|---|---|
| In 1956, the Dartmouth Conference marked the birth of AI as a field of study. A group of leading scientists and researchers gathered to explore the potential of AI. The conference defined AI as the "simulation of human intelligence by machines." | ||
| 3 | ||
| The Early AI Approaches | ||
|---|---|---|
| Symbolic AI focused on representing knowledge using symbols and logical rules. Early AI programs used rule-based systems and expert systems to solve specific problems. These approaches aimed to mimic human reasoning and problem-solving processes. | ||
| 4 | ||
| The AI Winter | ||
|---|---|---|
| During the 1970s and 1980s, AI faced a period of reduced interest and funding, known as the "AI Winter." Expectations for AI had been set too high, leading to disappointment when progress was slower than anticipated. Limited computational power and lack of available data hindered AI research during this period. | ||
| 5 | ||
| The Rise of Machine Learning | ||
|---|---|---|
| Machine learning emerged as a new approach to AI in the 1980s. Instead of explicitly programming rules, machine learning algorithms could learn patterns and make predictions from data. This led to advancements in areas such as speech recognition, computer vision, and natural language processing. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Neural Networks and Deep Learning | ||
|---|---|---|
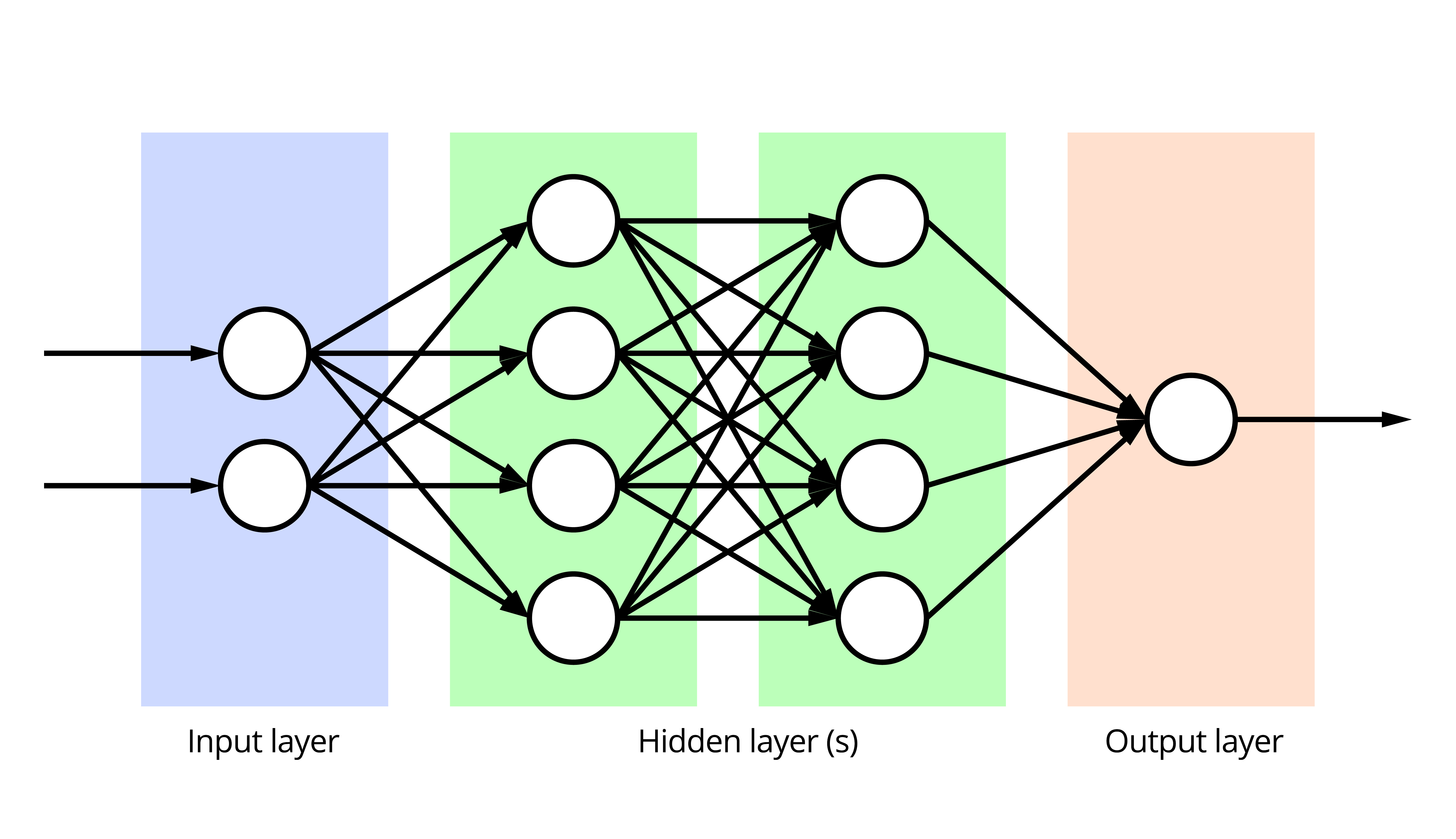
| Neural networks, inspired by the structure of the human brain, became popular in the 1990s. Deep learning, a subset of neural networks, gained attention in the 2010s for its ability to learn complex patterns from large datasets. Deep learning has revolutionized areas such as image and speech recognition, and natural language understanding. | ||
| 7 | ||
| AI in the Modern Era | ||
|---|---|---|
| AI is now integrated into various aspects of our lives, from virtual assistants to recommendation systems. Applications of AI include autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, and fraud detection. AI has the potential to transform industries and improve efficiency and decision-making across multiple domains. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Ethical Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| As AI advances, ethical considerations become increasingly important. Issues such as privacy, bias in algorithms, and job displacement need to be addressed. Responsible AI development and deployment should prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Future of AI | ||
|---|---|---|
| The future of AI holds exciting possibilities, including advancements in robotics, natural language understanding, and personalized AI assistants. AI will continue to augment human capabilities, enabling us to solve complex problems and make better-informed decisions. Continued research, collaboration, and ethical frameworks will shape the path of AI in the years to come. | ||
| 10 | ||