Compensation Theorem Presentation
| Compensation Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Compensation Theorem is a fundamental concept in engineering and physics. It allows us to simplify complex electrical circuits by replacing them with simpler circuits that have equivalent behavior. This theorem is based on the principle of superposition, where the response of a linear system can be obtained by combining the responses to individual inputs. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Statement of the Compensation Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
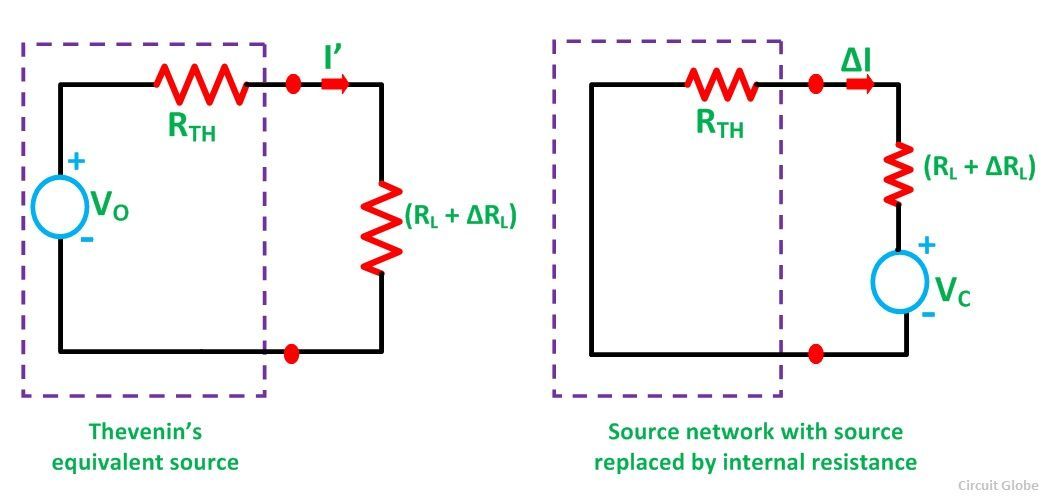
| The Compensation Theorem states that any two linear electric circuits are equivalent if they have the same open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current at a given pair of terminals. This means that we can replace a complex circuit with a simpler one, as long as the voltage and current at the terminals are the same. The theorem is a powerful tool for circuit analysis and design, simplifying calculations and reducing complexity. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Application of the Compensation Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Compensation Theorem is commonly used in electrical network analysis, especially in the design and analysis of amplifiers, filters, and control systems. It allows engineers to break down complex circuits into smaller, more manageable parts, making it easier to analyze and design. By applying the theorem, we can determine the equivalent circuit parameters and transfer functions of a complex system. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Steps to Apply the Compensation Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
| Identify the complex circuit that needs to be simplified. Select the terminals at which the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current will be measured. Calculate the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current at the selected terminals. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Limitations of the Compensation Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Compensation Theorem is only applicable to linear circuits, where the components follow linear relationships between voltage and current. It assumes that the circuit is at steady-state, meaning that all transient effects have settled. The theorem may not provide accurate results for circuits with nonlinear or time-varying elements. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Advantages of the Compensation Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Compensation Theorem allows engineers to simplify complex circuits and focus on specific parts of the system, making analysis and design more manageable. It reduces the computational burden, as we can replace complex circuit elements with simpler ones without sacrificing accuracy. The theorem provides a systematic approach to circuit analysis and design, saving time and effort. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Examples of Compensation Theorem Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Designing an audio amplifier: By using the Compensation Theorem, we can simplify the amplifier circuit and analyze its behavior more easily, ensuring optimal performance. Analyzing a control system: The Compensation Theorem helps us break down a complex control system into smaller subsystems, facilitating stability analysis and controller design. Designing a filter: By applying the Compensation Theorem, we can simplify the filter circuit and determine its transfer function, allowing us to select appropriate component values for desired filtering characteristics. |  | |
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Compensation Theorem is a powerful tool in circuit analysis and design, allowing engineers to simplify complex circuits and focus on specific parts of the system. It provides a systematic approach to analyzing and designing linear circuits, reducing complexity and computational burden. By understanding and applying the Compensation Theorem, engineers can optimize circuit performance, save time, and improve efficiency. | ||
| 8 | ||