Comparative Analysis Of Green Building And General Buildings Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building and General Building Comparison Importance of Sustainable Construction Objectives of the Comparative Analysis | ||
| 1 | ||
| Definition and Benefits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Definition of Green Building
- Emphasizes on sustainability, energy efficiency, and environmental responsibility. Definition of General Building - Traditional construction methods with no specific focus on sustainability. Benefits of Green Building - Reduced environmental impact, energy and water efficiency, improved indoor air quality. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Energy Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Utilizes renewable energy sources and energy-efficient systems.
- Solar panels, geothermal energy, LED lighting, and smart HVAC systems. General Building: Traditional energy systems with higher energy consumption. - Standard electrical grid, incandescent lighting, and conventional HVAC systems. Energy consumption and utility cost comparison between the two approaches. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Material Selection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Uses eco-friendly and sustainable materials.
- Recycled steel, bamboo flooring, low VOC paint, and reclaimed wood. General Building: Utilizes conventional materials with no specific sustainability considerations. - Traditional steel, concrete, and wood products. Comparison of environmental impact, durability, and maintenance requirements. | ||
| 4 | ||
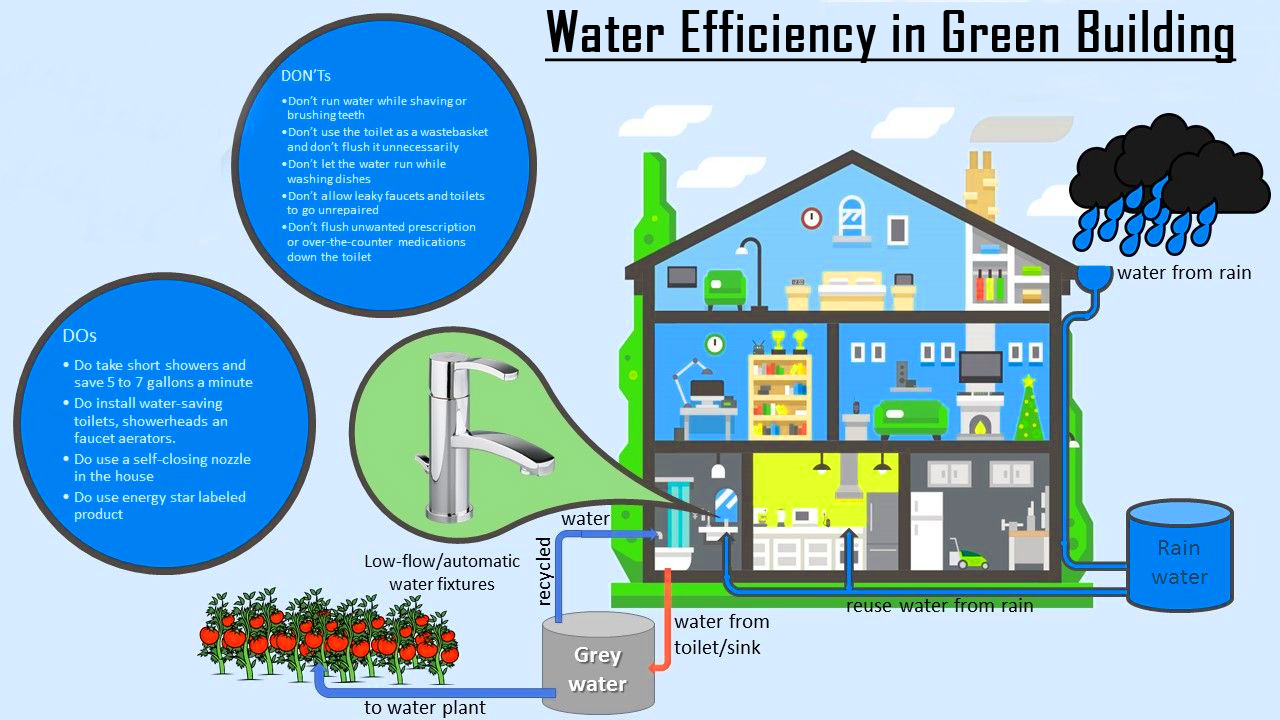
| Water Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Implements water-saving technologies and practices.
- Low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting, and greywater recycling. General Building: Uses standard water systems without specific efficiency measures. - Traditional fixtures and conventional wastewater disposal. Water consumption and conservation comparison between the two approaches. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Indoor Environmental Quality | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Focuses on creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.
- Adequate natural lighting, proper ventilation, and use of non-toxic materials. General Building: May not prioritize indoor air quality or occupant comfort. - Limited natural lighting, inefficient ventilation, and use of potentially harmful materials. Comparison of air quality, thermal comfort, and occupant satisfaction. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Cost Considerations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Initial costs may be higher due to specialized materials and technologies.
- Long-term operational savings through reduced energy and water consumption. General Building: Initial costs may be lower but higher operational expenses. - Higher energy bills and maintenance costs over time. Comparison of upfront costs, return on investment, and long-term financial benefits. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Environmental Impact | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Minimizes carbon footprint and environmental degradation.
- Reduced energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation. General Building: Higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. - Higher energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation. Comparison of environmental impact and sustainability performance. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Regulatory and Certification Programs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building: Compliance with green building codes and certifications.
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), and other regional programs. General Building: Adherence to standard building codes and regulations. - Compliance with local building codes and safety standards. Comparison of regulatory requirements and certification processes. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Summary of key findings and differences between green building and general building. Importance of considering sustainability in construction practices. Encouragement for future adoption of green building principles for a more sustainable future. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Green Building Council. (n.d.). What is a gre... U.S. Department of Energy. (n.d.). Green Buil... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 11 | ||