Cloud Computing Presentation
| Introduction to Cloud Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet. It allows users to access and use a range of resources, applications, and data without the need for local hardware or infrastructure. Key benefits include scalability, cost savings, and increased flexibility. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Cloud Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Public cloud: Services are provided by third-party providers and accessible to anyone over the internet. Private cloud: Services are dedicated to a specific organization and not shared with others. Hybrid cloud: Combination of public and private clouds, allowing organizations to take advantage of both. | ||
| 2 | ||
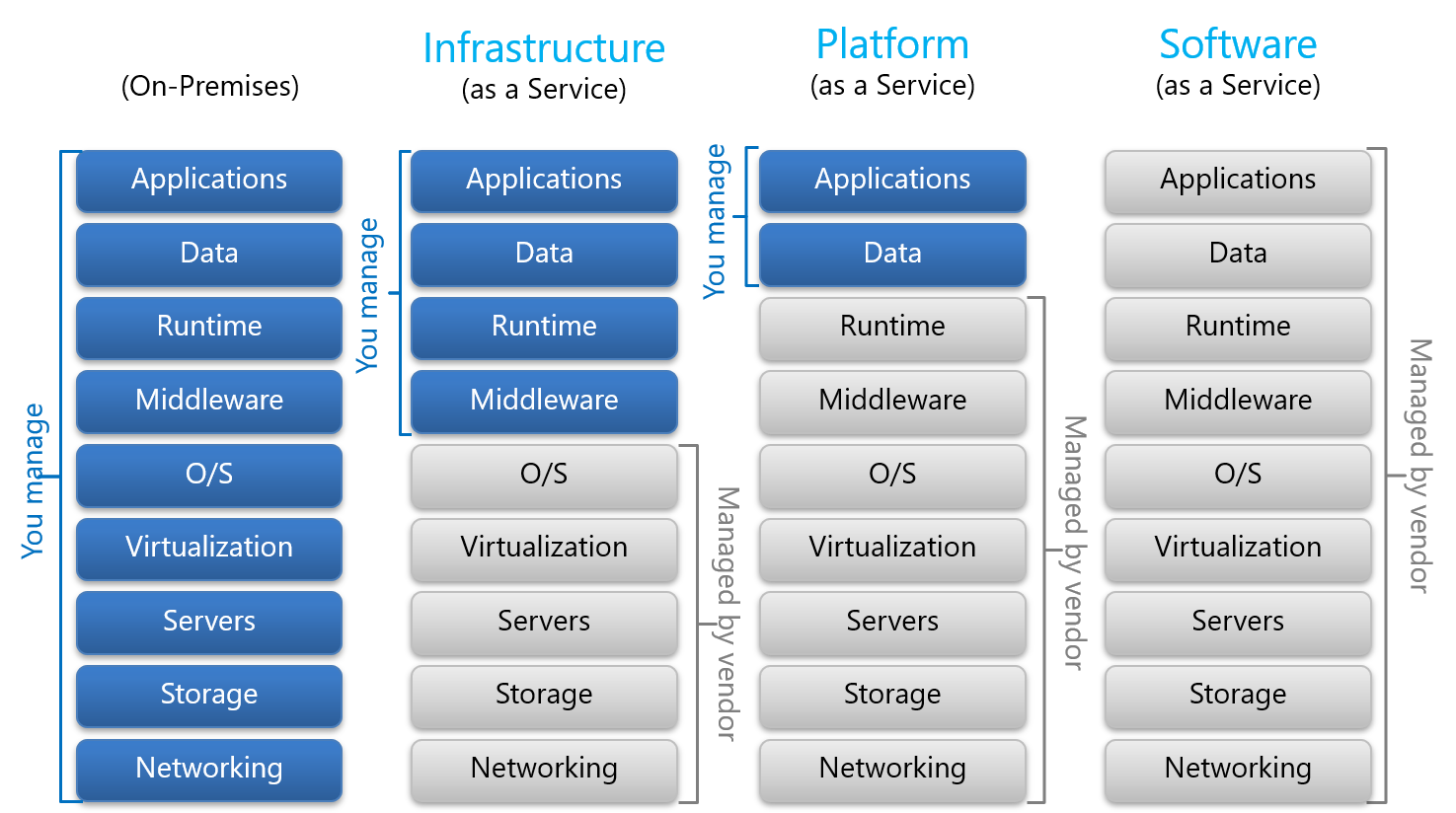
| Cloud Computing Models | ||
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offers virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications without worrying about infrastructure. Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Advantages of Cloud Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cost savings: Lower upfront investment, no need for hardware maintenance, and pay-as-you-go pricing models. Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance. Accessibility: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Security in Cloud Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Data encryption: Protects data in transit and at rest, ensuring confidentiality. Access controls: Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. Regular audits and compliance: Cloud providers adhere to industry standards and undergo regular audits to ensure data integrity. | ||
| 5 | ||
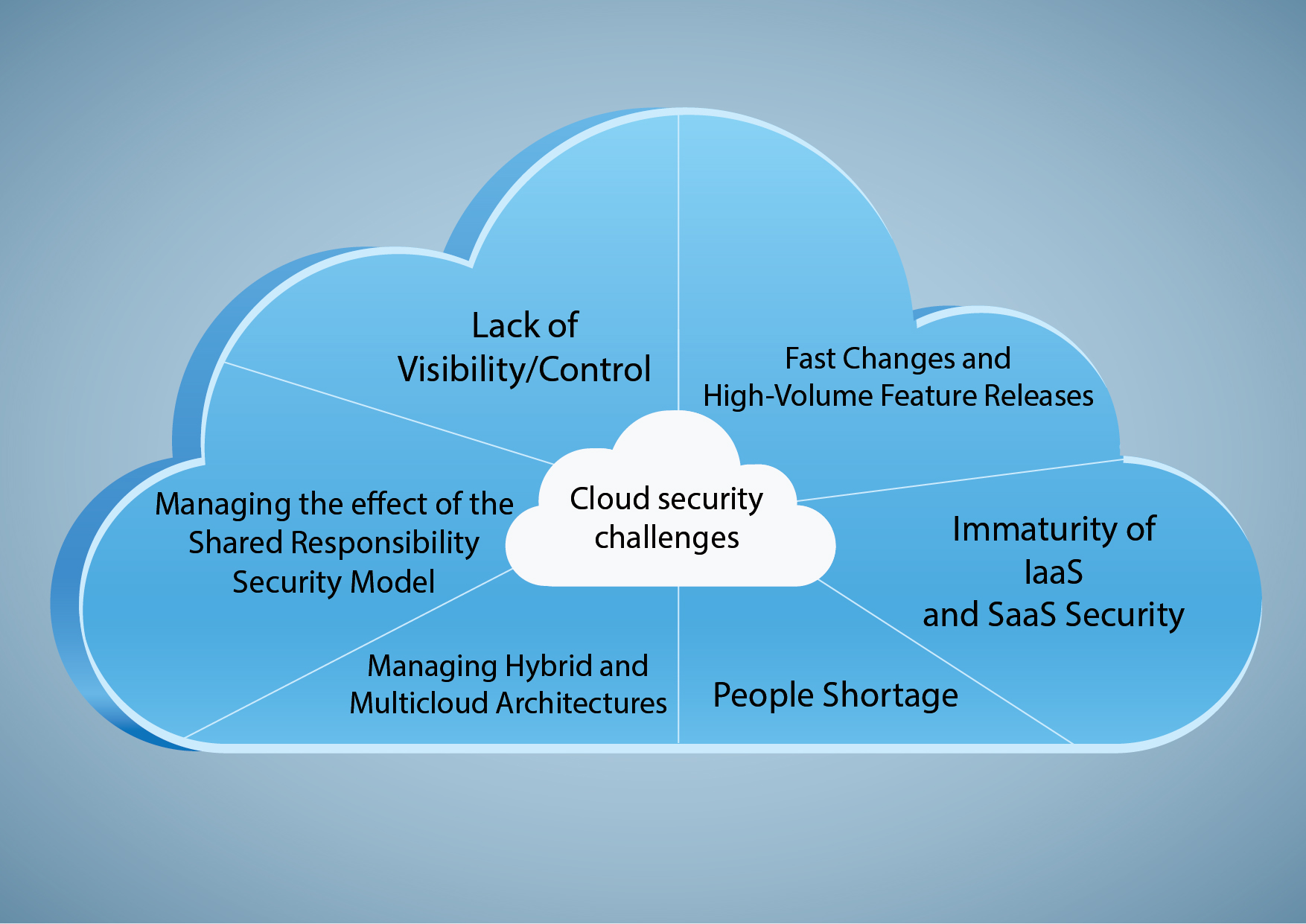
| Challenges of Cloud Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Data privacy: Concerns about who has access to sensitive data and where it is stored. Reliability and downtime: Reliance on internet connectivity and potential disruptions in service availability. Vendor lock-in: Potential difficulties in switching cloud providers due to dependencies on proprietary technologies. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Cloud Computing Use Cases | ||
|---|---|---|
| Data storage and backup: Cloud storage solutions offer scalable and reliable data storage and backup options. Software development and testing: Cloud platforms provide a flexible environment for development and testing purposes. Big data analytics: Cloud computing enables the processing and analysis of large datasets without the need for extensive local infrastructure. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Cloud Computing Adoption | ||
|---|---|---|
| Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) benefit from cost savings and access to enterprise-grade technologies. Large enterprises leverage cloud computing for scalability, agility, and global reach. Public sector organizations adopt cloud computing to optimize operations, enhance citizen services, and reduce costs. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Cloud Computing Providers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a wide range of cloud services and is a market leader. Microsoft Azure: Provides a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including infrastructure, platform, and software. Google Cloud Platform: Offers scalable and flexible cloud services with a focus on data analytics and machine learning. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations access and use computing resources. It offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. As technology advances and security measures improve, cloud computing will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of IT. | ||
| 10 | ||