Clamping Circuit Theorem Presentation
| Introduction to Clamping Circuit Theorem | ||
|---|---|---|
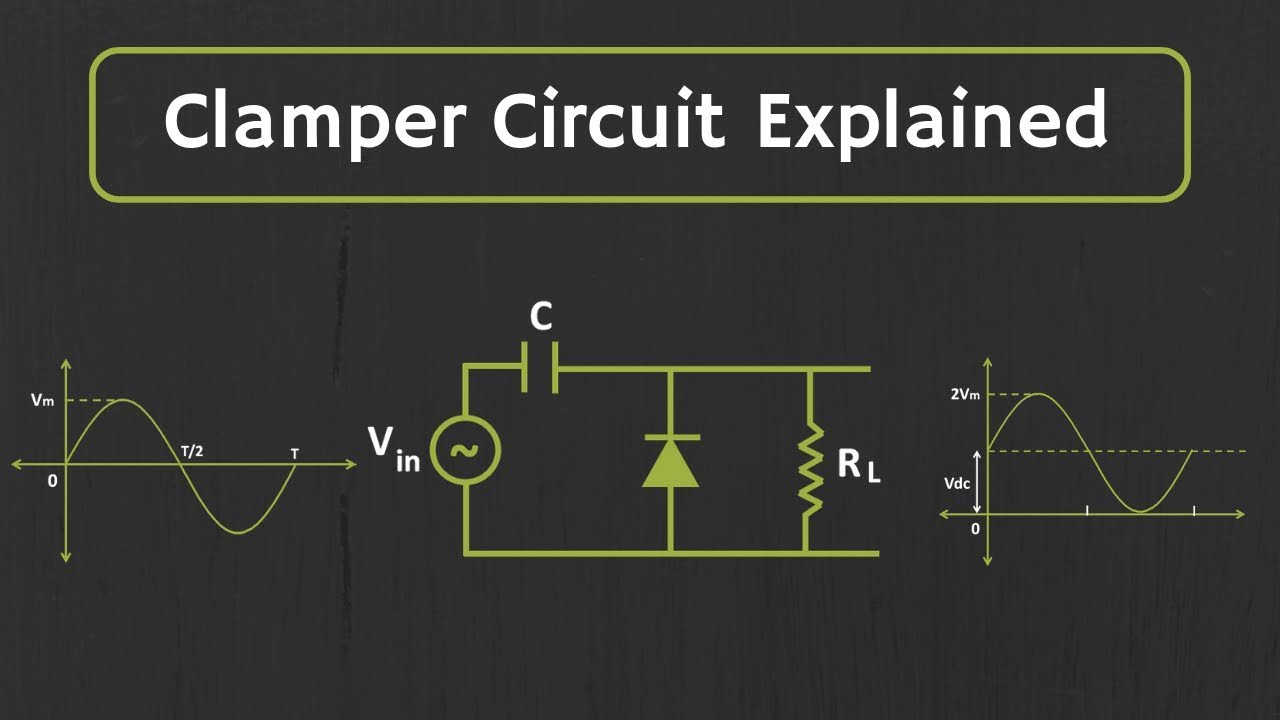
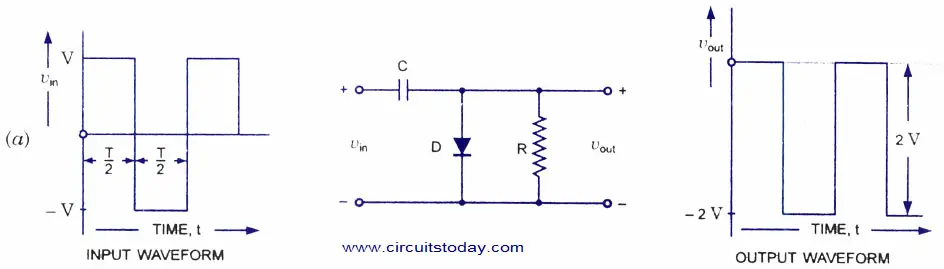
| The Clamping Circuit Theorem is a fundamental concept in electronics. It allows us to shift the DC level of a waveform without altering its shape. This theorem is widely used in various applications, including signal processing and power supply circuits. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Understanding Clamping Circuit Operation | ||
|---|---|---|
| A clamping circuit consists of a diode and a capacitor connected in parallel. The diode ensures that the voltage across the capacitor never goes below a certain level. By controlling the diode conduction, we can shift the waveform's DC level to a desired value. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Clamping Circuits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Positive Clamping Circuit: Shifts the waveform's DC level to a higher value. Negative Clamping Circuit: Shifts the waveform's DC level to a lower value. Biased Clamping Circuit: Allows us to set a specific DC level for the waveform. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Applications of Clamping Circuits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Video Signal Processing: Clamping circuits are used to set the black level in video signals. DC Restoration: Clamping circuits help restore the DC component of AC-coupled signals. Voltage Level Shifting: These circuits enable shifting the voltage level of a signal to match the input requirements of subsequent stages. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Design Considerations for Clamping Circuits | ||
|---|---|---|
| Choosing the correct diode and capacitor values is crucial for proper clamping operation. Diode characteristics, such as reverse recovery time, should be considered for accurate waveform clamping. The capacitor's value affects the time constant and the clamping circuit's response to the input waveform. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Clamping Circuit Theorem is a powerful tool for shifting the DC level of a waveform. It finds applications in various fields, including video signal processing and voltage level shifting. Careful consideration of diode and capacitor values is essential for successful clamping circuit design. | ||
| 6 | ||