Child Labour Presentation
| Introduction to Child Labour | ||
|---|---|---|
| Child labour is the employment of children in work that is harmful to their physical and mental development. It is a global issue that affects millions of children worldwide. Child labour deprives children of their childhood and denies them the opportunity to fulfill their potential. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Causes of Child Labour | ||
|---|---|---|
| Poverty: Families living in poverty often rely on child labour to contribute to household income. Lack of access to education: Limited access to quality education pushes children into work at an early age. Cultural norms and traditions: Some societies have long-standing traditions that normalize child labour. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of Child Labour | ||
|---|---|---|
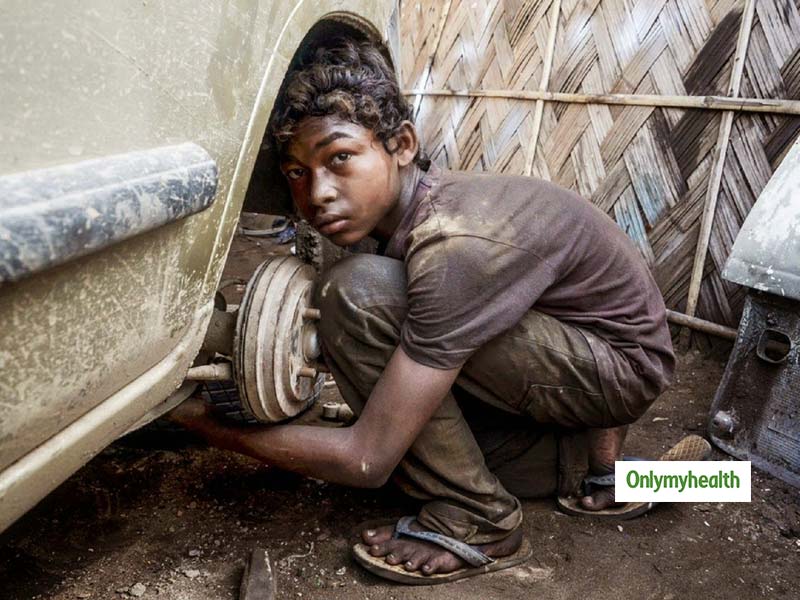
| Agricultural labour: Children are forced to work on farms, often exposed to hazardous conditions. Domestic work: Children are employed as domestic helpers, subjected to long hours and physical abuse. Manufacturing industries: Children are exploited in factories, working in dangerous conditions for meager wages. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Impact on Children | ||
|---|---|---|
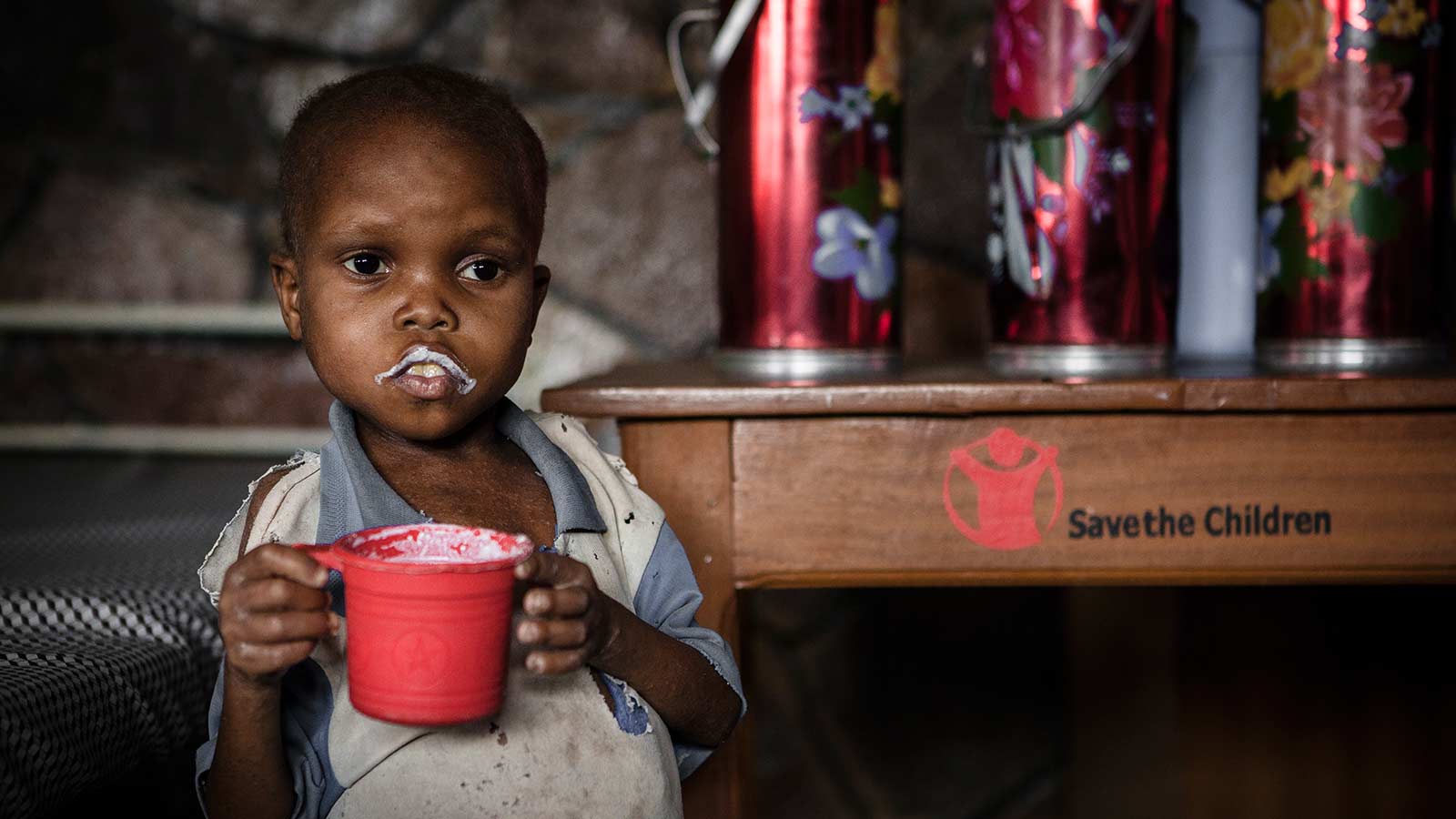
| Physical and mental health: Child labour exposes children to hazardous substances and long working hours, affecting their physical and mental well-being. Lack of education: Child labour prevents children from attending school, hindering their access to knowledge and opportunities for a better future. Vulnerability to exploitation: Working in exploitative conditions leaves children susceptible to abuse, trafficking, and other forms of exploitation. | ||
| 4 | ||
| International Laws and Conventions | ||
|---|---|---|
| International Labour Organization (ILO): Sets standards and promotes the elimination of child labour through various conventions and initiatives. United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC): Recognizes the right of every child to be protected from economic exploitation and harmful work. Sustainable Development Goal 8.7: Aims to end child labour in all its forms by 2025. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Efforts and Progress | ||
|---|---|---|
| Awareness campaigns: Governments, organizations, and individuals raise awareness about child labour to mobilize action. Legislation and enforcement: Many countries have enacted laws and regulations to prohibit child labour and ensure its enforcement. Social programs: Education initiatives and poverty alleviation programs help address the root causes of child labour. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges and Roadblocks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Poverty and inequality: Economic disparities and lack of resources make it difficult to eradicate child labour entirely. Weak enforcement: Inadequate monitoring and enforcement mechanisms allow child labour to persist in some regions. Lack of awareness: Many people are unaware of the extent of child labour and its consequences, hindering collective action. | ||
| 7 | ||
| What Can Be Done? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Strengthen legal frameworks: Governments should enact and enforce laws that prohibit child labour, ensuring penalties for violators. Improve access to education: Investing in quality education and removing barriers can help prevent children from entering the workforce. Promote responsible business practices: Companies should adopt ethical supply chain practices and eliminate child labour from their operations. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Child labour is a violation of children's rights and a barrier to their well-being and development. Collective efforts from governments, organizations, and individuals are crucial in eliminating child labour. Every child deserves a childhood free from exploitation and the opportunity to thrive and reach their full potential. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| International Labour Organization (ILO)... United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)... Global March Against Child Labour... |  | |
| 10 | ||