Chemical Process Safety Presentation
| Introduction to Chemical Process Safety | ||
|---|---|---|
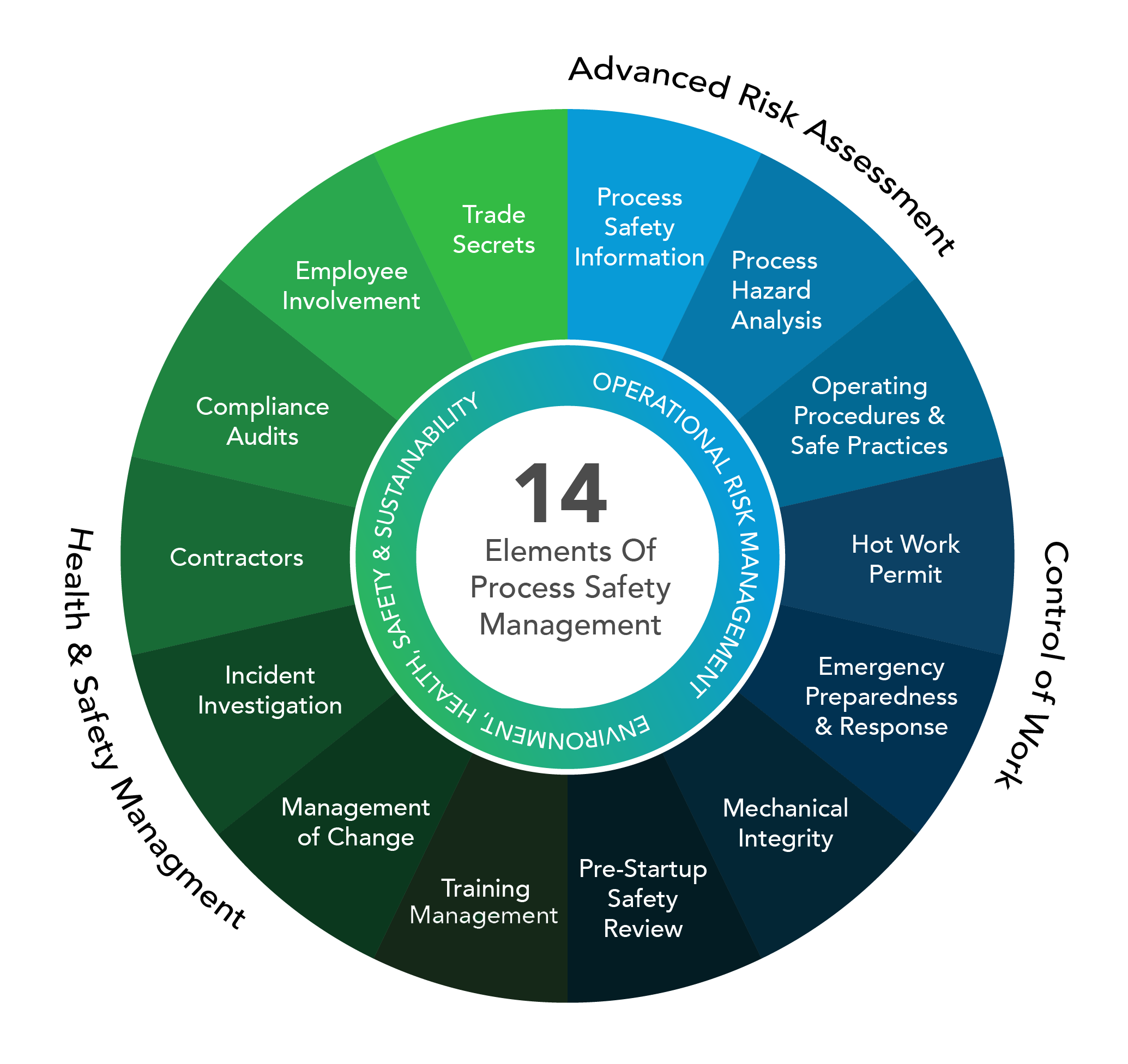
| Chemical process safety involves the management of hazards and risks associated with chemical processes. It aims to prevent accidents, protect personnel, and minimize environmental and property damage. Key aspects of chemical process safety include process design, equipment integrity, and safe operating procedures. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Importance of Process Safety Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Process safety management is crucial to prevent major accidents and protect human lives. It helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements related to process safety. Effective process safety management can enhance the reputation and trustworthiness of an organization. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Hazard Identification and Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|
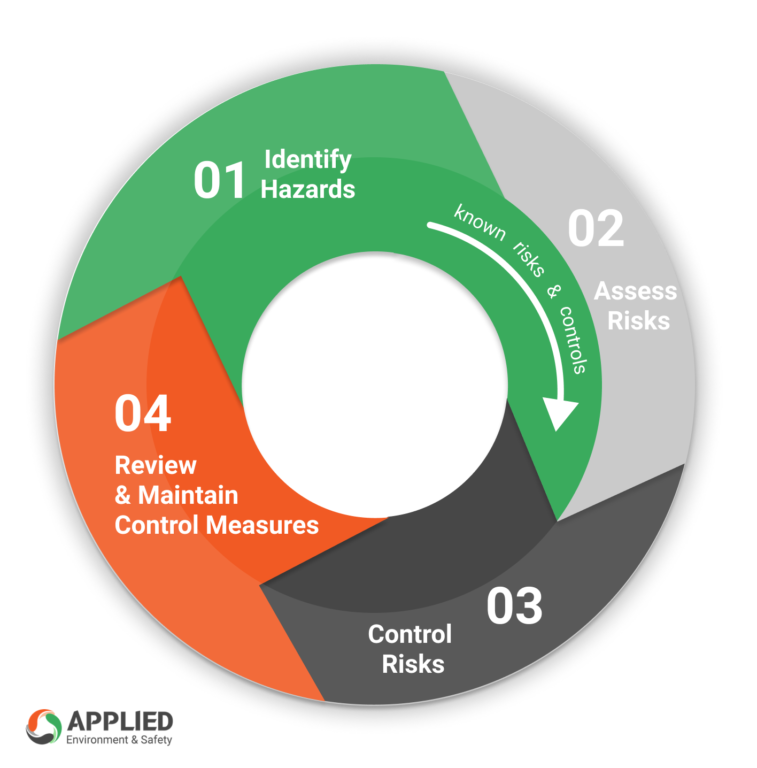
| Identifying and evaluating hazards is essential to ensure process safety. Hazard identification methods include process hazard analysis, hazard and operability studies, and safety audits. By understanding the hazards, organizations can implement appropriate control measures to mitigate risks. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Risk Assessment and Management | ||
|---|---|---|
| Risk assessment involves quantifying the likelihood and consequences of potential accidents. Risk management strategies include risk reduction, risk transfer, risk avoidance, and risk acceptance. Organizations should develop risk management plans to prioritize and address identified risks. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Process Design and Engineering | ||
|---|---|---|
| Proper process design and engineering can prevent accidents and reduce risks. Design considerations include material selection, equipment specifications, and layout optimization. Engineering controls, such as relief systems and interlocks, are implemented to manage process hazards. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Safe Operating Procedures | ||
|---|---|---|
| Safe operating procedures provide guidelines for personnel to safely handle hazardous materials and operate equipment. Training and competency development are crucial for ensuring that employees adhere to these procedures. Regular audits and inspections help verify compliance with safe operating procedures. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Emergency Preparedness and Response | ||
|---|---|---|
| Emergency preparedness involves planning for potential accidents and developing response procedures. Emergency response plans should include evacuation procedures, communication protocols, and mitigation measures. Regular drills and exercises help evaluate the effectiveness of emergency response plans. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Maintenance and Inspection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regular maintenance and inspection of equipment ensure their integrity and reliability. Preventive maintenance programs help identify and address potential failures before they cause accidents. Inspection protocols, such as non-destructive testing, are used to detect hidden defects in equipment. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Incident Investigation and Lessons Learned | ||
|---|---|---|
| Incident investigation is essential to understand the root causes of accidents and prevent their recurrence. Lessons learned from incidents help improve safety procedures, equipment design, and operational practices. Organizations should establish a culture of reporting incidents and near misses to facilitate learning and continuous improvement. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Continuous Improvement and Safety Culture | ||
|---|---|---|
| Continuous improvement is vital for enhancing process safety performance. Organizations should encourage employee involvement and engagement in safety initiatives. A strong safety culture promotes open communication, accountability, and a proactive approach to managing process safety. (Note: These are just suggested sub-bullets. You can modify them or add more information based on your specific requirements and knowledge on the topic.) | ||
| 10 | ||