Carboxylic Acids Presentation
| Introduction to Carboxylic Acids | ||
|---|---|---|
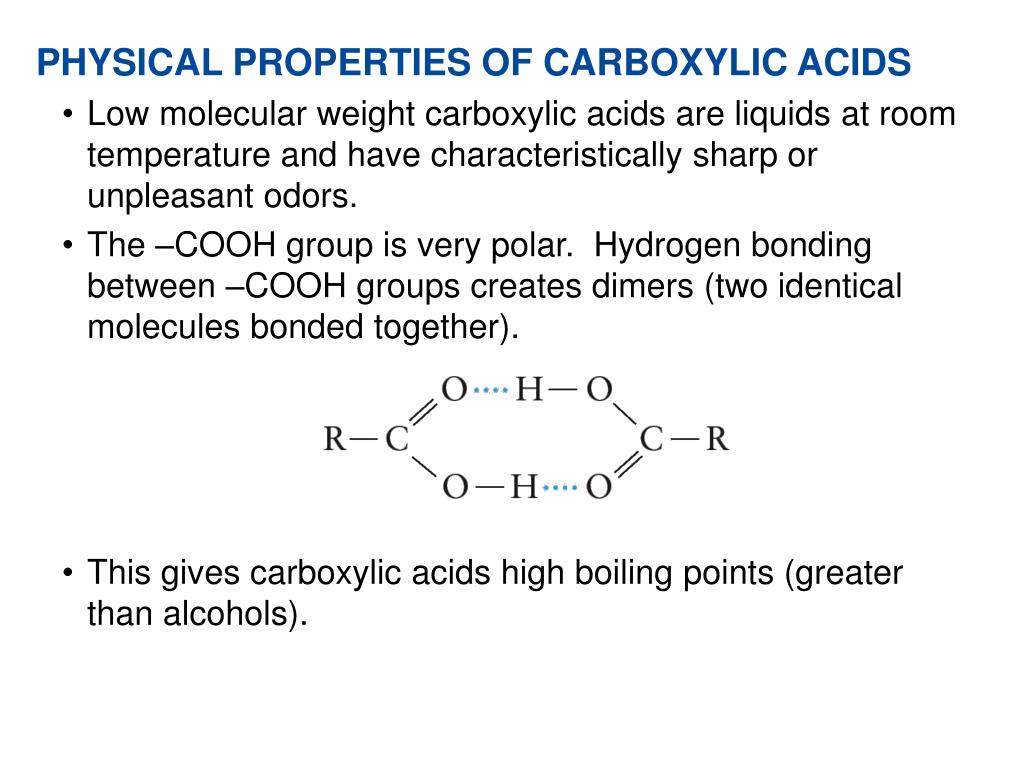
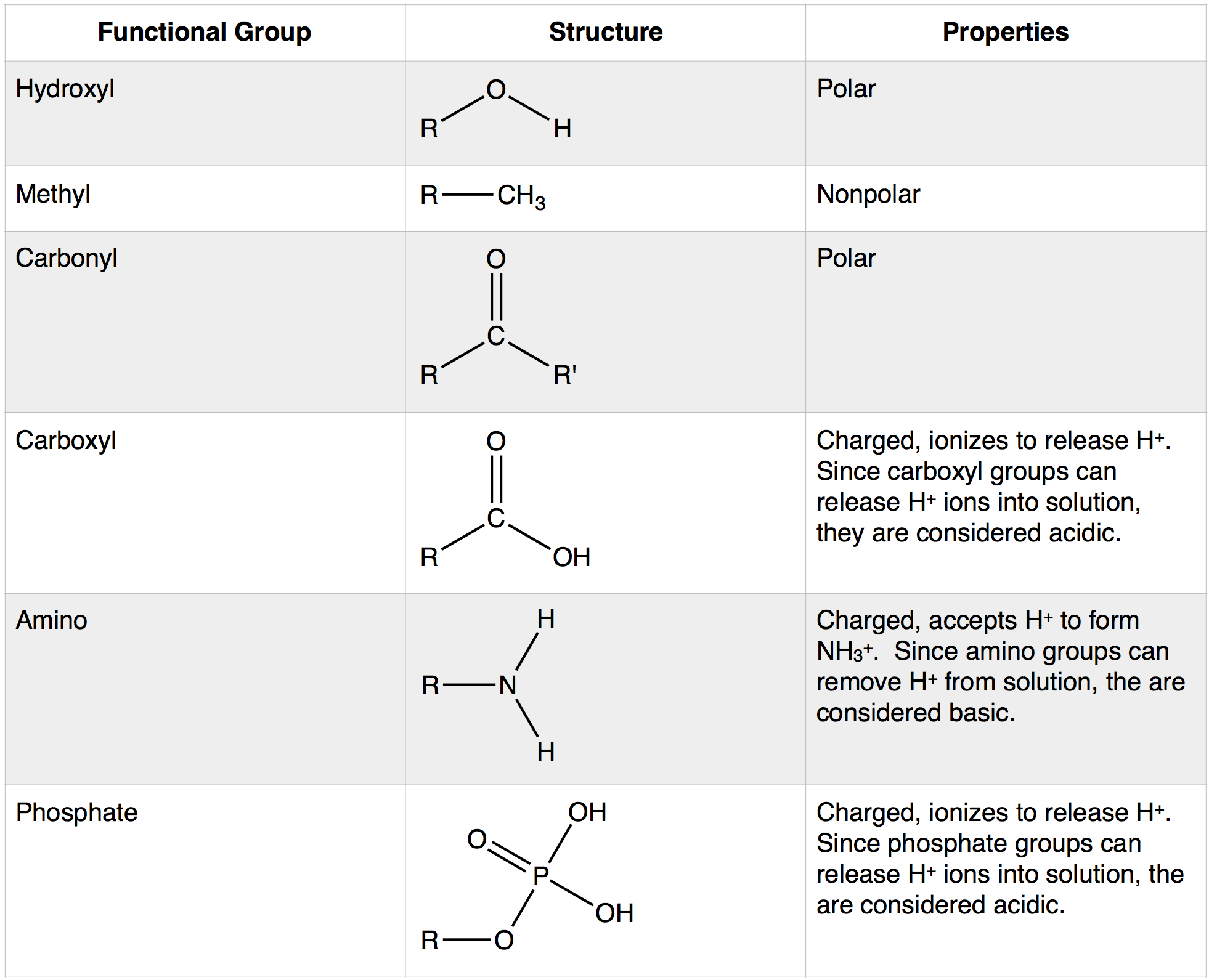
| Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) as their functional group. They are derived from the oxidation of aldehydes or primary alcohols. Carboxylic acids are commonly found in nature, such as in fruits, vinegar, and fatty acids. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Structure and Properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| The carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH) bonded to the same carbon atom. Carboxylic acids are polar due to the presence of the electronegative oxygen atom in the carboxyl group. They have higher boiling points compared to alcohols and ethers due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Nomenclature | ||
|---|---|---|
| The naming of carboxylic acids follows the IUPAC system, where the suffix "-oic acid" is added to the parent hydrocarbon name. Common carboxylic acids include acetic acid (CH3COOH) and formic acid (HCOOH). The position of the carboxyl group is indicated by a numerical prefix before the parent hydrocarbon name. |  | |
| 3 | ||
| Reactions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids can undergo various reactions, including esterification, acid-base reactions, and oxidation. Esterification involves the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester and water. Acid-base reactions occur when carboxylic acids react with bases to form carboxylate salts and water. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Uses | ||
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids have numerous applications, such as in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and plastics. They are used as preservatives in food and beverages, acting as antimicrobial agents. Some carboxylic acids, like acetic acid, are used in vinegar for culinary and cleaning purposes. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Importance in Biochemistry | ||
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids play a crucial role in biochemistry as they are involved in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids. They participate in the citric acid cycle, a key metabolic pathway for energy production in cells. Some carboxylic acids, such as acetyl-CoA, serve as important precursors for the synthesis of biomolecules. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylic acids are organic compounds with a carboxyl group (-COOH) as their functional group. They have unique structural and chemical properties, including polarity and the ability to form hydrogen bonds. Carboxylic acids find applications in various industries and play vital roles in biochemistry. | ||
| 7 | ||