COPD Presentation
| Introduction to COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
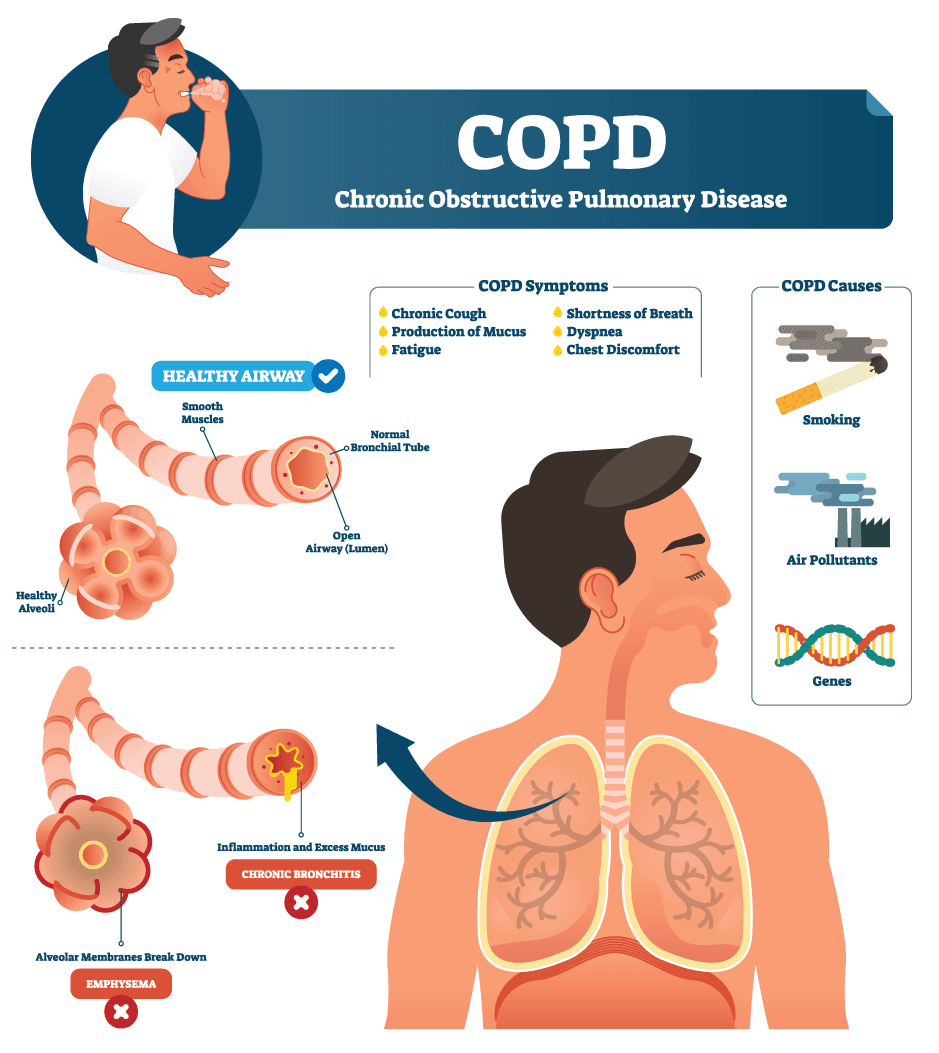
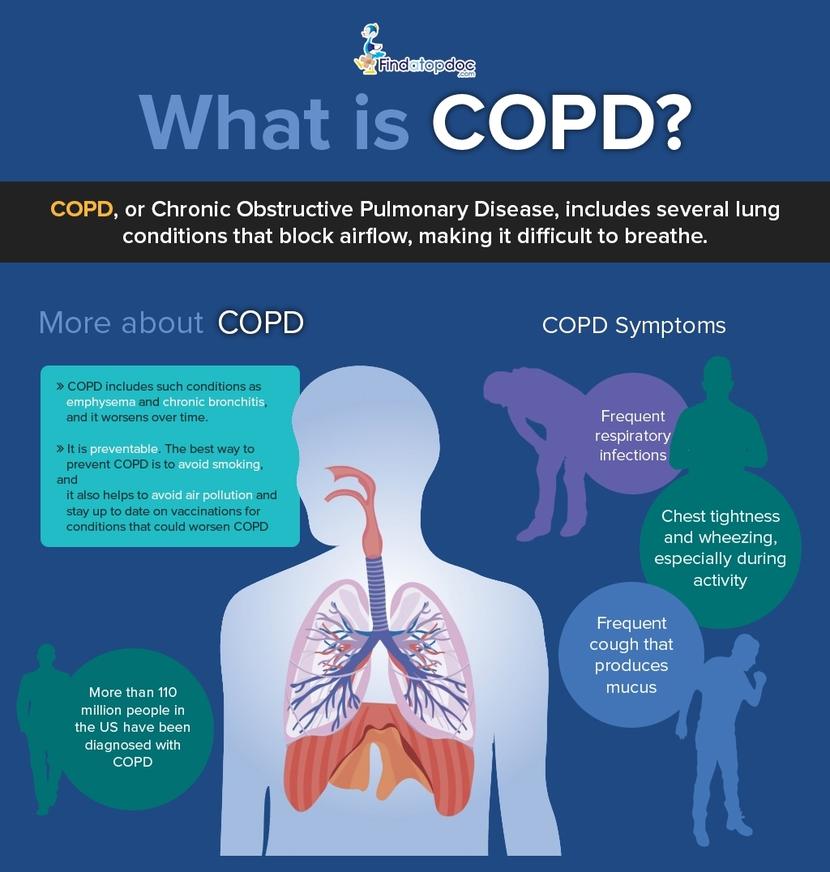
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease. It is characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. COPD is caused by long-term exposure to irritating particles or gases, most commonly from tobacco smoke. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Symptoms of COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Common symptoms of COPD include shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing. People with COPD may experience frequent respiratory infections. They may also have difficulty performing physical activities due to decreased lung function. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Types of COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| The two main types of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis is characterized by a chronic cough and excessive mucus production. Emphysema is marked by the destruction of the air sacs in the lungs, leading to poor airflow. | ||
| 3 | ||
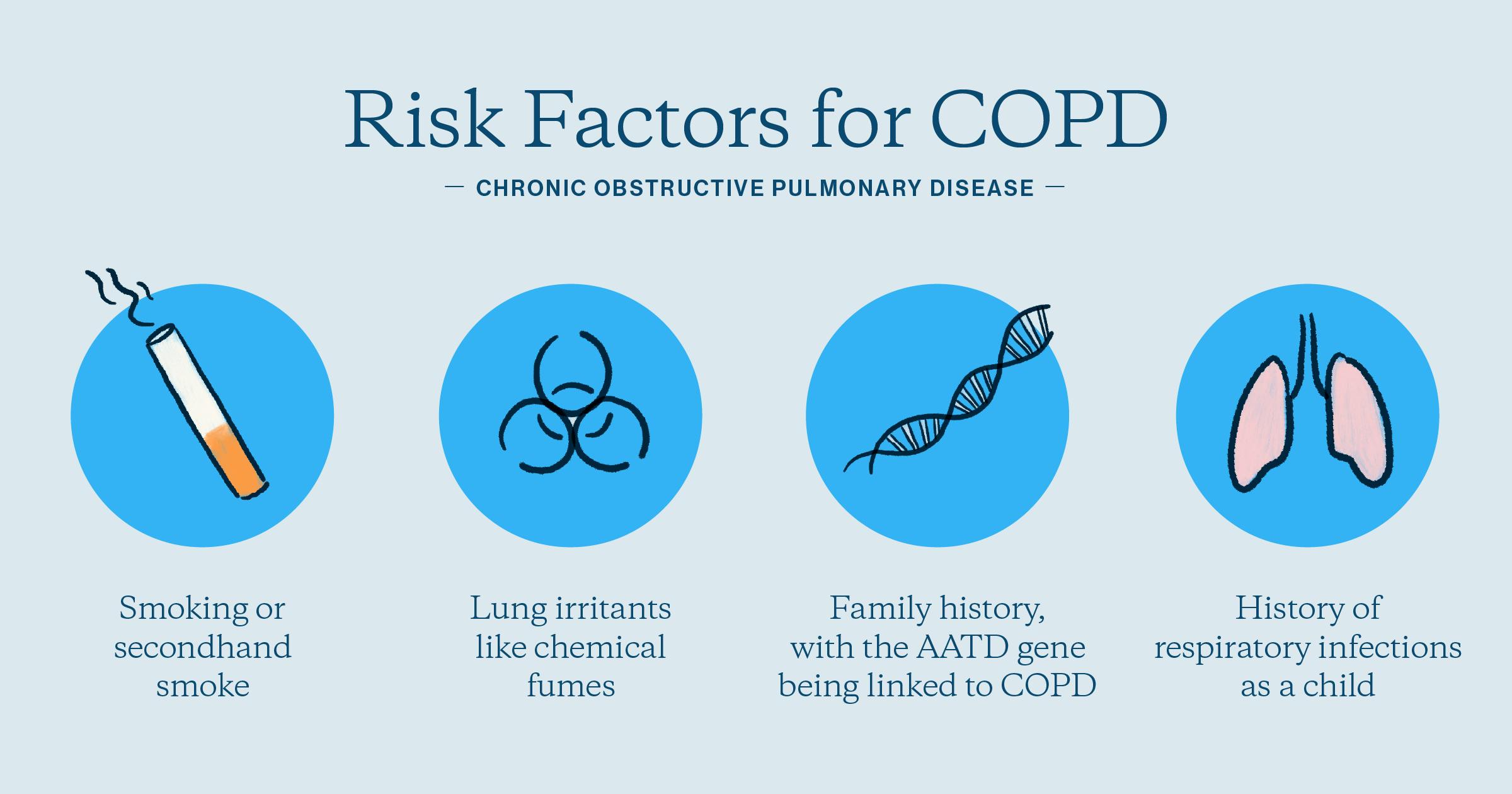
| Risk Factors for COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| The primary risk factor for COPD is smoking, including both active and passive smoking. Long-term exposure to air pollutants, such as dust and chemicals, can also contribute to COPD. Genetic factors, such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, can increase the risk of developing COPD. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Diagnosis of COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis of COPD involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests. Spirometry is the most common lung function test used to diagnose COPD. Chest X-rays and CT scans may be performed to assess the severity and extent of lung damage. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Treatment Options for COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Smoking cessation is the most crucial step in managing COPD and slowing its progression. Medications, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, can help relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs, including exercise and education, can improve lung function and quality of life. | ||
| 6 | ||
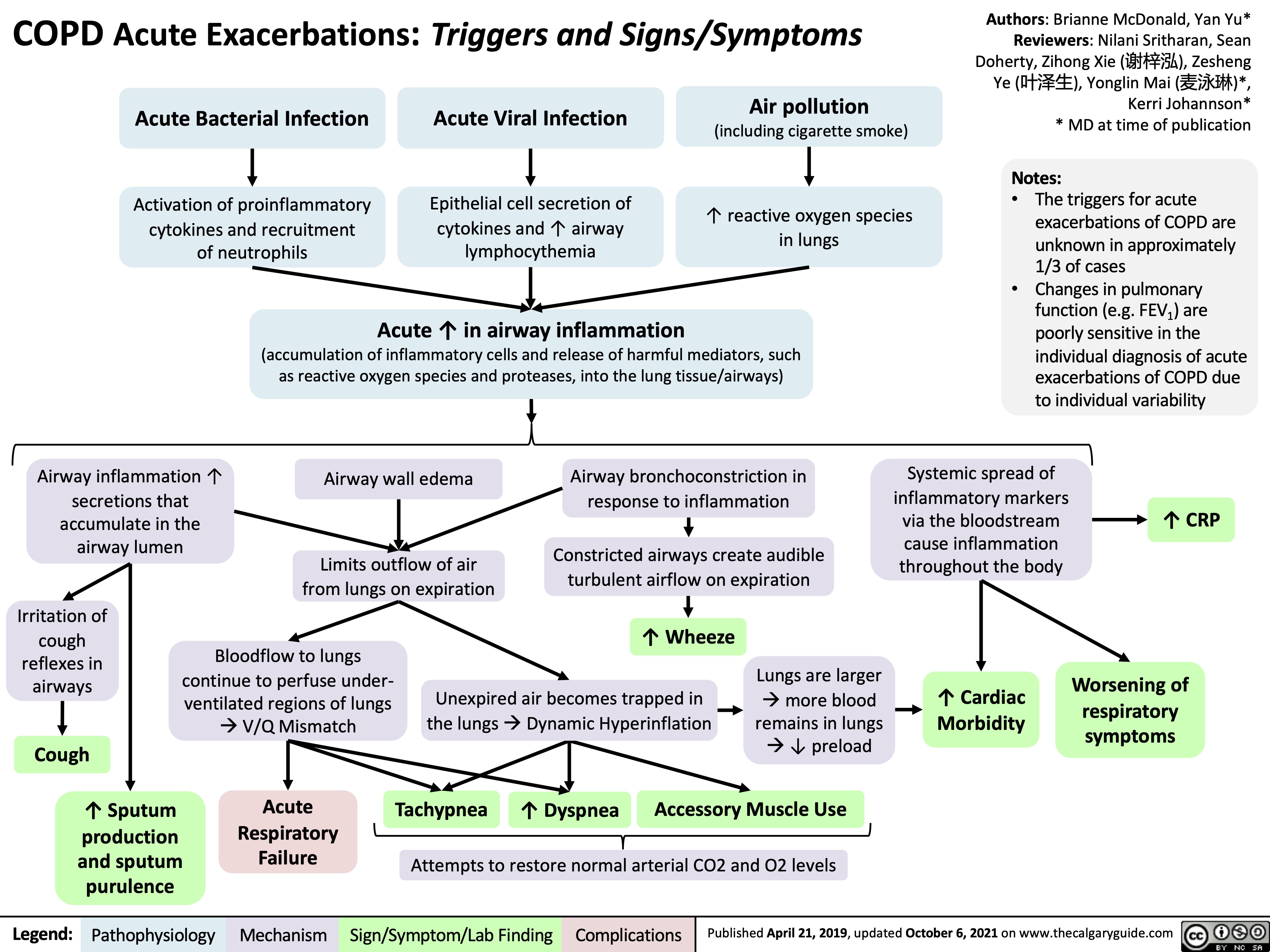
| Management of COPD Exacerbations | ||
|---|---|---|
| COPD exacerbations are acute worsening of symptoms and lung function. Exacerbations are often triggered by respiratory infections or exposure to environmental irritants. Treatment of exacerbations may include antibiotics, bronchodilators, and supplemental oxygen. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Lifestyle Modifications for COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| Avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke and other lung irritants is essential for managing COPD. Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve lung function and overall fitness. Proper nutrition, including a balanced diet and adequate hydration, is important for maintaining optimal health. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Prognosis and Complications of COPD | ||
|---|---|---|
| COPD is a progressive disease, meaning it worsens over time. Complications of COPD can include respiratory infections, heart problems, and depression. The prognosis for COPD varies depending on the severity of the disease and the individual's response to treatment. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| COPD is a chronic lung disease characterized by airflow limitation. It is primarily caused by smoking and long-term exposure to lung irritants. Early diagnosis, smoking cessation, and appropriate management can help slow the progression of COPD and improve quality of life. | ||
| 10 | ||