Bridge Rectifier Presentation
| Introduction to Bridge Rectifier | ||
|---|---|---|
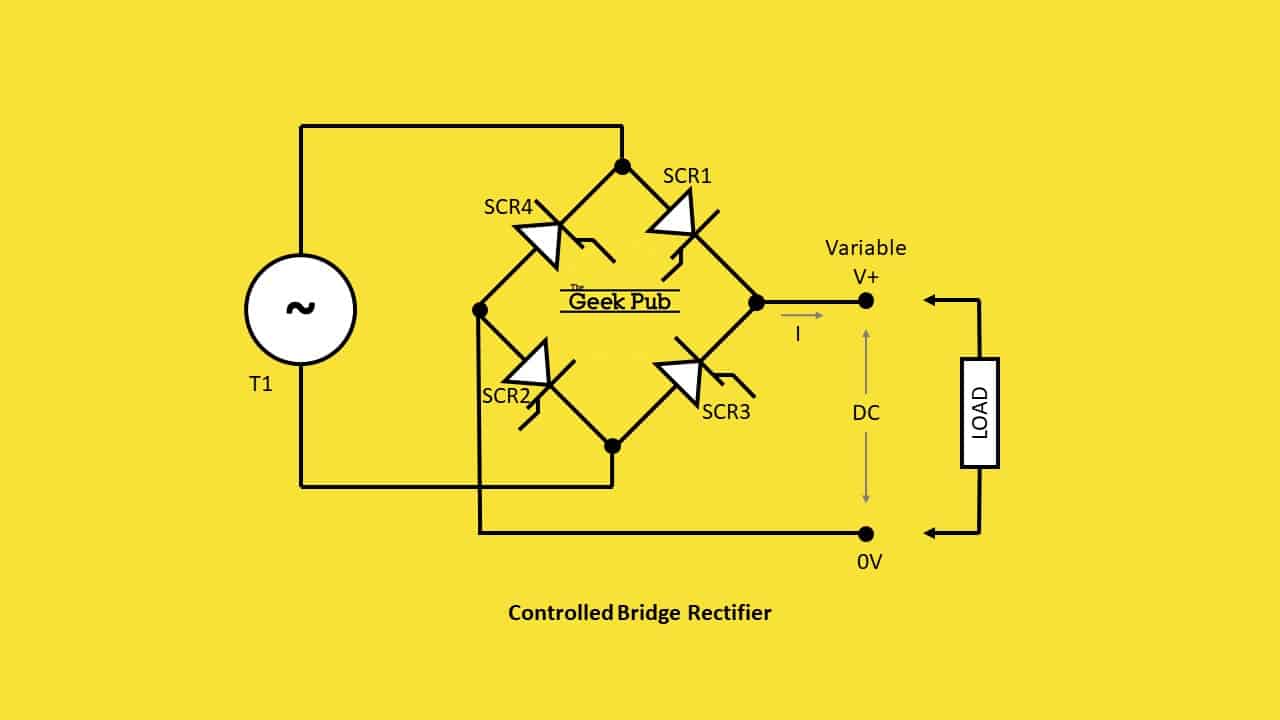
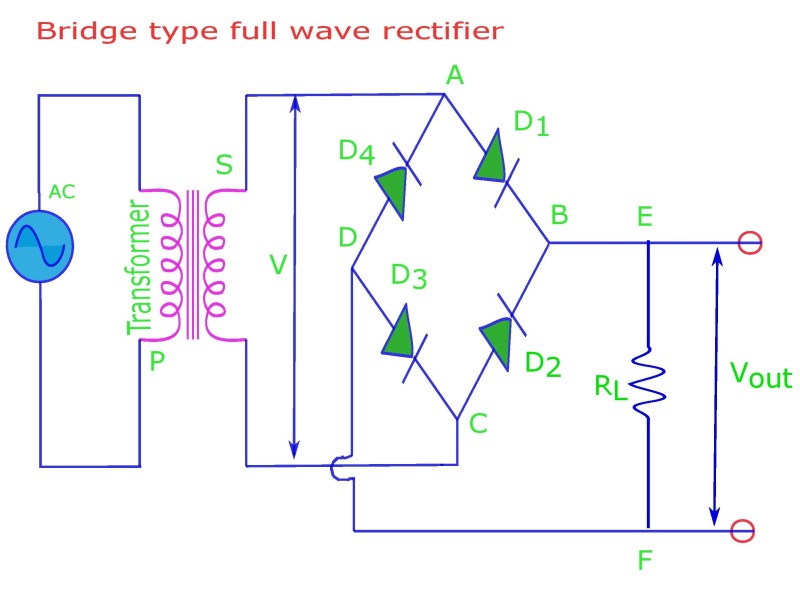
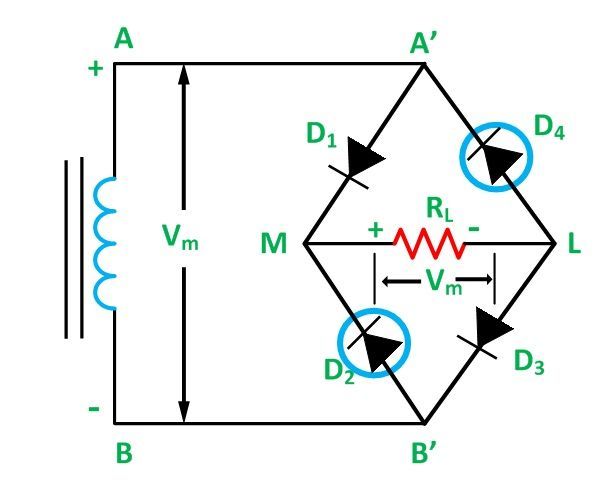
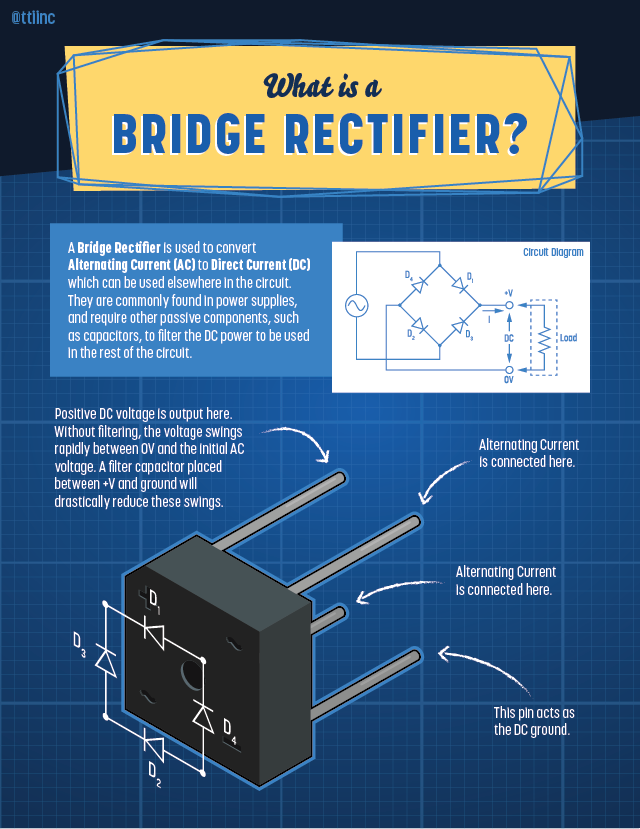
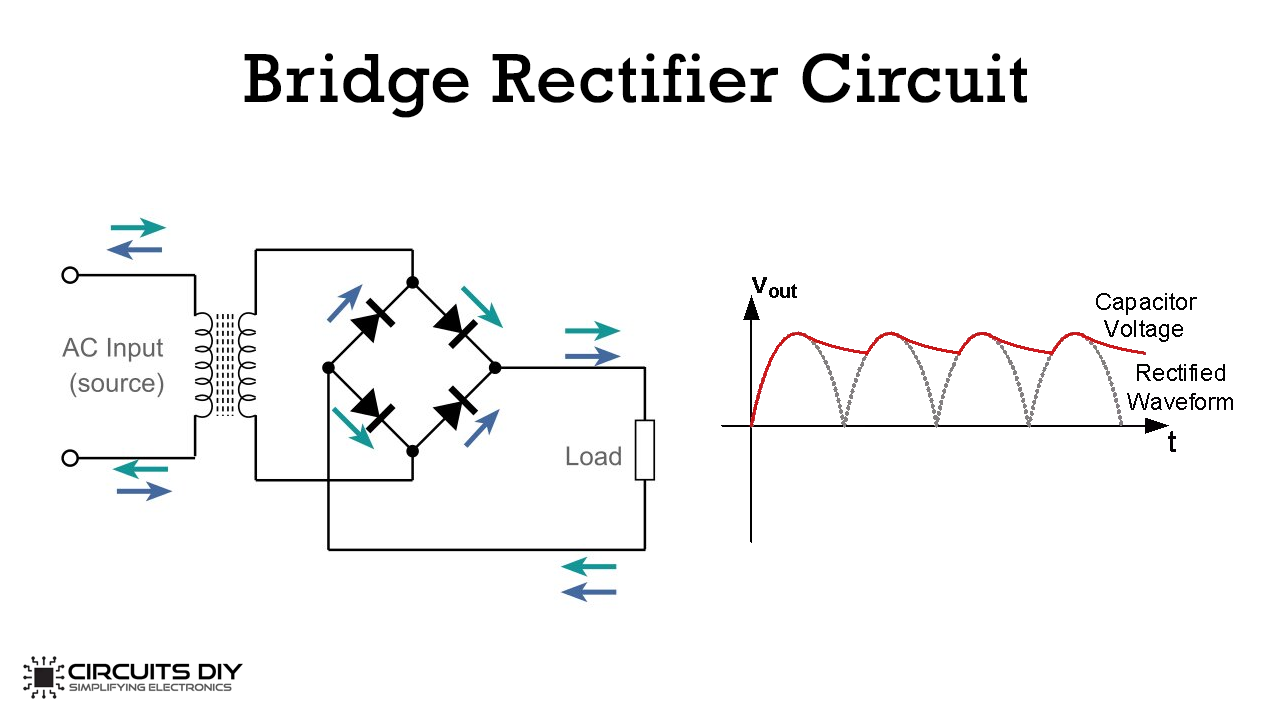
| A bridge rectifier is an electronic device used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is widely used in power supplies and electronic circuits to convert the AC voltage from the mains into a suitable DC voltage for powering various electronic devices. The bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, hence the name "bridge rectifier." | ||
| 1 | ||
| Working Principle | ||
|---|---|---|
| The input AC voltage is connected to the two diagonally opposite ends of the bridge rectifier configuration. During the positive half-cycle of the AC voltage, two diodes conduct and provide a current path through the load in one direction. During the negative half-cycle, the other two diodes conduct and provide a current path through the load in the opposite direction. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Advantages of Bridge Rectifier | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bridge rectifiers have a higher efficiency compared to other rectifier configurations. They provide a higher output voltage due to the use of both halves of the input AC waveform. The use of four diodes in the bridge configuration ensures better reliability and redundancy. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Applications of Bridge Rectifier | ||
|---|---|---|
| Power supplies: Bridge rectifiers are commonly used in power supplies for electronic devices, appliances, and industrial equipment. Battery charging: Bridge rectifiers are used in battery chargers to convert AC voltage to DC for charging batteries. Motor control: Bridge rectifiers are essential components in motor control circuits, allowing for the conversion of AC to DC power for driving motors. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Types of Bridge Rectifiers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Single-phase bridge rectifier: The most common type, used for converting single-phase AC voltage into DC. Three-phase bridge rectifier: Used for converting three-phase AC voltage into DC, commonly found in industrial applications. Center-tapped bridge rectifier: Utilizes a center-tapped transformer for converting AC voltage into DC, commonly used in power supplies. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Rectification Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|
| The rectification efficiency of a bridge rectifier is calculated by dividing the DC output power by the AC input power and multiplying by 100%. The ideal rectification efficiency of a bridge rectifier is 81.2%. The actual rectification efficiency is affected by diode losses, transformer losses, and other circuit losses. |  | |
| 6 | ||
| Diode Selection for Bridge Rectifier | ||
|---|---|---|
| The diodes used in bridge rectifiers should have a high peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating to withstand the maximum voltage across them. Fast recovery diodes or Schottky diodes are commonly used for high-frequency applications. High current rating diodes should be chosen to handle the maximum expected current in the circuit. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bridge rectifiers are essential components in converting AC voltage to DC in various applications. They offer higher efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness compared to other rectifier configurations. Understanding the working principle, types, and diode selection is crucial for proper implementation of bridge rectifiers in electronic circuits and power supplies. | ||
| 8 | ||